Abstract
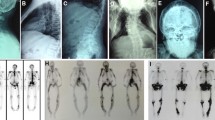
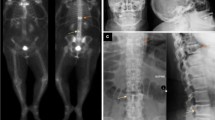
Paget’s disease of bone (PDB) is a rare metabolic bone disorder, which is extremely rare in Asian population. This study aimed to investigate the phenotypes and the pathogenic mutations of woman with early-onset PDB. The clinical features, bone mineral density, x-ray, radionuclide bone scan, and serum levels of alkaline phosphatase (ALP), procollagen type 1 N-terminal propeptide (P1NP), and β-carboxy-terminal cross-linked telopeptide of type 1 collagen (β-CTX) were measured in detail. The pathogenic mutations were identified by whole-exon sequencing and confirmed by Sanger sequencing. We also evaluated the effects of intravenous infusion of zoledronic acid on the bones of the patient and summarized the phenotypic characteristics of reported patients with mutation at position 155 of the valosin-containing protein (VCP). The patient only exhibited bone pain as the initial manifestation with vertebral compression fracture and extremely elevated ALP, P1NP, and β-CTX levels; she had no inclusion body myopathy and frontotemporal dementia. The missense mutation in exon 5 of the VCP gene (p.Arg155His) was identified by whole-exome sequencing and further confirmed by Sanger sequencing. No mutation in candidate genes of PDB, such as SQSTM1, CSF1, TM7SF4, OPTN, PFN1, and TNFRSF11A, were identified in the patient by Sanger sequencing. Rapid relief of bone pain and a marked decline in ALP, P1NP, and β-CTX levels were observed after zoledronic acid treatment. Previously reported patients with VCP missense mutation at position 155 (R155H) always had myopathy, frontotemporal dementia, and PDB, but the patient in this study exhibited only PDB. This was the first report of R155H mutation-induced early-onset in the VCP gene in Asian population. PDB was the only manifestation having a favorable response to zoledronic acid treatment. We broadened the genetic and clinical phenotype spectra of the VCP mutation.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tuck SP (2020) Adult Paget disease of bone: a tale of two guidelines. Rheumatology (Oxford) 59:2197–2198
Albagha OM, Wani SE, Visconti MR, Alonso N, Goodman K, Brandi ML, Cundy T, Chung PY, Dargie R, Devogelaer JP, Falchetti A, Fraser WD, Gennari L, Gianfrancesco F, Hooper MJ, Van Hul W, Isaia G, Nicholson GC, Nuti R, Papapoulos S, Montes Jdel P, Ratajczak T, Rea SL, Rendina D, Gonzalez-Sarmiento R, Di Stefano M, Ward LC, Walsh JP, Ralston SH (2011) Genome-wide association identifies three new susceptibility loci for Paget’s disease of bone. Nat Genet 43:685–689
Singer FR (2016) Bone quality in Paget’s disease of bone. Curr Osteoporos Rep 14:39–42
Makaram NS, Ralston SH (2021) Genetic determinants of Paget’s disease of bone. Curr Osteoporos Rep 19:327–337
Hsu E (2019) Paget’s disease of bone: updates for clinicians. Curr Opin Endocrinol Diabetes Obes 26:329–334
Merlotti D, Materozzi M, Bianciardi S, Guarnieri V, Rendina D, Volterrani L, Bellan C, Mingiano C, Picchioni T, Frosali A, Orfanelli U, Cenci S, Gennari L (2020) Mutation of PFN1 gene in an early onset, polyostotic Paget-like disease. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 105:2553–2565
Ralston SH, Albagha OM (2014) Genetics of Paget’s disease of bone. Curr Osteoporos Rep 12:263–271
Wei Z, Li S, Tao X, Zhu G, Sun Z, Wei Z, Jiao Q, Zhang H, Chen L, Li B, Zhang Z, Yue H (2021) Mutations in profilin 1 cause early-onset Paget’s disease of bone with giant cell tumors. J Bone Miner Res 36:1088–1103
Whyte MP (2006) Paget’s disease of bone and genetic disorders of RANKL/OPG/RANK/NF-kappaB signaling. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1068:143–164
Watts GD, Thomasova D, Ramdeen SK, Fulchiero EC, Mehta SG, Drachman DA, Weihl CC, Jamrozik Z, Kwiecinski H, Kaminska A, Kimonis VE (2007) Novel VCP mutations in inclusion body myopathy associated with Paget disease of bone and frontotemporal dementia. Clin Genet 72:420–426
