Abstract
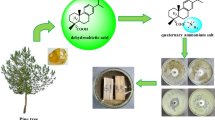
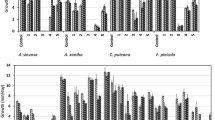
The biological activity of 17 potential wood preservatives—quaternary ammonium and imidazolium compounds—was determined employing screening agar-plate and agar-block methods. Experiments were carried out on Scots pine (Pinus sylvestris L.) wood. The fungicidal value of new compounds with cycloalkyl substituents for Coniophora puteana ranged from 0.64 kg/m3 to 2.2 kg/m3. Aspergillus niger turned out to be the most resistant fungus to the action of modified ICs, whereas Sclerophoma pityophila was effectively inhibited by the examined salts. It was stated that the antifungal and surface active properties of new compounds depend upon the alkyl chain and the size of the cycloalkyl ring in the molecule. The presented results demonstrate the relationship between the effective dose (ED) and the lethal dose (LD) and critical micelle concentration of new QACs and ICs as well as the relation between inhibition of fungal colonies and concentration of compounds in the substrate.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Emerson MF, Holtzer A (1965) On the ionic strength dependence of micelle number. J Phys Chem 69:3718
Kourai HF, Machikowa H, Takechi T, Horie K, Takeichi K, Shibasak J (1985) The antimicrobial characteristics of quaternary ammonium salts. Part IX. Quantitative structure-activity correlation of antimicrobial activity and hydrophobilicity of N-alkylpyridium iodide derivatives. J Antibact Antifung Agent 11:553–562
Mosquera V, del Rio M, Attwood D, Garcia M, Jones MN, Prieto G, Suaez M, Sarmieto F (1998) A study of the aggregation behavior of hexyltrimethylammonium bromide in aqueous solution. J Colloid Interf Sci 206:66–76
Pernak J, Skrzypczak A, Bogacki MB (1995) Quantitative relation between surface active properties and antibiotic activity of 1-alkyl-3-alkylthiomethylimidazolium chlorides. Chem Pharm Bull 43(11):2010–2019
Pernak J, Zabielska-Matejuk J, Urbanik E (1998) New quaternary ammonium chlorides—wood preservatives. Holzforschung 52(3):249–254
Polish Standard PN-EN 113 (2000) Wood preservatives—test method for determining the protective effectiveness against wood destroying Basidiomycetes—determination of the toxic values (in Polish). Polish Standardization Committee, Warsaw, Poland
Polish Standard PN-76/C-04903 (1976) Wood preservatives. Determination of the toxic value against Basidiomycetes by agar-block method (in Polish). Polish Standardization Committee, Warsaw, Poland
Tsunoda KT (1990) Effect of alkyl chain length on the fungicidal efficacy of benzalkonium chloride. Bokin Bobai 18:185–189
Urbanik E, Zabielska-Matejuk J, Skrzypczak A (1999) Quantitative relation between surface active properties and antifungal activity of quaternary imidazolium chlorides (new wood preservatives). For Prod J 49(10):53–58
Urbanik E, Zabielska-Matejuk J, Skrzypczak A, Pernak J (1997) Antifungal properties of new imidazolium chlorides against Coniophora puteana (Schum.: Fr.) Karst., Trametes versicolor (L.: Fr.) Pilát and Chaetomium globosum (Kunze: Fr.). Mater Org 31(4):247–263
Ważny J, Krajewski KJ (1994) New conception for shortening the duration of fungitoxic test on wood preservatives. Part 3. Proposal for inter-laboratory test on miniaturisation of wood specimens. Document no. IRG/WP/94–20053. International Research Group on Wood Preservatives, IRG Secretariat, Stockholm, Sweden
Ważny J, Thornton ID (1986) Comparative testing of strains of the dry rot fungus Serpula lacrymans (Schum. Ex Fr.) S.F. Gray II. The action of some wood preservatives in agar media. Holzforschung 40(6):383–388
Zabielska-Matejuk J (1999) Synthesis and fungicidal properties of quaternary imidazolium salts with an alkoxymethyl substituent. Pr Instit Techn Drew R.XLII(3/4):1–72
Zabielska-Matejuk J (2004) The influence of cation and anion structure of new quaternary ammonium salts on adsorption and leaching. Holzforschung (in press)
Zabielska-Matejuk J, Urbanik E, Pernak J (2004) New bis-quaternary and bis-imidazolium chlorides wood preservatives. Holzforschung 58(3):292–299
Zieliński R (2001) Długołańcuchowe czwartorzędowe sole amoniowe i zjawiska ich agregacji w roztworach wodnych. Monografia pt” Czwartorzędowe sole amoniowe i obszary ich zastosowania w gospodarce” Wydawnictwo ITD, Poznań (in Polish), pp 49–66
Acknowledgements
This investigation received financial support from the Polish Committee of Scientific research, Grant 4 T08E 069 24. I would like to thank Dr. Andrzej Skrzypczak from University of Technology in Poznań for the preparation of compounds.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zabielska-Matejuk, J. Antifungal properties of new quaternary ammonium compounds in relation to their surface activity. Wood Sci Technol 39, 235–243 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00226-004-0286-9
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00226-004-0286-9