Abstract
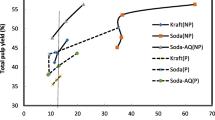
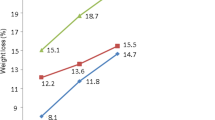
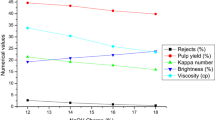
Dissolving pulps are the raw materials for the production of many different end-products. Jute is a very good source of cellulose. In this investigation, jute fiber was subjected to pulping in soda process in order to produce dissolving pulp under different prehydrolysis conditions and compared with prehydrolysed kraft pulp from jute. An increase of the prehydrolysis temperature or H2SO4 in prehydrolysis liquor increased the α-cellulose content and decreased the viscosity of pulp. The effect of ethylenediamine in soda liquor was also investigated when producing dissolving pulp. Jute fiber produced pulp having 90–97% α-cellulose. Ethylenediamine in soda liquor produced pulp of higher yield, viscosity and higher α-cellulose content than that of prehydrolysis soda or kraft pulp. The α-cellulose content and viscosity were increased with the increase of amine in soda liquor. The kappa number of dissolving pulp from jute was very low (9–5), which indicated that less bleaching chemicals are required for bleaching. The bleachability of soda-ethylenediamine pulp was lower than prehydrolysed soda and kraft pulp in ECF bleaching sequences. The bleachability of soda-ethylenediamine pulp was improved at the sacrifice of pulp yield when prehydrolysis was done prior to pulping. The alkali solubility S 10 and S 18 were 4–9 and 2–4%, respectively.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akhtaruzzamen AFM, Shafi M (1995) Pulping of jute. Tappi 78(2):106
Bhowmic K (1999) Dissolving pulp from jute stem by water prehydrolysis kraft process. IPPTA J 11(1):37–42
Biermann CJ (1993) Essentials of Pulping and Papermaking. Academic Press, New York, pp 72–100
Engström AC, Monica E, Henriksson G (2006) Improved accessibility and reactivity of dissolving pulp for the viscose process: pretreatment with monocomponent endoglucanase 7:2027–2031
Gübitz GM, Stebbing DW, Johansson CJ, Saddler JN (1998) Lignin-hemicellulose complexes restrict enzymatic solubilization of mannan and xylan from dissolving pulp. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 50:390–395
Helmy SA, State MA (1991) Viscose pulps from Egyptian bagasse with high chemical reactivity. Holzforschung 45:433–436
Henriksson G, Nutt A, Henriksson H, Pettersson B, Stahlberg J, Johansson G, Pettersson G (1999) Endoglucanase 28 (Cel12A)—a new Phanerochaete chrysosporium cellulase. Eur J Biochem 259(1/2):88–95
Hessler LE, Power RE (1954) The use of iodine adsorption as a measure of cellulose fiber crystallinity. Textile Res J 24:822–827
Hinck JF, Casebier RL, Hamilton JK (1985) Pulp and paper manufacture. In: Ingruder OV, Kocurek JJ, Wong W (eds) vol. 4 Tappi Press, Atlanta, pp 213–243
Jahan MS (2001) Evaluation of additives in soda pulping of jute. Tappi J 84(8):1–11
Jahan MS, Farouqui FI (2000) Pulping of whole jute plant (C. Capsularis) by soda-amine process. Holzforschung 54(6):625–630
Jahan MS, Farouqui FI (2001) Pulping of jute with amine. Cellulol Chem Technol 35(1–2):177–187
Jahan MS, Al-Maruf A, Quaiyyum MA (2007) Comparative studies of pulping of jute fiber, jute cutting and jute caddis. Bangladesh J Sci Ind Res 42(4):425–434
Jahan MS, Kanna GH, Mun SP, Nasima Chowdhury DA (2008) Variations in chemical characteristics and pulpability within jute plant (Chorcorus capsularis). Ind Crops Prod 28:199–205
Julien LM, Sun BCH (1979) Pulping with amine and soda-amine systems. Tappi J 62(8):63–65
Krässig HA (1993) Cellulose—structure, accessibility and reactivity. In: Huglin MB (ed) Polymer monographs, vol 11. Gordon and Breach science Publishers, Amsterdam
