Abstract
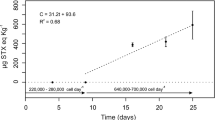
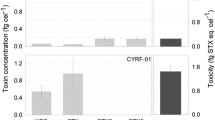
Under laboratory conditions, the scallop Chlamys nobilis and the mussel Perna viridis were exposed to N-sulfocarbamoyl toxins (C2 toxin), a paralytic shellfish toxin (PST), by feeding a local toxic strain of the dinoflagellate Alexandrium tamarense (ATDP) that produced C2 toxin exclusively. The bivalves were subsequently depurated in the field, and their depuration kinetics, biotransformation and toxin distribution were quantified. Depuration was characterized by a rapid loss within the first day, followed by a secondary slower loss of toxins. In the fast depuration phase, scallops detoxified PSTs more quickly than the mussels (depuration rate constants for scallops and mussels were 1.16 day−1 and 0.87 day−1, respectively). In contrast, the mussels detoxified PSTs more quickly than the scallops in the slow depuration phase, and the calculated depuration rate constants (mean+SE) from day 2 to day 13 were 0.063+0.009 day−1 and 0.040+0.019 day−1 for mussels and scallops, respectively. The differences in the appearances of gonyautoxins, GTX2 and GTX3, and their decarbamoyl derivatives, dcGTX2, dcGTX3 and GTX5, which are all derivatives of C2 toxin, indicated active and species-specific biotransformation of the algal toxins in the two bivalves. In both species of bivalves, the non-viscera tissue contained fewer toxins and lower concentrations than the viscera-containing tissue compartment. In scallops, very little toxin was distributed in the adductor muscle. In mussels, most of the PSTs were found in the digestive gland with significant transport of toxins into the digestive gland from other tissues during the course of depuration. The toxin profiles of scallops and mussels differed from each other and from that of the toxic algae fed. A significant fraction of GTX5 was detected in the mussels but not in the scallops. Our study demonstrates a species specificity in the depuration kinetics, biotransformation and tissue distribution of PSTs among different bivalves.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson DM, Kulis DM, Doucette GJ, Gallagher JC, Balech E (1994) Biogeography of toxic dinoflagellates in the genus Alexandrium from the northeastern United States and Canada. Mar Biol 120:467–478
Anderson DM, Kulis DM, Qi Y, Zheng L, Lu S, Lin YT (1996) Paralytic shellfish poisoning in southern China. Toxicon 34:579–590
Asakawa M, Miyazawa K, Takayama H, Noguchi T (1995) Dinoflagellate Alexandrium tamarense as the source of paralytic shellfish poison (PSP) contained in bivalves from Hiroshima Bay, Hiroshima Prefecture, Japan. Toxicon 33:691–697
Bricelj VM, Shumway SE (1998) Paralytic shellfish toxins in bivalve molluscs: occurrence, transfer kinetics and biotransformation. Rev Fish Sci 6:315–383
Bricelj VM, Lee JH, Cemebella AD, Anderson DM (1990) Uptake kinetics of paralytic shellfish toxins from the dinoflagellate Alexandrium fundyense in the mussel Mytilus edulis. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 63:177–188
Bricelj VM, Lee JH, Cembella AD (1991) Influence of dinoflagellate cell toxicity on uptake and loss of paralytic shellfish toxins in the northern quahog, Mercenaria mercenaria. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 74:33–46
Bricelj VM, Cembella AD, Laby D, Shumway SE, Cucci TL (1996) Comparative physiological and behavioral responses to PSP toxins in two bivalve molluscs, the softshell clam, Mya arenaria, and surfclam, Spisula solidissima. In: Yasumoto T, Fukuyo Y (eds) Harmful and toxic algal blooms. Intergovernmental Oceanographic Commission of UNESCO. Paris, pp 405–408
Cembella AD, Sullivan JJ, Boyer GL, Taylor FJR, Andersen RJ (1987) Variation in paralytic shellfish toxin composition within the Protogonyaulax tamarensis/catenella species complex: red-tide dinoflagellates. Biochem Syst Ecol 15:171–186
Cembella AD, Shumway SE, Lewis NI (1993) Anatomical distribution and spatio-temporal variation in paralytic shellfish toxin composition in two bivalve species from the Gulf of Maine. J Shellfish Res 12:389–403
Cembella AD, Shumway SE, Larocque R (1994) Sequestering and putative biotransformation of paralytic shellfish toxins by the sea scallop Placopecten magellanius: seasonal and spatial scales in natural populations. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 180:1–22
Chen CY, Chou HN (2001) Accumulation and depuration of paralytic shellfish poisoning toxins by purple clam Hiatula rostrata Lighttoot. Toxicon 39:1029–1034
Guillard RRL, Ryther JH (1962) Studies of marine planktonic diatoms. I. Cyclotella nana Hustedt and Detonula confervacea (Cleve) Gran. Can J Microb 8:229–239
Hsieh DPH, Chang GH, Huxtable S (2003) Total production of C2 toxin by Alexandrium tamarense. In: Proceedings in HAB2000. Hobart, Australia (in press)
Jiang T, Yin Y, Luo Y, Chen J, Qi Y (2000) Paralytic shellfish toxins in shellfish from Daya and Dapeng Bay. Mar Environ Sci 19:1–5
Keller MD, Selvin RC, Claus W, Guillard RRL (1987) Media for the culture of oceanic ultraphytoplankton. J Phycol 23:633–638
Laycock MV, Kralovec J, Richards R (1995) Some in vitro chemical interconversions of paralytic shellfish poisoning (PSP) toxins useful in the preparation of analytical standards. J Mar Biotechnol 3:121–125
Lee J (1993) The kinetics of PSP toxin transfer from the toxic dinoflagellate Alexandrium spp. to two bivalve mollusc species, Mytilus edulis and Mercenaria mercenaria. MS thesis, State University of New York, Stony Brook, N.Y.
