Abstract
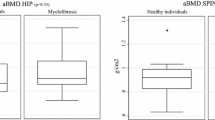
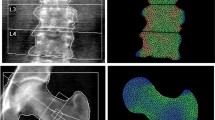
Patients with systemic mastocytosis (SM) are at high risk of bone deterioration. However, the evaluation of bone microarchitecture in this disease remains unclear. We aimed to assess bone microarchitecture in patients with SM. This was a cross-sectional study of 21 adult patients with SM conducted in a quaternary referral hospital in Sao Paulo, Brazil. A healthy, age-, weight-, and sex-matched cohort of 63 participants was used to provide reference values for bone microarchitecture, assessed by high resolution peripheral quantitative computed tomography (HR-pQCT). Total volumetric bone mineral density (vBMD), cortical vBMD, and cortical thickness at the radius were significantly lower in the control group compared with the SM group (all P < 0.001). Patients with aggressive SM had significantly lower trabecular number (Tb.N) (P = 0.035) and estimated failure load (F.load) (P = 0.032) at the tibia compared with those with indolent SM. Handgrip strength was significantly higher in patients who had more Tb.N at the radius (ρ, 0.46; P = 0.036) and tibia (ρ, 0.49; P = 0.002), and lower who had more trabecular separation at the radius (ρ, −0.46; P = 0.035) and tibia (ρ, −0.52; P = 0.016). Strong and positive associations between F.load (ρ, 0.75; P < 0.001) and stiffness (ρ, 0.70; P < 0.001) at the radius, and between F.load at the tibia (ρ, 0.45; P = 0.038) were observed with handgrip strength. In this cross-sectional study, aggressive SM was more susceptible to bone deterioration compared with indolent SM. In addition, the findings demonstrated that handgrip strength was associated with bone microarchitecture and bone strength.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pardanani A (2021) Systemic mastocytosis in adults: 2021 Update on diagnosis, risk stratification and management. Am J Hematol 96:508–525
Theoharides TC, Valent P, Akin C (2015) Mast cells, mastocytosis, and related disorders. N Engl J Med 373:163–172
Broesby-Olsen S, Farkas DK, Vestergaard H, Hermann AP, Møller MB, Mortz CG, Kristensen TK, Bindslev-Jensen C, Sørensen HT, Frederiksen H (2016) Risk of solid cancer, cardiovascular disease, anaphylaxis, osteoporosis and fractures in patients with systemic mastocytosis: a nationwide population-based study. Am J Hematol 91:1069–1075
Rossini M, Zanotti R, Bonadonna P, Artuso A, Caruso B, Schena D, Vecchiato D, Bonifacio M, Viapiana O, Gatti D, Senna G, Riccio A, Passalacqua G, Pizzolo G, Adami S (2011) Bone mineral density, bone turnover markers and fractures in patients with indolent systemic mastocytosis. Bone 49:880–885
van der Veer E, van der Goot W, de Monchy JG, Kluin-Nelemans HC, van Doormaal JJ (2012) High prevalence of fractures and osteoporosis in patients with indolent systemic mastocytosis. Allergy 67:431–438
Degboé Y, Eischen M, Nigon D, Apoil PA, Mailhol C, Tournier E, Laurent C, Hanssens K, Hermine O, Paul C, Laroche M, Bulai-Livideanu C (2017) Prevalence and risk factors for fragility fracture in systemic mastocytosis. Bone 105:219–225
Orsolini G, Viapiana O, Rossini M, Bonifacio M, Zanotti R (2018) Bone disease in mastocytosis. Immunol Allergy Clin North Am 38:443–454
Rossini M, Zanotti R, Viapiana O, Tripi G, Orsolini G, Idolazzi L, Bonadonna P, Schena D, Escribano L, Adami S, Gatti D (2014) Bone involvement and osteoporosis in mastocytosis. Immunol Allergy Clin North Am 34:383–396
Seitz S, Barvencik F, Koehne T, Priemel M, Pogoda P, Semler J, Minne H, Pfeiffer M, Zustin J, Püschel K, Eulenburg C, Schinke T, Amling M (2013) Increased osteoblast and osteoclast indices in individuals with systemic mastocytosis. Osteoporos Int 24:2325–2334
Gehlen M, Schmidt N, Pfeifer M, Balasingam S, Schwarz-Eywill M, Maier A, Werner M, Siggelkow H (2021) Osteoporosis caused by systemic mastocytosis: prevalence in a Cohort of 8392 patients with osteoporosis. Calcif Tissue Int 109:685–695
Hans D, Barthe N, Boutroy S, Pothuaud L, Winzenrieth R, Krieg MA (2011) Correlations between trabecular bone score, measured using anteroposterior dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry acquisition, and 3-dimensional parameters of bone microarchitecture: an experimental study on human cadaver vertebrae. J Clin Densitom 14:302–312
Ulivieri FM, Rinaudo L (2022) The bone strain index: an innovative dual X-ray absorptiometry bone strength index and its helpfulness in clinical medicine. J Clin Med 11:2284–2296
Ulivieri FM, Rinaudo L, Piodi LP, Barbieri V, Marotta G, Sciumè M, Grifoni FI, Cesana BM (2020) Usefulness of dual X-ray absorptiometry-derived bone geometry and structural indexes in mastocytosis. Calcif Tissue Int 107:551–558
Fuller H, Fuller R, Pereira RM (2015) High resolution peripheral quantitative computed tomography for the assessment of morphological and mechanical bone parameters. Rev Bras Reumatol 55:352–362
Valent P, Akin C, Metcalfe DD (2017) Mastocytosis: 2016 updated WHO classification and novel emerging treatment concepts. Blood 129:1420–1427
