Abstract
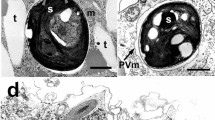
The chemoautotrophic potential of the two co-occurring larger and smaller bacterial endosymbionts of the gutless marine oligochaete Inanidrilus leukodermatus was determined using immunocytochemistry. An antibody directed against the Form I of ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase (RubisCO), the key CO2-fixing enzyme of the Calvin–Benson cycle, consistently labeled the larger symbionts. Electron microscopic spectroscopy showed that the larger symbionts contained sulfur in intracellular globules and to a lesser degree in the cytoplasm. The presence of RubisCO and sulfur indicates that the larger endosymbionts of I. leukodermatus are chemoautotrophic sulfur-oxidizing bacteria. In contrast, no RubisCO or sulfur was detected in the smaller endosymbionts of this host.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 28 September 1999 / Accepted: 29 May 2000
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Krieger, J., Giere, O. & Dubilier, N. Localization of RubisCO and sulfur in endosymbiotic bacteria of the gutless marine oligochaete Inanidrilus leukodermatus (Annelida). Marine Biology 137, 239–244 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002270000355
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002270000355