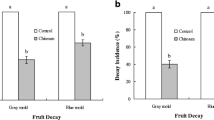
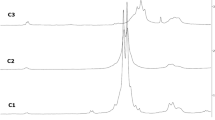
Abstract
Mould fungi can grow on virtually any substrate and are particularly common on cellulosic materials such as wood. Fungicides can limit the risk of mould attack, but increasing concerns about pesticide use have encouraged a search for more natural protection methods. Cinnamaldehyde is a promising antifungal candidate, but has not been fully effective. In this study, chitosan and cinnamaldehyde were used to prepare an emulsion to reduce the volatility of cinnamaldehyde, and the antimould performance of the emulsion-treated wood was evaluated. The ability of cinnamaldehyde chitosan emulsion was assessed for inhibiting mould growth as well as its effect on membrane function and hyphal morphology of Aspergillus niger. Cinnamaldehyde chitosan emulsion can reduce the amount of free cinnamaldehyde, thereby increasing the retention rate of cinnamaldehyde. The control ability of wood treated with 3.0:1.0 molar ratio of aldehyde to amino group in cinnamaldehyde chitosan emulsion against A. niger was 95.8%. Mould growth was limited in the presence of the emulsion. The treatment appeared to disrupt cell membrane function as evidenced by increased levels of extracellular proteins and nucleic acids. The results suggest that the cinnamaldehyde chitosan emulsion improved the stability of cinnamaldehyde in aqueous solution as well as effectively protected wood from mould.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahn SH, Oh SC, Choi IG, Han GS, Jeong HS, Kim KW, Yoon YH, Yang I (2010) Environmentally friendly wood preservatives formulated with enzymatic-hydrolyzed okara, copper and/or boron salts. J Hazard Mater 178(1):604–611. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2010.01.128
Bahmani M, Schmidt O (2018) Plant essential oils for environment-friendly protection of wood objects against fungi. Maderas-Cienc Tecnol 20:325–332. https://doi.org/10.4067/S0718-221X2018005003301
Bi ZJ, Zhao Y, Lei YF, Morrell JJ, Yan L (2021) The antifungal mechanism of konjac flying powder extract and its active compounds against wood decay fungi. Ind Crop Prod 164:113406. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2021.113406
Bobadilha GS, Stokes CE, Kirker G, Ahmed SA, Ohno KM, Lopes DJV (2020) Effect of exterior wood coatings on the durability of cross -laminated timber against mold and decay fungi. BioResources 15(4):8420–8433. https://doi.org/10.15376/biores.15.4.8420-8433
Broda M (2020) Natural compounds for wood protection against fungi-A review. Molecules. 25(15):3538. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25153538
Brugnerotto J, Lizardi J, Goycoolea FM, Arguelles-Monal W, Desbrieres J, Rinaudo M (2001) An infrared investigation in relation with chitin and chitosan characterization. Polymer 42(8):3569–3580. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0032-3861(00)00713-8
Cai LL, Hyungsuk L, Darrel DN, Kim Y (2020) Bio-based preservative using methyl-β-cyclodextrin-essential oil complexes for wood protection. Int J Biol Macromol 147:420–427. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.01.056
Chen HL, Hu XR, Chen EM, Wu S, McClements DJ, Liu SL, Li B, Li Y (2016) Preparation, characterization, and properties of chitosan films with cinnamaldehyde nanoemulsions. Food Hydrocoll 61:662–671. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodhyd.2016.06.034
Chittenden C, Wakeling R, Kreber B (2003) Growth of two selected sapstain fungi and one mould on chitosan amended nutrient medium. International Research Group on Wood Preservation Document No. IRG/WP/03–10466, Stockholm, Sweden. 10 pages.
