Abstract
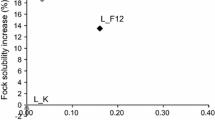
Since xylanases can differ widely in their bleaching efficiency, the performance of one new and two commercial xylanases was evaluated in an eucalyptus kraft pulp following XD (X: xylanase; D: chlorine dioxide) and XP (P: hydrogen peroxide) sequences. The new xylanase did not show a significant bleach boosting effect but increased the hexenuronic acid (HexA) removal by 10% after the D stage. The two commercial xylanases behaved in a different way, being one of them (XC) the most effective in increasing delignification (9%) and brightness (3%ISO). Its effectiveness was related to its greater action on releasing the xylan polymer, thus producing also a strong decrease in the HexA contents during the enzymatic stage (15%). All xylanases produced morphological changes in the fibre surfaces, but only with XC cracks and holes that improved the diffusion of reactives were observed. Finally, the best bleaching results were obtained with the XD sequence and therefore, a complete bleaching sequence XDEopD1 (Eop: alkaline extraction with oxygen and peroxide) was carried out with the best enzyme.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amin HM (2006) Extended usage of xylanase enzyme to enhance the bleaching of softwood kraft pulp. Tappi J 5:23–26
Bajpai P (2004) Biological bleaching of chemical pulps. Crit Rev Biotechnol 24:1–58
Biely P, Vrsanská M, Tenkanen M, Kluepfel D (1997) Endo-β-1,4-xylanase families: Differences in catalytic properties. J Biotechnol 57:151–166
Blanco A, Díaz P, Martínez J, López O, Soler C, Pastor FIJ (1996) Cloning of a bacillus sp. BP-23 gene encoding a xylanase with high activity against aryl xylosides. FEMS Microbiol Lett 137:285–290
Cadena EM, Vidal T, Torres AL (2010) Influence of the hexenuronic acid content on refining and ageing in eucalyptus TCF pulp. Bioresour Technol 101:3554–3560
Chai XS, Zhu JY, Li J (2001) A simple and rapid method to determine hexeneuronic acid groups in chemical pulps. J Pulp Pap Sci 27:165–170
Christov L, Biely P, Kalogeris E, Christakopoulos P, Prior BA, Bhat MK (2000) Effects of purified endo-[beta]-1,4-xylanases of family 10 and 11 and acetyl xylan esterases on eucalypt sulfite dissolving pulp. J Biotechnol 83:231–244
Clarke JH, Rixon JE, Ciruela A, Gilbert HJ, Hazlewood GP (1997) Family-10 and family-11 xylanases differ in their capacity to enhance the bleachability of hardwood and softwood paper pulps. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 48:177–183
Costa MM, Colodette JL (2007) The impact of kappa number composition on eucalyptus kraft pulp bleachability. Brazil J Chem Eng 24:61–71
Fillat U, Sacón VM, Bassa A (2008) Selection of commercial xylanases to improve pulp bleaching in Jacarei mill (Votorantim Celulose e Papel). Influence of pH and COD in process efficiency. IPBC Conf Proc, Canada, pp 207–208
Gallardo O, Díaz P, Pastor FIJ (2003) Characterization of a Paenibacillus cell-associated xylanase with high activity on aryl-xylosides: a new subclass of family 10 xylanases. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 61:226–233
Gallardo O, Díaz P, Pastor FIJ (2007) Cloning and production of xylanase B from Paenibacillus barcinonensis in Bacillus subtillis hosts. Biocatal Biotrans 25:157–162
García O, Camarero S, Colom JF, Martínez AT, Martínez MJ, Monje R, Vidal T (2003) Optimization of a laccase-mediator stage for TCF bleaching of flax pulp. Holzforschung 57:513–519
Hatam A, Pourtahmasi K, Resalati H, Lohrasebi AH (2008) Modeling hydrogen peroxide bleaching to predict optical properties of bleached hardwood CMP. Wood Sci Technol 42:353–367
