Abstract
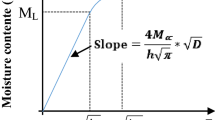
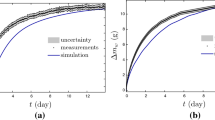
The objective of this study was to investigate the moisture absorption process for wood-based composites subjected to over-saturated moisture conditions. Two stages are comprised in the moisture transfer process at the over-saturated moisture conditions, an initial stage which is the moisture transfer process mainly under fiber saturation point (FSP), and a second stage which is the moisture transfer process beyond the FSP. A model was developed based on two-part equations to describe the process, from which three coefficients (k 1 , k 21 , and k 22) can be used to quantitatively describe the moisture transfer process under the conditions. Two different wood-based composites, wood fiberboard and wood fiber/polymer composites (polymer content: 30%), were used to test the model at four different ambient temperatures (30, 45, 62, and 80°C). It was shown that the two-part equation can accurately describe the moisture absorption process under over-saturated moisture conditions. The moisture absorption rate in the initial stage was about 30–60% greater than that in the second stage for most of the cases evaluated in this study. The higher the temperature, the greater moisture absorption parameters were obtained. At both moisture absorption stages (below FSP and above FSP), the calculated activation energy for the moisture absorption rate of wood fiberboard was very close to that of wood fiber/polymer composites.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Avramidis ST, Siau JF (1987) An investigation of the external and internal resistance to moisture diffusion in wood. Wood Sci Technol 21:249–256
Cai L, Shang D (1992) Modeling pf the moisture transfer process in particleboard. Holz Roh Werkst 50:395–399
Chen Y, Choong ET, Wetzel DM (1995) Evaluation of diffusion coefficient and surface emission coefficient by an optimization technique. Wood Fiber Sci 27(2):178–182
Cloutier A, Fortin Y (1993) A model of moisture movement in wood based on water potential and determination of the effective water conductivity. Wood Sci Technol 27:95–114
Hartley LD, Schneider MH (1993) Water vapour diffusion and adsorption characteristics of sugar maple (Acer saccharum, Marsh.) wood polymer composites. Wood Sci Technol 27:421–427
Liu JY (1989) A new method for separating diffusion coefficient and surface emission coefficient. Wood Fiber Sci 21(2):133–141
Shi SQ (1997) Composites processed from wood fibers and automobile polymer fluff. PhD dissertation, Michigan Technological University
Shi SQ (2007a) Diffusion model based on Fick’s second law for the moisture absorption process in wood fiber-based composites: is it suitable or not? Wood Sci Technol 41(8):645–658
Shi SQ (2007b) A simple model for moisture absorption process in wood-based composite and wood-polymer composites under water vapor conditions. Forest Products Society 61st International Convention, Knoxville, Tennessee, USA, June 10–13
Shi SQ, Gardner DJ (2006a) Hygroscopic thickness swelling rate of compression molded wood fiberboard and wood fiber/polymer composites. Compos A Appl Sci Manufact 37(9):1276–1285
Shi SQ, Gardner DJ (2006b) Effect of density and polymer content on the hygroscopic thickness swelling rate of compression molded wood fiber/polymer composites. Wood Fiber Sci 38(3):520–526
Skaar C (1958) Moisture movement in beech below the fiber saturation point. Forest Prod J 8:352–357
Wu Q, Suchsland O (1996) Prediction of moisture content and moisture gradient of an overlaid particleboard. Wood Fiber Sci 28(2):227–239
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This manuscript is approved for publication as Journal Article No. FP 398 of the Forest and Wildlife Research Center, Mississippi State University.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shi, S.Q., Wu, D. Modeling moisture absorption process of wood-based composites under over-saturated moisture conditions using two-part equations. Wood Sci Technol 43, 143–152 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00226-008-0201-x
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00226-008-0201-x