Abstract
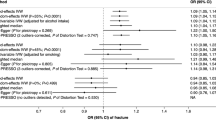
Observational studies examining associations of smoking and alcohol consumption with bone mineral density (BMD) have generated inconsistent results and suffer from several methodological limitations. We aim to evaluate whether there are causal associations between smoking, alcohol consumption, and BMD using a Mendelian randomization (MR) design. Genetic variants associated with smoking status (n = 142), no. of cigarettes smoked per day (CPD) (n = 3), smoking initiation (n = 1), and alcohol consumption (n = 6) identified in published genome-wide association studies (GWAS) were used as instruments. Summary statistics data of 32735, 28498, 8143, and 445921 European subjects included in The GEnetic Factors for Osteoporosis Consortium or UK Biobank were used to generate associations of genetically predicted smoking or alcohol consumption with femoral neck (FN-BMD), lumbar spine (LS-BMD), forearm (FA-BMD), and heel BMD, respectively, by using the inverse-variance weighted method. The BMD was measured using either ultrasound (for heel) or Dual-energy X-ray Absorptiometry (for others). In our analyses, smoking status tended to be negatively associated with several types of BMD (heel BMD: β = − 0.053, p = 0.003; FN-BMD: β = − 0.139, p = 0.053; FA-BMD: β = − 0.264, p = 0.077), although the association with LS-BMD was null. Smoking initiation was significantly inversely associated with heel BMD (β = − 0.201, p = 3.60 × 10−8). CPD was associated with a lower FN-BMD (β = − 0.014, p = 0.047) only. There was no clear association of genetically predicted alcohol consumption with BMD. Our study provided some evidence of a potential association between genetically predicted smoking and lower BMD, especially for heel BMD, but not for alcohol consumption. Considering the inconsistent findings with the different types of BMD and limitations of the current work, further studies are needed to better characterize the exact relationship between smoking, alcohol consumption, and BMD.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ward KD, Klesges RC (2001) A meta-analysis of the effects of cigarette smoking on bone mineral density. Calcif Tissue Int 68:259–270
Berg KM, Kunins HV, Jackson JL, Nahvi S, Chaudhry A, Harris KA Jr, Malik R, Arnsten JH (2008) Association between alcohol consumption and both osteoporotic fracture and bone density. Am J Med 121:406–418
Cosman F, de Beur SJ, LeBoff MS, Lewiecki EM, Tanner B, Randall S, Lindsay R, National Osteoporosis F (2014) Clinician’s guide to prevention and treatment of osteoporosis. Osteoporos Int 25:2359–2381
Haycock PC, Burgess S, Wade KH, Bowden J, Relton C, Davey Smith G (2016) Best (but oft-forgotten) practices: the design, analysis, and interpretation of Mendelian randomization studies. Am J Clin Nutr 103:965–978
Davey Smith G, Hemani G (2014) Mendelian randomization: genetic anchors for causal inference in epidemiological studies. Hum Mol Genet 23:R89–R98
Warodomwichit D, Sritara C, Thakkinstian A, Chailurkit LO, Yamwong S, Ratanachaiwong W, Ongphiphadhanakul B, Sritara P (2013) Causal inference of the effect of adiposity on bone mineral density in adults. Clin Endocrinol 78:694–699
Ahmad OS, Leong A, Miller JA, Morris JA, Forgetta V, Mujammami M, Richards JB (2017) A Mendelian randomization study of the effect of type-2 diabetes and glycemic traits on bone mineral density. J Bone Miner Res 32:1072–1081
Katikireddi SV, Green MJ, Taylor AE, Davey Smith G, Munafo MR (2017) Assessing causal relationships using genetic proxies for exposures: an introduction to Mendelian randomization. Addiction 113:764–774
The Tobacco and Genetics Consortium (2010) Genome-wide meta-analyses identify multiple loci associated with smoking behavior. Nat Genet 42:441–447