Clausen CA, Yang V (2007) Protecting wood from mould, decay, and termites with multi-component biocide systems. Int Biodeterior Biodegrad 9(1):20–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ibiod.2005.07.005
Fang SM, Feng XC, Lei YF, Chen ZJ, Yan L (2020) Improvement of wood decay resistance with cinnamaldehyde chitosan emulsion. Ind Crop Prod. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2020.113118
Goodell B, Nicholas DD, Schultz TP (2003) Wood deterioration and preservation: advances in our changing world. Wash DC: Am Chem Soc 2003:2–6
Higueras L, Lopez-Carballo G, Gavara R, Hernandez-Munoz P (2015) Reversible covalent immobilization of cinnamaldehyde on chitosan films via schiff base formation and their application in active food packaging. Food Bioprocess Tech 8(3):526–538. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-014-1421-8
Hussain A, Shrivastav A, Jain SK (2013) Antifungal activity of essential oils against local wood degrading cellulolytic filamentous fungi. Adv Bio Res 4(2):161–167
Kong M, Chen XG, Xing K, Park HJ (2010) Antimicrobial properties of chitosan and mode of action: a state of the art review. Int J Food Microbiol 144(1):51–63. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2010.09.012
Kong LZ, Guan H, Wang XQ (2018) In situ polymerization of furfuryl alcohol with ammonium dihydrogen phosphate in poplar wood for improved dimensional stability and flame retardancy. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 6(3):3349–3357. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.7b03518
Lagaron JM, Fernandez-Saiz P, Ocio MJ (2007) Using ATR-FTIR spectroscopy to design active antimicrobial food packaging structures based on high molecular weight chitosan polysaccharide. J Agric Food Chem 55(7):2554–2562. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf063110j
Larnoy E, Eikenes M, Militz H (2011) Detection of chlorine-labelled chitosan in scots pine by energy-dispersive x-ray spectroscopy. Wood Sci Technol 45(1):103–110. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00226-010-0306-x
Lee SY, Kim KBWR, Lim SI, Ahn DH (2014) Antibacterial mechanism of Myagropsis myagroides extract on listeria monocytogenes. Food Control 42:23–28. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodcont.2014.01.030
Li S, Freitag C, Morrell JJ (2008a) Preventing fungal attack of freshly sawn lumber using cinnamon extracts. For Prod J 58(7/8):77–81
Li XF, Feng XQ, Yang S, Wang TP, Su ZX (2008b) Effects of molecular weight and concentration of chitosan on antifungal activity against Aspergillus niger. Int Polym Proc 17(11):843–852. https://doi.org/10.3139/217.2192
Lonsdale D, Pautasso M, Holdenrieder O (2008) Wood-decaying fungi in the forest: conservation needs and management options. Eur J for Res 127(1):1–22. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10342-007-0182-6
Neto ACD, Maraschin M, Di Piero RM (2015) Antifungal activity of salicylic acid against Penicillium expansum and its possible mechanisms of action. Int J Food Microbiol 215:64–70. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2015.08.018
Nguyen TTH, Li S, Li SJ, Li J, Tao L (2013) Micro-distribution and fixation of a rosin-based micronized-copper preservative in poplar wood. Int Biodeterior Biodegrad 83:63–70. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ibiod.2013.02.017
Nostro A, Scaffaro R, D’Arrigo M, Botta L, Filocamo A, Marino A, Bisignano G (2012) Study on carvacrol and cinnamaldehyde polymeric films: mechanical properties, release kinetics and antibacterial and antibiofilm activities. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 96(4):1029–1038. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-012-4091-3
Rabea EI, Badawy MET, Stevens CV, Smagghe G, Steurbaut W (2003) Chitosan as antimicrobial agent: applications and mode of action. Biomacromol 4(6):1457–1465. https://doi.org/10.1021/bm034130m
Schmidt O (2006) Wood and tree fungi: biology, damage, protection, and use. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/3-540-32139-X
Shi JB, Guobao W, Chen HL, Zhong W, Qiu XZ, Xing MMQ (2014) Schiff based injectable hydrogel for in situ pH-triggered delivery of doxorubicin for breast tumor treatment. Polym Chem 5(21):6180–6189. https://doi.org/10.1039/c4py00631c
Sun Q, Li JM, Sun Y, Chen Q, Zhang L, Le T (2020) The antifungal effects of cinnamaldehyde against aspergillus niger and its application in bread preservation. Food Chem 317(5):126405. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2020.126405
Tian WL, Lei LL, Zhang Q, Li Y (2016) Physical stability and antimicrobial activity of encapsulated cinnamaldehyde by self-emulsifying nanoemulsion. J Food Process Eng 39(5):462–471. https://doi.org/10.1111/jfpe.12237
Tonyali B, McDaniel A, Amamcharla J, Trinetta V, Yucel U (2020) Release kinetics of cinnamaldehyde, eugenol, and thymol from sustainable and biodegradable active packaging films. Food Packag Shelf 24:100484. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fpsl.2020.100484
Wang JT, Lian ZR, Wang HD, Jin XX, Liu YJ (2012) Synthesis and antimicrobial activity of Schiff base of chitosan and acylated chitosan. J Appl Polym Sci 123(6):3242–3247. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.34997
Xie Y, Wang Z, Huang Q, Zhang D (2017) Antifungal activity of several essential oils and major components against wood-rot fungi. Ind Crops Prod 108:278–285. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2017.06.041
Yao YW, Gellerich A, Zauner M, Wang XX, Zhang K (2018) Differential anti-fungal effects from hydrophobic and superhydrophobic wood based on cellulose and glycerol stearoyl esters. Cellulose 25(2):1329–1338. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-017-1626-x
Yves KG, Chen TJ, Aladejana JT, Wu ZZ, Xie YQ (2020) Preparation, test, and Analysis of a novel aluminosilicate-based antimildew agent applied on the microporous structure of wood. ACS Omega 5(15):8784–8793. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.0c00357
Ziani K, Oses J, Coma V, Mate JI (2008) Effect of the presence of glycerol and Tween 20 on the chemical and physical properties of films based on chitosan with different degree of deacetylation. LWT-Food Sci Technol 41(10):2159–2165. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2007.11.023
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31971590).
We thank Mr Zhang Guoyun (State Key Laboratory of Crop Stress Biology for Arid Areas, Northwest A&F University, Yangling, China) for energy-dispersive X-ray (EDX) mapping experimental assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest in the submission of this manuscript, and manuscript has been approved by all authors for publication.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bi, Z., Fang, S., Gao, Q. et al. Improvement of mould resistance of wood with cinnamaldehyde chitosan emulsion. Wood Sci Technol 56, 187–204 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00226-021-01349-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00226-021-01349-8