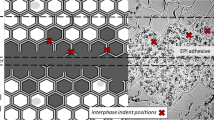
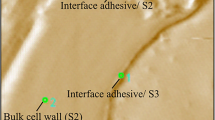
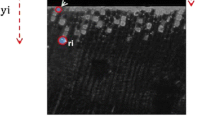
Abstract
Micromechanical properties of cured polymeric diphenylmethane diisocyanate (pMDI) and urea formaldehyde (UF) adhesive and wood cell walls (beech) in adhesive contact compared with cell walls without adhesive contact were measured in situ by means of nanoindentation. Using UV-microphotometry obtained absorbance spectra of micromechanical investigated cell wall regions gave a strong indicator for the presence of pMDI compounds in wood cell walls. Nanoindentation results reveal that both pure UF and UF-penetrated cell walls show a very brittle character. In contrast, pMDI adhesive is very tough and soft at the same time, and when diffused in cell walls, it does not mechanically embrittle the cell structure.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bao S, Daunch WA, Sun Y, Rinaldi PL, Marcinko JJ, Phanopoulos C (2003) Solid state two-dimensional NMR studies of polymeric diphenylmethane diisocyanate (PMDI) reaction in wood. Forest Prod J 53:63–71
Bolton AJ, Dinwoodie JM, Davies DA (1988) The validity of the use of SEM/EDAX as a tool for the detection of UF resin penetration into wood cell walls in particleboard. Wood Sci Technol 22:345–356
Buckley CJ, Phanopoulos C, Khaleque N, Engelen A, Holwill MEJ, Michette AG (2002) Examination of the penetration of polymeric methylene di-phenyl-di-isocyanate (pMDI) into wood structure using chemical-state x-ray microscopy. Holzforschung 56:215–222
Cyr PL, Riedl B, Wang XM, Shaler S (2006) Urea-melamine-formaldehyde (UMF) resin penetration in medium-density fiberboard (MDF) wood fibers. J Adhes Sci Technol 20:787–801
Fergus BJ, Procter AR, Scott JAN, Goring DAI (1969) The distribution of lignin in sprucewood as determined by ultraviolet microscopy. Wood Sci Technol 3:117–138
Frazier CE (2003) Isocyanate wood binders. In: Pizzi A, Mittal KL (eds) Handbook of adhesive technology, 2nd edn. Marcel Dekker, Inc., New York, pp 681–694
Frazier CE, Ni J (1998) On the occurrence of network interpenetration in the wood-isocyanate adhesive interphase. Int J Adhes Adhes 18:81–87
Frihart CR (2009) Adhesive groups and how they relate to the durability of bonded wood. J Adhes Sci Technol 23:601–617
Gierlinger N, Hansmann C, Röder T, Sixta H, Gindl W, Wimmer R (2005) Comparison of UV and confocal Raman microscopy to measure the melamine-formaldehyde resin content within cell walls of impregnated spruce wood. Holzforschung 59:210–213
Gindl W, Gupta HS (2002) Cell-wall hardness and young’s modulus of melamine-modified spruce wood by nano-indentation. Compos Part A Appl S 33:1141–1145
Gindl W, Dessipri E, Wimmer R (2002) Using UV-microscopy to study diffusion of melamine-urea-formaldehyde resin in cell walls of spruce wood. Holzforschung 56:103–107
Gindl W, Gupta HS, Schöberl T, Lichtenegger HC, Fratzl P (2004a) Mechanical properties of spruce wood cell walls by nanoindentation. Appl Phys A Mater Sci Process 79:2069–2073
Gindl W, Schöberl T, Jeronimidis G (2004b) Corrigendum to “The interphase in phenol-formaldehyde (PF) and polymeric methylene di-phenyl-di-isocyanate (pMDI) glue lines in wood” (vol 24, p 279, 2004). Int J Adhes Adhes 24:535
Gindl W, Schöberl T, Jeronimidis G (2004c) The interphase in phenol-formaldehyde and polymeric methylene di-phenyl-di-isocyanate glue lines in wood. Int J Adhes Adhes 24:279–286
Gruver TM, Brown NR (2006) Penetration and performance of isocyanate wood binders on selected wood species. Bioresources 1:233–247
Humphrey PE (1993) A device to test adhesive bonds. USA Patent 5.176.028, Jan. 5, 1993
Kamke FA, Lee JN (2007) Adhesive penetration in wood—a review. Wood Fiber Sci 39:205–220
Konnerth J, Gindl W (2006) Mechanical characterisation of wood-adhesive interphase cell walls by nanoindentation. Holzforschung 60:429–433
Konnerth J, Jäger A, Eberhardsteiner J, Müller U, Gindl W (2006) Elastic properties of adhesive polymers. II. Polymer films and bond lines by means of nanoindentation. J Appl Polym Sci 102:1234–1239
Konnerth J, Harper D, Lee SH, Rials TG, Gindl W (2008) Adhesive penetration of wood cell walls investigated by scanning thermal microscopy (SThM). Holzforschung 62:91–98
Konnerth J, Gierlinger N, Keckes J, Gindl W (2009) Actual versus apparent within cell wall variability of nanoindentation results from wood cell walls related to cellulose microfibril angle. J Mater Sci 44:4399–4406
Marcinko JJ, Devathala S, Rinaldi PL, Bao S (1998) Investigating the molecular and bulk dynamics of PMDI/wood and UF/wood composites. Forest Prod J 48:81–84
Oliver WC, Pharr GM (1992) Improved technique for determining hardness and elastic modulus using load and displacement sensing indentation experiments. J Mater Res 7:1564–1580
Rapp AO, Bestgen H, Adam W, Peek RD (1999) Electron energy loss spectroscopy (EELS) for quantification of cell-wall penetration of a melamine resin. Holzforschung 53:111–117
Roll H (1993) Mikrotechnologische Untersuchungen zum Verhalten des Klebstoffs Polymeres Diphenylmethan-4,4’-Diisocyanat auf Holzoberflächen im Hinblick auf seine Verteilung in Spanplatten. Dissertation, Ludwig-Maximilians-Universität, München
Scott JAN, Procter AR, Fergus BJ, Goring DAI (1969) The application of ultraviolet microscopy to the distribution of lignin in wood description and validity of the technique. Wood Sci Technol 3:73–92
Stöckel F, Konnerth J, Kantner W, Moser J, Gindl W (2010) Tensile shear strength of UF- and MUF-bonded veneer related to data of adhesives and cell walls measured by nanoindentation. Holzforschung 64:337–342
Volkersen O (1938) Die Nietkraftverteilung in zugbeanspruchten Nietverbindungen mit konstanten Laschenquerschnitten. Luftfahrtforschung 15:41–47
Xing C, Riedl B, Cloutier A, Shaler SM (2005) Characterization of urea-formaldehyde resin penetration into medium density fiberboard fibers. Wood Sci Technol 39:374–384
Zheng J, Fox SC, Frazier CE (2004) Rheological, wood penetration, and fracture performance studies of PF/pMDI hybrid resins. Forest Prod J 54:74–81
Zhou XB, Frazier CE (2001) Double labeled isocyanate resins for the solid-state NMR detection of urethane linkages to wood. Int J Adhes Adhes 21:259–264
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful for financial support of this work by Dynea Austria GmbH and Kompetenzzentrum Holz GmbH, Wood K plus.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stöckel, F., Konnerth, J., Moser, J. et al. Micromechanical properties of the interphase in pMDI and UF bond lines. Wood Sci Technol 46, 611–620 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00226-011-0432-0
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00226-011-0432-0