Abstract
Objective
Perospirone (PER) is a novel atypical antipsychotic drug for the treatment of schizophrenia and other psychotic disorders. The multidrug resistance transporter, P-glycoprotein (Pgp), is involved in the efflux transport of several antipsychotics across the blood-brain barrier (BBB).The aim of the present study was to evaluate the modulating effect of PER on both Pgp activity and expression in Caco-2 cell monolayers.
Methods
The effects of PER were analyzed by means of rhodamine 123 (Rhd 123) assays, and those of Pgp expression were analyzed by flow cytometry and reverse transcriptase-PCR.
Results
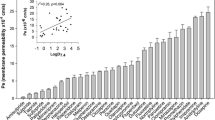
Perospirone at concentrations of 0.01–30 μM, which were found to be non-cytotoxic towards the Caco-2 cells, was observed to inhibit Pgp-mediated efflux transport of Rhd 123 in the cells as well as to down-regulate the cellular Pgp protein and MDR1 mRNA levels in a concentration-dependent manner. In the rhodamine accumulation assays, 30 μM PER produced a 429% increase of the cellular Rhd 123 concentration, which exceeded the inhibitory effect of the well-known Pgp inhibitor verapamil.
Conclusion
Our findings provide experimental evidence that PER is an inhibitor of Pgp which interferes directly and indirectly with the function of Pgp.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fromm MF (2004) Importance of P-glycoprotein at blood-tissue barriers. Trends Pharmacol Sci 25:423–429
Martin E, Uhr M (2006) ABC drug transporter at the blood-brain barrier: effects on drug metabolism and drug response. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci 256:294–298
Schinkel AH (1999) P-Glycoprotein, a gatekeeper in the blood-brain barrier. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 36:179–194
Loscher W, Potschka H (2005) Role of drug efflux transporters in the brain for drug disposition and treatment of brain diseases. Prog Neurobiol 76:22–76
Tellingen OV (2001) The importance of drug-transporting P-glycoproteins in toxicology. Toxicol Lett 120:31–41
Bodo A, Bakos E, Szeri F, Varadi A, Sarkadi B (2003) The role of multidrug transporters in drug availability, metabolism and toxicity. Toxicol Lett 140–141:133–143
Mueser KT, McGurk SR (2004) Schizophrenia. Lancet 363:2063–2072
Tandon R, Fleischhacker WW (2005) Comparative efficacy of antipsychotics in the treatment of schizophrenia: a critical assessment. Schizophr Res 79:145–155
El Ela AA, Hartter S, Schmitt U, Hiemke C, Spahn-Langguth H, Langguth P (2004) Identification of P-glycoprotein substrates and inhibitors among psychoactive compounds-implications for pharmacokinetics of selected substrates. J Pharm Pharmacol 56:967–975
Mahar Doan KM, Humphreys JE, Webster LO, Wring SA, Shampine LJ, Serabjit-Singh CJ, Adkison KK, Polli JW (2002) Passive permeability and P-glycoprotein-mediated efflux differentiate central nervous system (CNS) and non-CNS marked drugs. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 303:1029–1037
Onrust SV, McClellan K (2001) Perospirone. CNS Drugs 15:329–337
De Paulis T (2002) Perospirone (Sumitomo Pharmaceuticals). Curr Opin Invest Drugs 3:121–129
Hanelt M, Gareis M, Kollarczik B (1994) Cytotoxicity of mycotoxin evaluated by the MTT cell-culture assay. Mycopathologia 128:167–174
Aouali N, Eddabra L, Macadré J, Morjani H (2005) Immunosuppressors and reversion of multidrug-resistance. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol 56:61–70
Ejsing TB, Pedersen AD, Linnet K (2005) P-glycoprotein interaction with risperidone and 9-OH-risperidone studied in vitro, in knock-out mice and in drug-drug interaction experiments. Hum Psychopharmacol Clin Exp 20:493–500
Araki T, Kasai K, Rogers MA, Kato N, Iwanami A (2006) The effect of perospirone on auditory P300 in schizophrenia: a preliminary study. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 30:1083–1090
Araki T, Yamasue H, Sumiyoshi T, Kuwabara H, Suga M, Iwanami A, Kato N, Kasai K (2006) Perospirone in the treatment of schizophrenia: effect on verbal memory organization. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 30:204–208
Yoshino T, Nisijima K, Shioda K, Yui K, Katoh S (2004) Perospirone, a novel atypical antipsychotic drug, potentiates fluoxetine-induced increase in dopamine levels via multireceptor actions in the rat medial prefrontal cortex. Neurosci Lett 364:16–21
Shimakura J, Tani N, Mizuno Y, Komuro S, Kanamaru H (2003) In vitro drug-drug interactions with perospirone and concomitantly administered drugs in human liver microsomes. Eur J Drug Metab Pharmacokinet 28:67–72
Kitamura A, Mizuno Y, Natsui K, Yabuki M, Komuro S, Kanamaru H (2005) Characterization of human cytochrome P450 enzymes involved in the in vitro metabolism of perospirone. Biopharm Drug Dispos 26:59–65
