Abstract
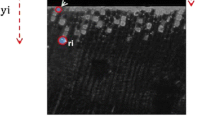
The importance of adhesion in production of wood-based composites is well-known. Adhesive penetration and interphase morphology play an important role in bond strength and product performance. Many studies offered different methods for interphase characterization and analysis. Both qualitative and quantitative methods have been used to analyze the bondline. Most of the quantitative methods were developed for bonded assemblies of veneer or wood blocks. Adhesive penetration measurement in particulate wood-based composites is the main scope of this study. For this purpose, uniform oriented strand board with veneer strands was produced by the use of phenol formaldehyde resin with 2, 6, and 10 % strand moisture content (MC). The strands were formed into well-organized mats to achieve a uniform structure for the composite. Cross-section specimens were prepared from each board and observed by epifluorescence microscopy. Six positions for growth-ring angle in adhesive joints were denoted to evaluate penetration in different directions of the wood. Four parameters were also determined to quantify resin penetration patterns by counting the quantity of the main anatomical elements of wood, which were filled with resin. Finally, it was determined that this method could recognize the differences between adhesive penetration in boards produced with different level of strand MC. Resin penetration in strands with 6 and 10 % MC was the greatest. Growth-ring angle of the strands influenced penetration as it was increased when both strands meet each other in an oblique position, although this effect was significant only in maximum penetration depth in fibers.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brady DE, Kamke FA (1988) Effects of hot-pressing parameters on resin penetration. For Prod J 38(11/12):63–68
Gindl W, Sretenovic A, Vincenti A, Müller U (2005) Direct measurement of strain distribution along a wood bond line. Part 2: effects of adhesive penetration on strain distribution. Holzforschung 59(3):307–310
Hass P, Wittel F, Mendoza M, Herrmann H, Niemz P (2012) Adhesive penetration in beech wood: experiments. Wood Sci Technol 46(1):243–256
Johnson SE, Kamke FA (1992) Quantitative analysis of gross adhesive penetration in wood using fluorescence microscopy. J Adhes 40(1):47–61
Kamke F, Lee J (2007) Adhesive penetration in wood—a review. Wood Fiber Sci 39(2):205–220
Modzel G (2010) Computed Tomography Analysis of Wood-Adhesive Bonds. Oregon State University, Corvallis
Modzel G, Kamke FA, Carlo F (2011) Comparative analysis of a wood: adhesive bondline. Wood Sci Technol 45(1):147–158
Müller U, Sretenovic A, Vincenti A, Gindl W (2005) Direct measurement of strain distribution along a wood bond line. Part 1: shear strain concentration in a lap joint specimen by means of electronic speckle pattern interferometry. Holzforschung 59(3):303–306
Sernek M, Resnik J, Kamke F (1999) Penetration of liquid urea–formaldehyde adhesive into beech wood. Wood Fiber Sci 31(1):41–48
Serrano E, Enquist B (2005) Contact-free measurement and non-linear finite element analyses of strain distribution along wood adhesive bonds. Holzforschung 59(6):641–646
White MS, Ifju G, Johnson JA (1977) Method for measuring resin penetration into wood. For Prod J 27(7):52–54
Acknowledgments
The WKI Fraunhofer institute for material and equipment support is acknowledged and the authors thank Dr. Frauke Cornelius from technology of wood-based material department of WKI for initial arrangements of research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Edalat, H., Faezipour, M., Thole, V. et al. A new quantitative method for evaluation of adhesive penetration pattern in particulate wood-based composites: elemental counting method. Wood Sci Technol 48, 703–712 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00226-014-0635-2
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00226-014-0635-2