Abstract
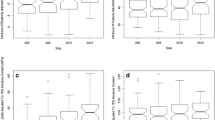
Visually graded Douglas-fir (DF) has wide variability within grade. Variability for 2 × 4 lumber has likely increased because harvest has shifted from federal forests to private plantation forests that contain high percentages of juvenile wood. To investigate resource variability, six No. 2, 2 × 4 DF packages were acquired from six mills. From each package, 124 samples were destructively tested in bending. Mean modulus of elasticity (MOE15) ranged from 9.8 to 13.4 GPa, and three mills did not meet the grade requirements (11.0 GPa). Bending strength (F b) ranged from 5.5 to 11.3 MPa, and three mills did not meet the grade requirements (9.3 MPa). ANOVA of MOE15 % and F b showed significant differences at the 0.05 significance level. MOE15 explained from 50 to 78 % of the variability in strength. These data suggest that variation between mills is high and destructive testing is critical for more accurate characterization of lumber properties.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdel-Gadir AY, Krahmer RL (1993) Estimating the age of demarcation of juvenile and mature wood in Douglas-fir. Wood Fiber Sci 25(3):242–249
Adams WT, Hobbs S, Johnson N (2005) Intensively managed forest plantations in the Pacific Northwest conclusions. J For 103(2):99–100
American Forest & Paper Association (AF&PA) (2005) National design specification (NSD) for wood construction with commentary and supplement: design values for wood construction 2005 edition
ASTM International (2007) ASTM D1990-07: standard practice for establishing allowable properties for visually-graded dimension lumber from in-grade tests of full-size specimens
ASTM International (2009) ASTM D198-09: standard test methods of static tests of lumber in structural sizes
ASTM International (2010) ASTM D2915-10: standard practice for evaluating allowable properties for grades of structural lumber
Azuma DL, Bednar LF, Heserote BA, Veneklase CF (2004) Timber resource statistics for western Oregon, 1997. US. For. Serv. Res. Bull. PNW-RB-237, p 120
Barbour RJ, Johnston S, Hayes JP, Tucker GF (1997) Simulated stand characteristics and wood product yields from Douglas-fir plantations managed for ecosystem objectives. For Ecol Manag 91:205–219
Briggs DG (2007) Management practices on Pacific Northwest west-side industrial forest lands, 1991–2005: with projections to 2010. Stand management cooperative. SMC working paper number 6. College of Forest Resources, University of Washington
Curtis RO (1995) Extended rotations and culmination age of coast Douglas-fir: old studies speak to current issues. Res. Pap. PNW-RP-485. U.S. Department of Agriculture, Forest Service, Pacific Northwest Research Station, Portland, p 49
Curtis RO, DeBell DS, Harrington CA, Lavender DP, St. Clair JB, Tappeiner JC, Walstad JD (1998) Silviculture for multiple objectives in the Douglas-fir region. USDA Forest Service. Pacific Northwest Research Station. PNW-GTR-435
Dahlen J, Jones PD, Seale RD, Shmulsky R (2012) Bending strength and stiffness of in-grade Douglas-fir and southern pine No. 2 2 × 4 lumber. Can J For Res 42:858–867
Dahlen J, Jones PD, Seale RD, Shmulsky R (2013) Mill variation in bending strength and stiffness of in-grade southern pine No. 2 2 × 4 lumber. Wood Sci Technol. doi:10.1007/s00226-013-0564-5
Erickson H, Harrison AT (1974) Douglas-fir wood quality studies. Part II: effects of age and stimulated growth on wood density and anatomy. Wood Sci Technol 8:207–226
Evans JW, Kretschmann DE, Herian VL, Green DW (2001) Procedures for developing allowable properties for a single species under ASTM D1990 and computer programs useful for the calculations. USDA Forest Service. Forest Products Laboratory. FPL-GTR-126
