Abstract
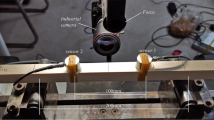
The Mode I fracture behaviour of two softwoods (spruce and pine) and three hardwoods (alder, oak and ash) was studied in the RL crack propagation system using the splitting test in combination with monitoring acoustic emission (AE) activity. Test parameters measured included notch tensile strength, specific fracture energy, characteristic length and AE cumulative counts, AE amplitudes as well as parameters characterizing the frequency spectra of the emitted acoustic emission events. The notch tensile strength was found to correlate with density. The specific fracture energy and characteristic length showed the different crack propagation process between the softwoods and hardwoods. The softwoods fractured in a more ductile way and the hardwoods showed a more linear elastic behaviour. This finding was supported by the AE measurements showing much less cumulative counts for the hardwoods indicating that less microcracks were formed and that processes like fiber bridging were not so effective. Differences in the frequency domain of the AE signals between softwoods and hardwoods could not be detected.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received 13 January 1999
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Reiterer, A., Stanzl-Tschegg, S. & Tschegg, E. Mode I fracture and acoustic emission of softwood and hardwood. Wood Science and Technology 34, 417–430 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002260000056
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002260000056