ISO standard 3688 (1977) Pulps -measurement of diffuse blue reflectance factor (ISO brightness)
ISO standard 302 (1981) Pulps -determination of kappa number
ISO 5351-1 (1981) Cellulose in dilute solutions -determination of limiting viscosity number -part 1: Method in cupri-ethylene-diamine (CED) solution
Jiang Z, van Lierop B, Berry R (2000) Hexenuronic acid groups in pulping and bleaching chemistry. Tappi J 83:167–175
Kawae A, Uchida Y (2005) Heat and moisture-induced yellowing of ECF-light bleached hardwood kraft pulp. Appita J 58:378–381
Kolenova K, Vrsanska M, Biely P (2006) Mode of action of endo-β-1,4-xylanases of families 10 and 11 on acidic xylooligosaccharides. J Biotechnol 121:338–345
Lachenal D, Chirat C (1999) Evaluation de l’efficacité des réactifs de blanchiment. Nouvelle approche. Revue ATIP 53:125–130
Li J, Gellerstedt G (1997) The contribution to kappa number from hexeneuronic acid groups in pulp xylan. Carbohydr Res 302:213–218
Loutfi H (1993) Researchers continue development of new bleaching agents for kraft pulp. Pulp Pap 68:122
Maddern KN, Neilson MJ, Jamieson AG (1993) The production of eucalypt kraft market pulp without the use of molecular chlorine. Appita J 46:419–423
Madlala AM, Bissoon S, Singh S, Christov L (2001) Xylanase-induced reduction of chlorine dioxide consumption during elemental chlorine-free bleaching of different pulp types. Biotechnol Lett 23:345–351
Mateo C (2004) Influence de la structure chimique des pâtes cellulosiques sur leur aptitude au blanchiment. Revue ATIP 58:29–39
Moreira MT, Feijoo G, Canaval J, Lema JM (2003) Semipilot-scale bleaching of Kraft pulp with manganese peroxide. Wood Sci Technol 37:117–123
Patel RN, Grabski AC, Jeffries TW (1993) Chromophore release from kraft pulp by purified streptomyces roseiscleroticus xylanases. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 39:405–412
Popovici C, Messier M, Thibault L, Charron D (2004) Multiples avantages du xylanase dans une usine nexfor papiers fraser de pâte kraft de feuillus. Pulp Pap Can 105:278–281
Roncero MB, Vidal T (2007) Optimización del tratamiento con ozono en el blanqueo TCF de pastas para papel. Afinidad 64:420–428
Roncero MB, Vidal T, Torres AL, Colom JF (1996) Use of xylanase in the totally chlorine-free bleaching of eucalyptus kraft pulp. ACS Symp Ser 655:219–227
Roncero MB, Torres AL, Colom JF, Vidal T (2000) Effects of a xylanase treatment on fibre morphology in totally chlorine free bleaching (TCF) of eucalyptus pulp. Proc Biochem 36:45–50
Roncero MB, Torres AL, Colom JF, Vidal T (2003a) Effect of xylanase on ozone bleaching kinetics and properties of eucalyptus kraft pulp. J Chem Tech Biotechnol 78:1023–1031
Roncero MB, Torres AL, Colom JF, Vidal T (2003b) TCF bleaching of wheat straw pulp using ozone and xylanase.: part b: kinetic studies. Bioresour Technol 87:315–323
Roncero MB, Colom JF, Vidal T (2003c) Influencia de los tratamientos enzimáticos con xilanasas en la composición de hidratos de carbono de pastas para papel. Afinidad 60:8–15
Roncero MB, Torres AL, Colom JF, Vidal T (2003d) TCF bleaching of wheat straw pulp using ozone and xylanase. Part A: paper quality assessment. Bioresour Technol 87:305–314
Roncero MB, Torres AL, Colom JF, Vidal T (2005) The effect of xylanase on lignocellulosic components during the bleaching of wood pulps. Bioresour Technol 96:21–30