Forest Products Laboratory (2011) NONPAR: Nonparametric estimation program. http://www1.fpl.fs.fed.us/nonpar.html. Accessed 26 Sep 2011
Gartner BL (2005) Assessing wood characteristics and wood quality in intensively managed plantations. J For 103(2):75–77
Glass SV and Zelinka SL (2010) Moisture relations and physical properties of wood. Wood handbook. USDA Forest Service. Forest Products Laboratory. FPL-GTR-190
Gray AN, Veneklase CF, Rhoads RD (2005) Timber resource statistics for nonnational forest land in western Washington, 2001. United States Forest Service Research Bulletin PNW-RB-246, p 117
Green DW, Evans JW (1988) Mechanical properties of visually graded lumber: volume 1. A summary. National Technical Information Service. PB-88-159-389, p 131
Harrington TB, Maden J (2005) Silvicultural technology and applications for forest plantation establishment west of the cascade crest. In: Productivity of western forests: a forest products focus. USDA Forest Service. PNW-GTR-64, p 186
Howard J (2007) U.S. timber production, trade, consumption, and price statistics 1965 to 2005. USDA: Forest Products Laboratory. FPL-RP-637, p 91
Huang CL, Briggs DG, Lowell E (2011) Log lumber value of type II thinned Douglas-fir installations. Stand management cooperative quarterly news. 3rd Quarter 2011. School of Forest Resources, University of Washington
Jones E (1989) Sampling procedures used in the in-grade lumber testing program. In: Proceedings of workshop sponsored by in-grade testing committee and forest products society. Proceedings 47363. Forest Products Society, Madison
Kennedy RW (1995) Coniferous wood quality in the future: concerns and strategies. Wood Sci Technol 29:321–338
Kretschmann DE (2010) Mechanical properties of wood. Wood Handbook. USDA Forest Service. Forest Products Laboratory. FPL-GTR-190
Kretschmann DE, Bendtsen BA (1992) Ultimate tensile stress and modulus of elasticity of fast-grown plantation loblolly pine lumber. Wood Fiber Sci 24(2):189–203
Kretschmann DE, Evans JW (2010) History of lumber submission under ASTM D 1990 since the North American in-grade testing program. United States Forest Service. Forest Products Laboratory. FPL-GTR-189
Kretschmann DE, Evans JW, Brown L (1999) Monitoring of visually graded structural lumber. USDA Forest Service. Forest Products Laboratory. FPL-RP-576
Lassen LE, Okkonen EA (1969) Effect of rainfall and elevation on specific gravity of coast Douglas-fir. Wood Fiber Sci 1(3):227–235
Oregon Forest Resources Institute (OFRI) (2004) Oregon forest sector contributions and potential. E.D. Hovee & Company, Oregon Forest Resources Institute
Pittman SD, Turnblom EC (2003) A study of self-thinning using coupled allometric equations: implications for coastal Douglas-fir stand dynamics. Can J For Res 33:1661–1669
Smith JHG (1980) Influence of spacing on radial growth and percentage latewood of Douglas-fir, western hemlock, and western red cedar. Can J For Res 10:169–175
Talbert C, Marshall D (2005) Plantation productivity in the douglas-fir region under intensive silvicultural practices: results from research and operations. J For 103(2):65–70
Vikram V, Cherry ML, Briggs D, Cress DW, Evans R, Howe GT (2011) Stiffness of Douglas-fir lumber: effects of wood properties and genetics. Can J For Res 41:1160–1173
Wagner E, Hansen E, Leavengood S, Punches J, Bowers S (2003) The big log project. Department of Wood Science and Engineering, Oregon State University, Corvallis, p 101
Conflict of interest
The authors declare they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dahlen, J., Jones, P.D., Seale, R.D. et al. Mill variation in bending strength and stiffness of in-grade Douglas-fir No. 2 2 × 4 lumber. Wood Sci Technol 47, 1167–1176 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00226-013-0566-3
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00226-013-0566-3