Mizuno Y, Tani N, Komuro S, Kanamaru H, Nakatsuka I (2003) In vitro metabolism of perospirone in rat, monkey and human liver microsomes. Eur J Drug Metab Pharmacokinet 28:59–65
Sekine Y, Ouchi Y, Takei N, Yoshikawa E, Okada H, Minabe Y, Nakamura K, Suzuki K, Iwata Y, Tsuchiya KJ, Sugihara G, Mori N (2006) Perospirone is a new generation antipsychotic: evidence from a positron emission tomography study of serotonin-2 and D2 receptor occupancy in the living human brain. J Clin Psychopharmacol 26:531–533
Yasui-Furukori N, Furukori H, Nakagami T, Saito M, Inoue Y, Kaneko S, Tateishi T (2004) Steady-state Pharmacokinetics of a new antipsychotic agent perospirone and its active metabolite, and its relationship with prolactin response. Ther Drug Monit 26:361–365
Mauri MC, Volonteri LS, Colasanti A, Fiorentini A, De Gaspari IF, Bareggi SR (2007) Clinical pharmacokinetics of atypical antipsychotics: a critical review of the relationship between plasma concentrations and clinical response. Clin Pharmacokinet 46:359–388
Gerlach M, Hünnerkopf R, Rothenhöfer S, Libal G, Burger R, Clement HW, Fegert JM, Wewetzer Ch, Mehler-Wex C (2007) Therapeutic drug monitoring of quetiapine in adolescents with psychotic disorders. Pharmacopsychiatry 40:72–76
Hiemke C, Dragicevic A, Gründer G, Hatter S, Sachse J, Vernaleken I, Muller MJ (2004) Therapeutic monitoring of new antipsychotic drugs. Ther Drug Monit 26:156–160
Szabó D, Szabó G Jr, Ocsovszki I, Aszalos A, Molnár J (1999) Anti-psychotic drugs reverse multidrug resistance of tumor cell lines and human AML cells ex-vivo. Cancer Lett 139:115–119
Wang RB, Kuo CL, Lien LL, Lien EJ (2003) Structure-activity relationship: analyses of p-glycoprotein substrates and inhibitors. J Clin Pharm Ther 28:203–228
Jin S, Gorfajn B, Faircloth G, Scotto KW (2000) Ecteinascidin 743, a transcription-targeted chemotherapeutic that inhibits MDR1 activation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:6775–6779
Anuchapreeda S, Leechanachai P, Smith MM, Ambudkar SV, Limtrakul PN (2002) Modulation of P-glycoprotein expression and function by curcumin in multidrug-resistant human KB cells. Biochem Pharmacol 64:573–582
Yu ST, Chen TM, Tseng SY, Chen YH (2007) Tryptanthrin inhibits MDR1 and reverses doxorubicin resistance in breast cancer cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 358:79–84
Mutoh K, Tsukahara S, Mitsuhashi J, Katayama K, Sugimoto Y (2006) Estrogen-mediated post transcriptional down-regulation of P-glycoprotein in MDR1-transduced human breast cancer cells. Cancer Sci 97:1198–1204
Kanzaki A, Takebayashi Y, Ren XQ, Miyashita H, Mori S, Akiyama S, Pommier Y (2002) Overcoming multidrug drug resistance in P-glycoprotein/MDR1-overexpressing cell lines by ecteinascidin 743. Mol Cancer Ther 1:1327–1334
Jetté L, Beaulieu E, Leclerc JM, Béliveau R (1996) Cyclosporin A treatment induces overexpression of P-glycoprotein in the kidney and other tissues. Am J Physiol 270:F756–F765
Herzog CE, Tsokos M, Bates SE, Fojo AT (1993) Increased mdr-1/P-glycoprotein expression after treatment of human colon carcinoma cells with P-glycoprotein antagonists. J Biol Chem 268:2946–2952
Keks NA, Altson K, Hope J, Krapivensky N, Culhane C, Tanaghow A, Doherty P, Bootle A (1999) Use of antipsychotics and adjunctive medications by an inner urban community psychiatric service. Aust N Z J Psychiatry 33:896–901
Boulton DW, DeVane CL, Liston HL, Markowitz JS (2002) In vitro P-glycoprotein affinity for atypical and conventional antipsychotics. Life Sci 71:163–169
Bettencourt MV, Bosne-David S, Amaral L (2000) Comparative in vitro activity of phenothiazines against multidrug-resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Int J Antimicrob Agents 16:69–71
Wang JS, Zhu HJ, Markowitz JS, Donovan JL, DeVane CL (2006) Evaluation of antipsychotic drugs as inhibitors of multidrug resistance transporter P-glycoprotein. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 187:415–423
Masui T, Kusumi I, Takahashi Y, Koyama T (2005) Efficacy of carbamazepine against neuroleptic-induced akathisia in treatment with perospirone: case series. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 29:343–346
Acknowledgments
We thank Dr Di-Lan Qin for excellent technical assistance. None of the authors have conflicting interests that interfere with the integrity of the content of the article.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, YG., Li, KY. & Li, HD. Effect of the novel antipsychotic drug perospirone on P-glycoprotein function and expression in Caco-2 cells. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 64, 697–703 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00228-008-0487-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00228-008-0487-5