Singer FR, Bone HG 3rd, Hosking DJ, Lyles KW, Murad MH, Reid IR, Siris ES (2014) Paget’s disease of bone: an endocrine society clinical practice guideline. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 99:4408–4422
Yin MC, Yan YJ, Tong ZY, Xu CQ, Qiao JJ, Zhou XN, Ye J, Mo W (2020) Development and validation of a novel scoring system for severity of plantar fasciitis. Orthop Surg 12:1882–1889
Bennell K, Dobson F, Hinman R (2011) Measures of physical performance assessments: self-paced walk test (SPWT), stair climb test (SCT), six-minute walk test (6MWT), chair stand test (CST), timed up & go (TUG), sock test, lift and carry test (LCT), and car task. Arthritis Care Res 63(Suppl 11):S350-370
Mehta SG, Khare M, Ramani R, Watts GD, Simon M, Osann KE, Donkervoort S, Dec E, Nalbandian A, Platt J, Pasquali M, Wang A, Mozaffar T, Smith CD, Kimonis VE (2013) Genotype-phenotype studies of VCP-associated inclusion body myopathy with Paget disease of bone and/or frontotemporal dementia. Clin Genet 83:422–431
Liu Y, Asan MD, Lv F, Xu X, Wang J, Xia W, Jiang Y, Wang O, Xing X, Yu W, Wang J, Sun J, Song L, Zhu Y, Yang H, Wang J, Li M (2017) Gene mutation spectrum and genotype-phenotype correlation in a cohort of Chinese osteogenesis imperfecta patients revealed by targeted next generation sequencing. Osteoporos Int 28:2985–2995
Tang WK, Li D, Li CC, Esser L, Dai R, Guo L, Xia D (2010) A novel ATP-dependent conformation in p97 N-D1 fragment revealed by crystal structures of disease-related mutants. EMBO J 29:2217–2229
Watts GD, Wymer J, Kovach MJ, Mehta SG, Mumm S, Darvish D, Pestronk A, Whyte MP, Kimonis VE (2004) Inclusion body myopathy associated with Paget disease of bone and frontotemporal dementia is caused by mutant valosin-containing protein. Nat Genet 36:377–381
Viassolo V, Previtali SC, Schiatti E, Magnani G, Minetti C, Zara F, Grasso M, Dagna-Bricarelli F, Di Maria E (2008) Inclusion body myopathy, Paget’s disease of the bone and frontotemporal dementia: recurrence of the VCP R155H mutation in an Italian family and implications for genetic counselling. Clin Genet 74:54–60
Hübbers CU, Clemen CS, Kesper K, Böddrich A, Hofmann A, Kämäräinen O, Tolksdorf K, Stumpf M, Reichelt J, Roth U, Krause S, Watts G, Kimonis V, Wattjes MP, Reimann J, Thal DR, Biermann K, Evert BO, Lochmüller H, Wanker EE, Schoser BG, Noegel AA, Schröder R (2007) Pathological consequences of VCP mutations on human striated muscle. Brain 130:381–393
Stojkovic T, el Hammouda H, Richard P, López de Munain A, Ruiz-Martinez J, Camaño P, Laforêt P, Pénisson-Besnier I, Ferrer X, Lacour A, Lacomblez L, Claeys KG, Maurage CA, Fardeau M, Eymard B (2009) Clinical outcome in 19 French and Spanish patients with valosin-containing protein myopathy associated with Paget’s disease of bone and frontotemporal dementia. Neuromuscul Disord 19:316–323
Jacquin A, Rouaud O, Soichot P, Bejot Y, Dygai-Cochet I, Sarazin M, Stojkovic T, Lemesle-Martin M, Giroud M, Moreau T (2013) Psychiatric presentation of frontotemporal dementia associated with inclusion body myopathy due to the VCP mutation (R155H) in a French family. Case Rep Neurol 5:187–194
Jerath NU (2019) Resolving a multi-generational neuromuscular mystery in a family presenting with a variable scapuloperoneal syndrome in a c.464G>A, p.Arg155His VCP mutation. Case Rep Genet 2019:2403024
Gu JM, Ke YH, Yue H, Liu YJ, Zhang Z, Zhang H, Hu WW, Wang C, He JW, Hu YQ, Li M, Fu WZ, Zhang ZL (2013) A novel VCP mutation as the cause of atypical IBMPFD in a Chinese family. Bone 52:9–16
Tresse E, Salomons FA, Vesa J, Bott LC, Kimonis V, Yao TP, Dantuma NP, Taylor JP (2010) VCP/p97 is essential for maturation of ubiquitin-containing autophagosomes and this function is impaired by mutations that cause IBMPFD. Autophagy 6:217–227
Nalbandian A, Ghimbovschi S, Wang Z, Knoblach S, Llewellyn KJ, Vesa J, Hoffman EP, Kimonis VE (2015) Global gene expression profiling in R155H knock-in murine model of VCP disease. Clin Transl Sci 8:8–16
Li H, Cui Y, Wei J, Liu C, Chen Y, Cui CP, Li L, Zhang X, Zhang L (2019) VCP/p97 increases BMP signaling by accelerating ubiquitin ligase Smurf1 degradation. FASEB J 33:2928–2943