Lin Y, Yang M, Chen R, Hu S, Jin G (1994) Study of paralytic shellfish poison in shellfish from Guangdong coast (in Chinese with English abstract). Oceanol Limnol Sin 25:220–225
Lin Y, Yang M, Chen R, Hu S, Jin G (1995) Paralytic shellfish poison in bivalves from Pearl River Estuary (in Chinese with English abstract). In: Wong CK, Chu KH, Chen QC, Ma XL (eds) Environmental research in the Pearl River and coastal areas. Higher Education Press, Guangzhou, pp 91–97
MOA (Ministry of Agriculture) (1998) Environmental sanitary supervision and management regulation in shellfish production. Paper no. 002, MOA, Beijing, PR China
Noguchi T, Chen S, Arakawa O, Hashimoto K (1989) A unique composition of PSP in "hoigi" scallop Chlamys nobilis. In: Natori S, Hashimoto K, Ueno Y (eds) Mycotoxins and phycotoxins '88. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 351–358
Okumura M, Yamada S, Oshima Y, Ishikawa N (1994) Characteristics of paralytic shellfish poisoning toxins derived from short-neck clams (Tapes japonica) in Mikawa Bay. Nat Toxins 2:141–143
Oshima Y (1995a) Postcolumn derivatization liquid chromatography method for paralytic shellfish toxins. J AOAC Int 78:528–532
Oshima Y (1995b) Chemical and enzymatic transformation of paralytic shellfish toxins in marine organisms. In: Lassus P, Arzul G, Erard-Le Denn E, Gentien P, Marcaillou-Le Baut C (eds) Harmful marine algal bloom. Lavoisier, Paris, pp 475–480
Oshima Y, Sugino K, Itakura H, Hirota M, Yasumoto T (1990) Comparative studies on paralytic shellfish toxin profile of dinoflagellates and bivalves. In: Graneli E, Sundstrom B, Edler L, Anderson DM (eds) Toxic marine phytoplankton. Elsevier, New York, pp 391–396
Parsons TR, Maita Y, Lalli CM (1984) A manual of chemical and biological methods for seawater analysis. Pergamon, Oxford
Shimizu Y, Yoshioka M (1981) Transformation of paralytic shellfish toxins as demonstrated in scallop homogenates. Science 212:547–549
Shimizu Y, Fallon WE, Wekell JC, Gerber D, Gauglitz EJ Jr, Gauglitz EJ (1978) Analysis of toxic mussels (Mytilus sp.) from Alaskan inside passage. J Agric Food Chem 26:878–881
Shumway SE, Cembella AD (1993) The impact of toxic algae on scallop culture and fisheries. Rev Fish Sci 1:121–150
Shumway SE, Sheman-Caswell S, Hurst JW Jr (1988) Paralytic shellfish poisoning in Maine: monitoring a monster. J Shellfish Res 7:643–652
Shumway SE, Sherman SA, Cembella AD, Selvin R (1994) Accumulation of paralytic shellfish toxins by surfclams, Spisula solidissima (Dilwayn, 1897) in the Gulf of Maine: seasonal changes, distribution between tissues, and notes on feeding habits. Nat Toxins 2:236–251
Silvert W, Bricelj M, Cembella A (1998) Dynamic modelling of PSP toxicity in the surfclam (Spisula solidissima): multicompartmental kinetics and biotransformation. In: Reguera B, Blanco J, Fernandez ML, Wyatt T (eds) Harmful algae, VIII International Conference. Intergovernmental Oceanographic Commission of UNESCO, Paris, pp 437–440
Sullivan JJ (1982) Paralytic shellfish poisoning: analytical and biochemical investigations. PhD thesis, University of Washington, Seattle
Sullivan JJ, Iwaoka WT, Liston J (1983) Enzymatic transformation of PSP toxins in the littleneck clam (Prothaca staminea). Biochem Biophys Res Commun 114:465–472
Wang D, Hsieh DPH (2001) Dynamics of C2 toxin and chlorophyll a formation in the dinoflagellate Alexandrium tamarense during large scale cultivation. Toxicon 39:1533–1536
Wang L, Li X (1998) Management of shellfish safety in China. J Shellfish Res 17:1609–1611
Zhou M, Li J, Luckas B, Yu R, Yan T, Hummert C, Kastrups S (1999) A recent shellfish toxin investigation in China. Mar Pollut Bull 39:331–334
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr. W. Silvert for his helpful comments on this work. This study was supported by a Central Allocation Grant (8730011) and an Earmarked Research Grant (CityU1103/00 M) awarded by the Research Grant Council, Hong Kong Government, HKSAR.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by T. Ikeda, Hakodate
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Choi, MC., Hsieh, D.P.H., Lam, P.K.S. et al. Field depuration and biotransformation of paralytic shellfish toxins in scallop Chlamys nobilis and green-lipped mussel Perna viridis . Marine Biology 143, 927–934 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00227-003-1148-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00227-003-1148-y