Alvarenga JC, Fuller H, Pasoto SG, Pereira RM (2017) Age-related reference curves of volumetric bone density, structure, and biomechanical parameters adjusted for weight and height in a population of healthy women: an HR-pQCT study. Osteoporos Int 28:1335–1346
Alvarenga JC, Caparbo VF, Domiciano DS, Pereira RMR (2022) Age-related reference data of bone microarchitecture, volumetric bone density, and bone strength parameters in a population of healthy Brazilian men: an HR-pQCT study. Osteoporos Int 33:1309–1321
Genant HK, Wu CY, van Kuijk C, Nevitt MC (1993) Vertebral fracture assessment using a semiquantitative technique. J Bone Miner Res 8:1137–1148
Greiner G, Gurbisz M, Ratzinger F, Witzeneder N, Simonitsch-Klupp I, Mitterbauer-Hohendanner G, Mayerhofer M, Müllauer L, Sperr WR, Valent P, Hoermann G (2018) Digital PCR: a sensitive and precise method for KIT D816V quantification in mastocytosis. Clin Chem 64:547–555
Siebenhaar F, Sander B, Ho LHT, Ellrich A, Maurer M, Weller K (2018) Development and validation of the mastocytosis activity score. Allergy 73:1489–1496
Guillaume N, Desoutter J, Chandesris O, Merlusca L, Henry I, Georgin-Lavialle S, Barete S, Hirsch I, Bouredji D, Royer B, Gruson B, Lok C, Sevestre H, Mentaverri R, Brazier M, Meynier J, Hermine O, Marolleau JP, Kamel S, Damaj G (2013) Bone complications of mastocytosis: a link between clinical and biological characteristics. Am J Med 126:75.e71-77
Fitzpatrick LA, Buzas E, Gagne TJ, Nagy A, Horvath C, Ferencz V, Mester A, Kari B, Ruan M, Falus A, Barsony J (2003) Targeted deletion of histidine decarboxylase gene in mice increases bone formation and protects against ovariectomy-induced bone loss. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:6027–6032
Biosse-Duplan M, Baroukh B, Dy M, de Vernejoul MC, Saffar JL (2009) Histamine promotes osteoclastogenesis through the differential expression of histamine receptors on osteoclasts and osteoblasts. Am J Pathol 174:1426–1434
Dobigny C, Saffar JL (1997) H1 and H2 histamine receptors modulate osteoclastic resorption by different pathways: evidence obtained by using receptor antagonists in a rat synchronized resorption model. J Cell Physiol 173:10–18
Degboé Y, Eischen M, Apoil PA, Mailhol C, Dubreuil P, Hermine O, Paul C, Bulai Livideanu C, Laroche M (2019) Higher prevalence of vertebral fractures in systemic mastocytosis, but not in cutaneous mastocytosis and idiopathic mast cell activation syndrome. Osteoporos Int 30:1235–1241
Figueiredo CP, Perez MO, Sales LP, Domiciano DS, Sampaio-Barros MM, Caparbo VF, Pereira RMR (2022) Lower hand grip in rheumatoid arthritis patients is associated with low finite element analysis using high resolution peripheral quantitative computed tomography scan of the 2nd metacarpophalangeal joint. Int J Rheum Dis 25:1038–1045
Funding
This study was supported by Sao Paulo Research Foundation (FAPESP) (grants 19/24782-4).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
ASF had full access to all of the data in the study and take responsibility for the integrity of the data and the accuracy of the data analysis. Concept and design: ASF, IHM, EDRPV, RMRP.Acquisition, analysis, and interpretation: All authors. Drafting of the manuscript: ASF, IHM. Critical revision of the manuscript for important intellectual content: All authors. Statistical analysis: ASF, IHM, EDRPV. Obtained funding: EDRPV, RMRP. Supervision: EDRPV, RMRP. Administrative, technical, or material support: LT, VFC. Dra Luciana Nardinelli (Laboratory of Tumor Biology of Hospital das Clínicas da FMUSP for performing the dPCR KIT D816V studies) and Dr. Elaine Aparecida Rosseto (Clinical Laboratory of Hospital Israelita Albert Einstein) for performing tryptase tests. The authors are thankful to all the patients who participated in this study. All the individuals described in this section received no compensation for their participation in the study.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Andre S. Franco, Igor H. Murai, Liliam Takayama, Valeria F. Caparbo, Luan L. Marchi, Elvira D. R. P. Velloso, and Rosa M. R. Pereira declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Role of the Funder/Sponsor
The funders had no role in the design and conduct of the study; collection, management, analysis, and interpretation of the data; preparation, review, or approval of the manuscript; and decision to submit the manuscript for publication.
Human and Animal Rights and Informed Consent
The study was approved by the ethics committee of the Hospital das Clinicas of the School of Medicine of the University of Sao Paulo (#19821519.0.0000.0068, date of approval September 4, 2019) and all the patients provided written informed consent before participation.
Additional information
Rosa M. R. Pereira in memoriam.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Franco, A.S., Murai, I.H., Takayama, L. et al. Assessment of Bone Microarchitecture in Patients with Systemic Mastocytosis and its Association with Clinical and Biochemical Parameters of the Disease. Calcif Tissue Int 113, 276–285 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00223-023-01107-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00223-023-01107-x