Roodman GD, Windle JJ (2005) Paget disease of bone. J Clin Invest 115:200–208
Dai RM, Li CC (2001) Valosin-containing protein is a multi-ubiquitin chain-targeting factor required in ubiquitin-proteasome degradation. Nat Cell Biol 3:740–744
Weihl CC, Dalal S, Pestronk A, Hanson PI (2006) Inclusion body myopathy-associated mutations in p97/VCP impair endoplasmic reticulum-associated degradation. Hum Mol Genet 15:189–199
Halawani D, LeBlanc AC, Rouiller I, Michnick SW, Servant MJ, Latterich M (2009) Hereditary inclusion body myopathy-linked p97/VCP mutations in the NH2 domain and the D1 ring modulate p97/VCP ATPase activity and D2 ring conformation. Mol Cell Biol 29:4484–4494
Weihl CC, Pestronk A, Kimonis VE (2009) Valosin-containing protein disease: inclusion body myopathy with Paget’s disease of the bone and fronto-temporal dementia. Neuromuscul Disord 19:308–315
Custer SK, Neumann M, Lu H, Wright AC, Taylor JP (2010) Transgenic mice expressing mutant forms VCP/p97 recapitulate the full spectrum of IBMPFD including degeneration in muscle, brain and bone. Hum Mol Genet 19:1741–1755
Greenblatt MB, Park KH, Oh H, Kim JM, Shin DY, Lee JM, Lee JW, Singh A, Lee KY, Hu D, Xiao C, Charles JF, Penninger JM, Lotinun S, Baron R, Ghosh S, Shim JH (2015) CHMP5 controls bone turnover rates by dampening NF-κB activity in osteoclasts. J Exp Med 212:1283–1301
Soysa NS, Alles N (2009) NF-kappaB functions in osteoclasts. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 378:1–5
Paccou J, Michou L, Kolta S, Debiais F, Cortet B, Guggenbuhl P (2018) High bone mass in adults. Jt Bone Spine 85:693–699
Bartolome F, Wu HC, Burchell VS, Preza E, Wray S, Mahoney CJ, Fox NC, Calvo A, Canosa A, Moglia C, Mandrioli J, Chiò A, Orrell RW, Houlden H, Hardy J, Abramov AY, Plun-Favreau H (2013) Pathogenic VCP mutations induce mitochondrial uncoupling and reduced ATP levels. Neuron 78:57–64
Ahn Y, Sabouny R, Villa BR, Yee NC, Mychasiuk R, Uddin GM, Rho JM, Shutt TE (2020) Aberrant mitochondrial morphology and function in the BTBR mouse model of autism is improved by two weeks of ketogenic diet. Int J Mol Sci 21:3266
Ralston SH, Corral-Gudino L, Cooper C, Francis RM, Fraser WD, Gennari L, Guañabens N, Javaid MK, Layfield R, O’Neill TW, Russell RGG, Stone MD, Simpson K, Wilkinson D, Wills R, Zillikens MC, Tuck SP (2019) Diagnosis and management of Paget’s disease of bone in adults: a clinical guideline. J Bone Miner Res 34:579–604
Devogelaer JP, Manicourt DH (2007) Zoledronic acid for treatment of Paget’s disease of bone. Expert Opin Pharmacother 8:2863–2869
Reid IR, Lyles K, Su G, Brown JP, Walsh JP, del Pino-Montes J, Miller PD, Fraser WD, Cafoncelli S, Bucci-Rechtweg C, Hosking DJ (2011) A single infusion of zoledronic acid produces sustained remissions in Paget disease: data to 6.5 years. J Bone Miner Res 26:2261–2270
Acknowledgements
We appreciate the patient and her family for their participation in the study.
Funding
This work is supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos.81873668, 82070908), Beijing Natural Science Foundation (7202153), and National Key R&D Program of China (2018YFA0800801).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Disclosure
Yongze Zhang, Peng Gao, Sunjie Yan, Qian Zhang, Ou Wang, Yan Jiang, Xiaoping Xing, Weibo Xia, and Mei Li declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Human and Animal Rights
All procedures were in accordance with the ethical standards of the responsible committee on human experimentation (institutional and national) and with the Helsinki Declaration.
Informed Consent
Informed consent was obtained from the proband in the study. The study protocol was approved by the Scientific Research Ethics Committee of PUMCH.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Y., Gao, P., Yan, S. et al. Clinical, Biochemical, Radiological, and Genetic Analyses of a Patient with VCP Gene Variant-Induced Paget’s Disease of Bone. Calcif Tissue Int 110, 518–528 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00223-021-00929-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00223-021-00929-x