Sanchez MM, Fritze D, Blanco A, Sproer C, Tindall BJ, Schumann P, Kroppenstedt RM, Diaz P, Pastor FIJ (2005) Paenibacillus barcinonensis sp. nov., a xylanase-producing bacterium isolated from a rice field in the ebro river delta. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 55:935–939
Sevastyanova O, Li J, Gellerstedt G (2006) Influence of various oxidizable structures on the brightness stability of fully bleached chemical pulps. Nord Pulp Pap Res J 21:49–53
Shah AK, Cooper D, Adolphson R, Eriksson KEL (2000) Xylanase treatment of oxygen-bleached hardwood kraft pulp at high temperature and alkaline pH levels gives substantial savings in bleaching chemicals. J Pulp Paper Sci 26:8–11
Siles FJ, Torres AL, Colom JF, Vidal T (1996) Blanqueo biológico de pasta kraft de frondosas. Afinidad 462:93–102
Spiro RG (1966) The nelson-somogyi copper reduction method. Analysis of sugars found in glycoprotein. Methods Enzymol 8:3–26
Tolan JS, Spence M (1997) On-line tracer system to improve enzyme performance. Pulp Pap Can 98:57–61
Torngren A (2002) Hexenuronic acid reactions in chlorine dioxide bleaching—aspects on in situ formation of molecular chlorine. Nordic Pulp Pap Res J 17:179–182
Torres AL, Roncero MB, Colom JF, Pastor FIJ, Blanco A, Vidal T (2000) Effect of a novel enzyme on fibre morphology during ECF bleaching of oxygen delignified eucalyptus kraft pulps. Bioresour Technol 74:135–140
Torres AL, Roncero MB, Colom JF, Martínez JA, Vidal T (2004) Application of an experimental design to modeling of ozone bleaching stage in TCF processes. Ozone Sci Eng 26:443–451
Valls C, Roncero MB (2009) Using both xylanase and laccase enzymes for pulp bleaching. Bioresour Technol 100:2032–2039
Valls C, Vidal T, Gallardo O, Díaz P, Pastor FIJ, Roncero MB (2010a) Obtaining low-HexA-content cellulose from eucalypt fibres: Which glycosil hydrolase family is more efficient? Carbohydr Polym 80:154–160
Valls C, Vidal T, Roncero MB (2010b) The role of xylanases and laccases on hexenuronic acid and lignin removal. Proc Biochem 45:425–430
Vidal T, Torres AL, Colom JF, Siles J (1997) Xylanase bleaching of eucalyptus kraft pulp—an economical ECF process. Appita J 50:144–148
Viikari L, Kantelinen A, Sundquist J, Linko M (1994) Xylanases in bleaching: from an idea to the industry. FEMS Microbiol Rev 13:335–350
Viikari L, Suurnäkki A, Buchert J (1996) Enzyme-aided bleaching of kraft pulps: fundamental mechanisms and practical applications. Enz Pulp Pap Process 655:15–24
Vuorinen T, Fagerström P, Buchert J, Tenkanen M, Teleman A (1999) Selective hydrolysis of hexenuronic acid groups and its application in ECF and TCF bleaching of kraft pulps. J Pulp Paper Sci 25:155–162
Wong KKY, Jong ED, Saddler JN, Allison RW (1997a) Mechanisms of xylanase aided bleaching of kraft pulp. Part 1: process parameters. Appita J 50:415–422
Wong KKY, Jong ED, Saddler JN, Allison RW (1997b) Mechanisms of xylanase aided bleaching of kraft pulp. Part 2: target substrates. Appita J 50:509–518
Acknowledgments
This work was funded within the framework of Spain’s MEC FUNCICEL (CTQ2009-12904) project. C. Valls is grateful to UPC for the research fellowship to finalize the PhD studies. Torraspapel S.A. (Zaragoza, Spain) and Buckmann Laboratories Ibérica S.A. are gratefully acknowledged for supplying the pulp and commercial enzymes, respectively.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Valls, C., Gallardo, Ó., Vidal, T. et al. Performance of new and commercial xylanases for ECF and TCF bleaching of eucalyptus kraft pulp. Wood Sci Technol 45, 433–448 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00226-010-0340-8
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00226-010-0340-8