Kutalik Z, Benyamin B, Bergmann S, Mooser V, Waeber G, Montgomery GW, Martin NG, Madden PA, Heath AC, Beckmann JS, Vollenweider P, Marques-Vidal P, Whitfield JB (2011) Genome-wide association study identifies two loci strongly affecting transferrin glycosylation. Hum Mol Genet 20:3710–3717
Kapoor M, Wang JC, Wetherill L, Le N, Bertelsen S, Hinrichs AL, Budde J, Agrawal A, Bucholz K, Dick D, Harari O, Hesselbrock V, Kramer J, Nurnberger JI Jr, Rice J, Saccone N, Schuckit M, Tischfield J, Porjesz B, Edenberg HJ, Bierut L, Foroud T, Goate A (2013) A meta-analysis of two genome-wide association studies to identify novel loci for maximum number of alcoholic drinks. Hum Genet 132:1141–1151
Schumann G, Coin LJ, Lourdusamy A, Charoen P, Berger KH, Stacey D, Desrivieres S, Aliev FA, Khan AA, Amin N, Aulchenko YS, Bakalkin G, Bakker SJ, Balkau B, Beulens JW, Bilbao A, de Boer RA, Beury D, Bots ML, Breetvelt EJ, Cauchi S, Cavalcanti-Proenca C, Chambers JC, Clarke TK, Dahmen N, de Geus EJ, Dick D, Ducci F, Easton A, Edenberg HJ, Esko T, Fernandez-Medarde A, Foroud T, Freimer NB, Girault JA, Grobbee DE, Guarrera S, Gudbjartsson DF, Hartikainen AL, Heath AC, Hesselbrock V, Hofman A, Hottenga JJ, Isohanni MK, Kaprio J, Khaw KT, Kuehnel B, Laitinen J, Lobbens S, Luan J, Mangino M, Maroteaux M, Matullo G, McCarthy MI, Mueller C, Navis G, Numans ME, Nunez A, Nyholt DR, Onland-Moret CN, Oostra BA, O’Reilly PF, Palkovits M, Penninx BW, Polidoro S, Pouta A, Prokopenko I, Ricceri F, Santos E, Smit JH, Soranzo N, Song K, Sovio U, Stumvoll M, Surakk I, Thorgeirsson TE, Thorsteinsdottir U, Troakes C, Tyrfingsson T, Tonjes A, Uiterwaal CS, Uitterlinden AG, van der Harst P, van der Schouw YT, Staehlin O, Vogelzangs N, Vollenweider P, Waeber G, Wareham NJ, Waterworth DM, Whitfield JB, Wichmann EH, Willemsen G, Witteman JC, Yuan X, Zhai G, Zhao JH, Zhang W, Martin NG, Metspalu A et al (2011) Genome-wide association and genetic functional studies identify autism susceptibility candidate 2 gene (AUTS2) in the regulation of alcohol consumption. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 108:7119–7124
Loh P-R, Kichaev G, Gazal S, Schoech AP, Price AL. Mixed model association for biobank-scale data sets. BioRXiv. https://doi.org/10.1101/194944 (2018)
Lawlor DA (2016) Commentary: two-sample Mendelian randomization: opportunities and challenges. Int J Epidemiol 45:908–915
Burgess S, Scott RA, Timpson NJ, Davey Smith G, Thompson SG, Consortium E-I (2015) Using published data in Mendelian randomization: a blueprint for efficient identification of causal risk factors. Eur J Epidemiol 30:543–552
Zheng HF, Forgetta V, Hsu YH, Estrada K, Rosello-Diez A, Leo PJ, Dahia CL, Park-Min KH, Tobias JH, Kooperberg C, Kleinman A, Styrkarsdottir U, Liu CT, Uggla C, Evans DS, Nielson CM, Walter K, Pettersson-Kymmer U, McCarthy S, Eriksson J, Kwan T, Jhamai M, Trajanoska K, Memari Y, Min J, Huang J, Danecek P, Wilmot B, Li R, Chou WC, Mokry LE, Moayyeri A, Claussnitzer M, Cheng CH, Cheung W, Medina-Gomez C, Ge B, Chen SH, Choi K, Oei L, Fraser J, Kraaij R, Hibbs MA, Gregson CL, Paquette D, Hofman A, Wibom C, Tranah GJ, Marshall M, Gardiner BB, Cremin K, Auer P, Hsu L, Ring S, Tung JY, Thorleifsson G, Enneman AW, van Schoor NM, de Groot LC, van der Velde N, Melin B, Kemp JP, Christiansen C, Sayers A, Zhou Y, Calderari S, van Rooij J, Carlson C, Peters U, Berlivet S, Dostie J, Uitterlinden AG, Williams SR, Farber C, Grinberg D, LaCroix AZ, Haessler J, Chasman DI, Giulianini F, Rose LM, Ridker PM, Eisman JA, Nguyen TV, Center JR, Nogues X, Garcia-Giralt N, Launer LL, Gudnason V, Mellstrom D, Vandenput L, Amin N, van Duijn CM, Karlsson MK, Ljunggren O, Svensson O, Hallmans G, Rousseau F, Giroux S, Bussiere J, Arp PP et al (2015) Whole-genome sequencing identifies EN1 as a determinant of bone density and fracture. Nature 526:112–117