Kirci H, Akgul M (2002) Production of dissolving pulp from poplar wood by ethanol-water process. Turk J Agric For 26:239–245
Kubes GJ, Bolker HI (1978) Sulphur free delignification I. Alkaline pulping with monoethanolamine and ethylene diamine. Cellulose Chem Technol 12(5):621–645
Kubes GJ, Fleming BI, MacLeod JM, Bolker HI (1978) Sulphur free delignification. Tappi 61(8):46–50
Lennholm H, Iversen T (1995a) Classification of pulp fibers from different wood species by multivariate data-analysis of C-13-CP/MAS-NMR-spectra. Holzforschung 49(5):462–464
Lennholm H, Iversen T (1995b) The effect of laboratory beating on cellulose structure. Nordic Pulp Paper Res J 10(2):104–109
MacLeod JM, Iwase H, Bolker HI (1984) The carbohydrate composition of soda-additive pulps. Tappi J 67(5):123–124
Masura M (1987) Prehydrolysis of beechwood. Wood Sci Technol 21(1):89–100
Nahar N (1987) Studies on carbohydrates in jute and pigeon pea. Swedish University of Agriculture Sciences, Uppsala, p 42
Pulps J, Saake B, Parajo JC, Abad S,Sixta H, Harms H, Fink HP Weigel P, Al Ghatta H, Glionna A (1999) Comparative production of dissolving pulps by acetosol, formacell and milox pulping. Proceedings of ISWPC, June 7–10
Rath RL, Bhattacharjee C, Jain S, Bhattacharya PK (2005) Treatment of prehydrolysis liquor from pulp mill using a biological route followed by reverse osmosis. Chem Eng Technol 28(10):1201–1211
Racz I, Borsa J, Bodor B (1996) Crystallinity and accessibility of fibrous carboxymethylcellulose by pad-roll technology. J Appl Polym Sci 62(12):2015–2024
Rabinovich ML, Melnik MS, Bolobova AV (2002) Microbial cellulases (review). Appl Biochem Microbiol 38(4):305–321
Roy TK, Mohindru VK, Behera NC, Kulkarni AG, Prasad A (1998) Jute for speciality pulp. Ippta J 10(3):81–86
Schlotter NE (1988) Rayon. In: Mark HF (ed) Encyclopedia of polymer science and engineering, vol 14 (CD-ROM), Paulo Alto, Dialog information service, pp 45–69
Sixta H, Schuster J, Krotscheck AW, Ruckl W (1994) Towards effluent-free TCF-bleaching of eucalyptus prehydrolysis kraft pulp. Proc non-chlorine bleaching conf, Amelia Island, USA
Sixta H, Harms H, Dapia S, Parajo JC, Pulps J, Saake B, Fink HP, Roeder T (2004) Evaluation of new organosolv dissolving pulps, Part 1: preparation, analytical characterization and viscose processability. Cellulose 11:73–83
Sjöström E (1981) Wood chemistry: fundamentals and applications. Academic Press, New York, pp 169–189
Tang A, Zhang H, Chen G, Wu S, Xie G, Liang W (2002) Emerging technologies of pulping and papermaking. Proceedings of the international symposium on emerging technologies of pulping and papermaking, 2nd, Guangzhou, China, October 9–11, 152–158
TAPPI Standard Methods (1953) Specific gravity (density) and moisture content of pulpwood (T 18 m-53). Tappi Press, GA
Vila C, Santos V, Parajo C (2004) Dissolving pulp from TCF bleached acetosolv beech pulp. J. Chem. Technol Biotechnol. 79:1098–1104
Vietor RJ, Newman RH, Ha M, Apperley DC, Jarvis MC (2002) Conformational features of crystal-surface cellulose from higher plants. Plant J. 30(6):721–731
Wickholm K (2001) Structural elements in native celluloses. PhD thesis. Royal Institute of Technology, Stockholm, Sweden
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jahan, M.S. Studies on the effect of prehydrolysis and amine in cooking liquor on producing dissolving pulp from jute (Corchorus capsularis). Wood Sci Technol 43, 213–224 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00226-008-0213-6
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00226-008-0213-6