Abstract
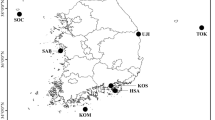
Samples of southern bluefin tuna, Thunnus maccoyii (Castelnau), taken from off the coasts of South Africa, Western Australia, South Australia and Tasmania from 1992 to 1994 were analysed for six polymorphic allozyme loci (ADA *, GDA *, GPI-A *, MPI *, PGDH * and PGM-1 *, n = 595 to 733 per locus) and for mitochondrial DNA variants revealed by three restriction enzymes (Bam HI, Bcl I and Eco RI) detecting polymorphic cut sites (n = 555). No significant spatial heterogeneity was detected. There were no sex-related differences in allele or mtDNA haplotype frequencies. Juveniles (30 to 35 cm and 46 to 54 cm) from what are thought to be two temporally-separated spawning peaks showed no significant genetic differentiation. There were also no significant differences in allele or haplotype frequencies between fish smaller than 70 cm and those larger than 70 cm. These data are consistent with the null hypothesis of a single unit stock of southern bluefin tuna, with a single spawning area. This is located to the south of Java and off the north-west coast of Australia.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 28 August 1996 / Accepted: 30 September 1996
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Grewe, P., Elliott, N., Innes, B. et al. Genetic population structure of southern bluefin tuna (Thunnus maccoyii ). Marine Biology 127, 555–561 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002270050045
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002270050045