Loh PR, Tucker G, Bulik-Sullivan BK, Vilhjalmsson BJ, Finucane HK, Salem RM, Chasman DI, Ridker PM, Neale BM, Berger B, Patterson N, Price AL (2015) Efficient Bayesian mixed-model analysis increases association power in large cohorts. Nat Genet 47:284–290
Burgess S, Butterworth A, Thompson SG (2013) Mendelian randomization analysis with multiple genetic variants using summarized data. Genet Epidemiol 37:658–665
Bowden J, Davey Smith G, Burgess S (2015) Mendelian randomization with invalid instruments: effect estimation and bias detection through Egger regression. Int J Epidemiol 44:512–525
Clarke TK, Adams MJ, Davies G, Howard DM, Hall LS, Padmanabhan S, Murray AD, Smith BH, Campbell A, Hayward C, Porteous DJ, Deary IJ, McIntosh AM (2017) Genome-wide association study of alcohol consumption and genetic overlap with other health-related traits in UK Biobank (N = 112 117). Mol Psychiatry 22:1376–1384
Law MR, Hackshaw AK (1997) A meta-analysis of cigarette smoking, bone mineral density and risk of hip fracture: recognition of a major effect. BMJ 315:841–846
Stevenson JC, Lees B, Devenport M, Cust MP, Ganger KF (1989) Determinants of bone density in normal women: risk factors for future osteoporosis? BMJ 298:924–928
Johnell O, Nilsson BE (1984) Life-style and bone mineral mass in perimenopausal women. Calcif Tissue Int 36:354–356
Willett W, Stampfer MJ, Bain C, Lipnick R, Speizer FE, Rosner B, Cramer D, Hennekens CH (1983) Cigarette smoking, relative weight, and menopause. Am J Epidemiol 117:651–658
Jick H, Porter J (1977) Relation between smoking and age of natural menopause. Report from the Boston Collaborative Drug Surveillance Program, Boston University Medical Center. Lancet 1:1354–1355
Svartberg J, Jorde R (2007) Endogenous testosterone levels and smoking in men. The fifth Tromso study. Int J Androl 30:137–143
English KM, Pugh PJ, Parry H, Scutt NE, Channer KS, Jones TH (2001) Effect of cigarette smoking on levels of bioavailable testosterone in healthy men. Clin Sci 100:661–665
Murphy S, Khaw KT, Cassidy A, Compston JE (1993) Sex hormones and bone mineral density in elderly men. Bone Miner 20:133–140
Foresta C, Ruzza G, Mioni R, Guarneri G, Gribaldo R, Meneghello A, Mastrogiacomo I (1984) Osteoporosis and decline of gonadal function in the elderly male. Horm Res 19:18–22
Riebel GD, Boden SD, Whitesides TE, Hutton WC (1995) The effect of nicotine on incorporation of cancellous bone graft in an animal model. Spine 20:2198–2202
Broulik PD, Jarab J (1993) The effect of chronic nicotine administration on bone mineral content in mice. Horm Metab Res 25:219–221
Krall EA, Dawson-Hughes B (1991) Smoking and bone loss among postmenopausal women. J Bone Miner Res 6:331–338
Gordon T (1993) Factors associated with serum alkaline phosphatase level. Arch Pathol Lab Med 117:187–190
Landin-Wilhelmsen K, Wilhelmsen L, Lappas G, Rosen T, Lindstedt G, Lundberg PA, Wilske J, Bengtsson BA (1995) Serum intact parathyroid hormone in a random population sample of men and women: relationship to anthropometry, life-style factors, blood pressure, and vitamin D. Calcif Tissue Int 56:104–108
Forrest CR, Pang CY, Lindsay WK (1987) Dose and time effects of nicotine treatment on the capillary blood flow and viability of random pattern skin flaps in the rat. Br J Plast Surg 40:295–299
Matsuo K, Hirohata T, Sugioka Y, Ikeda M, Fukuda A (1988) Influence of alcohol intake, cigarette smoking, and occupational status on idiopathic osteonecrosis of the femoral head. Clin Orthop Relat Res 234:115–123
Hirota Y, Hirohata T, Fukuda K, Mori M, Yanagawa H, Ohno Y, Sugioka Y (1993) Association of alcohol intake, cigarette smoking, and occupational status with the risk of idiopathic osteonecrosis of the femoral head. Am J Epidemiol 137:530–538
NIH Consensus Development Panel on Osteoporosis Prevention D, Therapy (2001) Osteoporosis prevention, diagnosis, and therapy. JAMA 285:785–795
Feskanich D, Korrick SA, Greenspan SL, Rosen HN, Colditz GA (1999) Moderate alcohol consumption and bone density among postmenopausal women. J Women’s Health 8:65–73
Cauley JA, Fullman RL, Stone KL, Zmuda JM, Bauer DC, Barrett-Connor E, Ensrud K, Lau EM, Orwoll ES, Mr OSRG (2005) Factors associated with the lumbar spine and proximal femur bone mineral density in older men. Osteoporos Int 16:1525–1537
May H, Murphy S, Khaw KT (1995) Alcohol consumption and bone mineral density in older men. Gerontology 41:152–158
Felson DT, Zhang Y, Hannan MT, Kannel WB, Kiel DP (1995) Alcohol intake and bone mineral density in elderly men and women. The Framingham study. Am J Epidemiol 142:485–492
Orwoll ES, Bauer DC, Vogt TM, Fox KM (1996) Axial bone mass in older women. Study of Osteoporotic Fractures Research Group. Ann Intern Med 124:187–196
Nguyen TV, Kelly PJ, Sambrook PN, Gilbert C, Pocock NA, Eisman JA (1994) Lifestyle factors and bone density in the elderly: implications for osteoporosis prevention. J Bone Miner Res 9:1339–1346
Williams FM, Cherkas LF, Spector TD, MacGregor AJ (2005) The effect of moderate alcohol consumption on bone mineral density: a study of female twins. Ann Rheum Dis 64:309–310
Hankinson SE, Willett WC, Manson JE, Hunter DJ, Colditz GA, Stampfer MJ, Longcope C, Speizer FE (1995) Alcohol, height, and adiposity in relation to estrogen and prolactin levels in postmenopausal women. J Natl Cancer Inst 87:1297–1302
Purohit V (1998) Moderate alcohol consumption and estrogen levels in postmenopausal women: a review. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 22:994–997
Ginsburg ES, Mello NK, Mendelson JH, Barbieri RL, Teoh SK, Rothman M, Gao X, Sholar JW (1996) Effects of alcohol ingestion on estrogens in postmenopausal women. JAMA 276:1747–1751
Nielsen NR, Schnohr P, Jensen G, Gronbaek M (2004) Is the relationship between type of alcohol and mortality influenced by socio-economic status? J Intern Med 255:280–288
Rimm EB (1996) Alcohol consumption and coronary heart disease: good habits may be more important than just good wine. Am J Epidemiol 143:1094–1098 (discussion 1099)
Burgess S, Davies NM, Thompson SG (2016) Bias due to participant overlap in two-sample Mendelian randomization. Genet Epidemiol 40:597–608
Funding
This study was supported by the General project for scientific research of Liaoning Provincial Education Department (No. L2015572 for Ran Guo). The sponsors are not involved in study design; in the collection, analysis and interpretation of data; in the writing of the report; and in the decision to submit the article for publication.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
RG, LW, and QF designed this study. RG and QF performed the catalog and literature search and data extraction with suggestions and help from LW. RG, LW, and QF performed the statistical analyses. All authors contributed to the data interpretation and manuscript writing. QF is responsible for the overall content as the guarantor of the paper.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Ran Guo, Lang Wu, and Qin Fu declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Human and Animal Rights and Informed Consent
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects performed by any of the authors.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guo, R., Wu, L. & Fu, Q. Is There Causal Relationship of Smoking and Alcohol Consumption with Bone Mineral Density? A Mendelian Randomization Study. Calcif Tissue Int 103, 546–553 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00223-018-0452-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00223-018-0452-y