Abstract
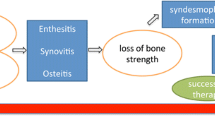
Axial spondyloarthritis is a chronic inflammatory skeletal disorder with an important burden of disease, affecting the spine and sacroiliac joints and typically presenting in young adults. Ankylosing spondylitis, diagnosed by the presence of structural changes to the skeleton, is the prototype of this disease group. Bone disease in axial spondyloarthritis is a complex phenomenon with the coexistence of bone loss and new bone formation, both contributing to the morbidity of the disease, in addition to pain caused by inflammation. The skeletal structural changes respectively lead to increased fracture risk and to permanent disability caused by ankylosis of the sacroiliac joints and the spine. The mechanism of this new bone formation leading to ankylosis is insufficiently known. The process appears to originate from entheses, specialized structures that provide a transition zone in which tendon and ligaments insert into the underlying bone. Growth factor signaling pathways such as bone morphogenetic proteins, Wnts, and Hedgehogs have been identified as molecular drivers of new bone formation, but the relationship between inflammation and activation of these pathways remains debated. Long-standing control of inflammation appears necessary to avoid ankylosis. Recent evidence and concepts suggest an important role for biomechanical factors in both the onset and progression of the disease. With regard to new bone formation, these processes can be understood as ectopic repair responses secondary to inflammation-induced bone loss and instability. In this review, we discuss the clinical implications of the skeletal changes as well as the underlying molecular mechanisms, the relation between inflammation and new bone formation, and the potential role of biomechanical stress.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rudwaleit M, van der Heijde D, Landewe R, Listing J, Akkoc N, Brandt J, Braun J, Chou CT, Collantes-Estevez E, Dougados M, Huang F, Gu J, Khan MA, Kirazli Y, Maksymowych WP, Mielants H, Sorensen IJ, Ozgocmen S, Roussou E, Valle-Onate R, Weber U, Wei J, Sieper J (2009) The development of assessment of spondyloarthritis international society classification criteria for axial spondyloarthritis (part II): validation and final selection. Ann Rheum Dis 68(6):777–783. https://doi.org/10.1136/ard.2009.108233
van der Linden S, Valkenburg HA, Cats A (1984) Evaluation of diagnostic criteria for ankylosing spondylitis. A proposal for modification of the New York criteria. Arthritis Rheum 27(4):361–368
McGonagle D, Lories RJ, Tan AL, Benjamin M (2007) The concept of a “synovio-entheseal complex” and its implications for understanding joint inflammation and damage in psoriatic arthritis and beyond. Arthritis Rheum 56(8):2482–2491. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.22758
McGonagle D, Gibbon W, Emery P (1998) Classification of inflammatory arthritis by enthesitis. Lancet 352(9134):1137–1140. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(97)12004-9
Sieper J, Poddubnyy D (2017) Axial spondyloarthritis. Lancet. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(16)31591-4
Rudwaleit M, van der Heijde D, Landewe R, Akkoc N, Brandt J, Chou CT, Dougados M, Huang F, Gu J, Kirazli Y, Van den Bosch F, Olivieri I, Roussou E, Scarpato S, Sorensen IJ, Valle-Onate R, Weber U, Wei J, Sieper J (2011) The assessment of spondyloarthritis international society classification criteria for peripheral spondyloarthritis and for spondyloarthritis in general. Ann Rheum Dis 70(1):25–31. https://doi.org/10.1136/ard.2010.133645
Carter S, Lories RJ (2011) Osteoporosis: a paradox in ankylosing spondylitis. Curr Osteoporos Rep 9(3):112–115. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11914-011-0058-z
Schett G, Gravallese E (2012) Bone erosion in rheumatoid arthritis: mechanisms, diagnosis and treatment. Nat Rev Rheumatol 8(11):656–664. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrrheum.2012.153
Shaw AT, Gravallese EM (2016) Mediators of inflammation and bone remodeling in rheumatic disease. Semin Cell Dev Biol 49:2–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.semcdb.2015.10.013
Navallas M, Ares J, Beltran B, Lisbona MP, Maymo J, Solano A (2013) Sacroiliitis associated with axial spondyloarthropathy: new concepts and latest trends. Radiographics 33(4):933–956. https://doi.org/10.1148/rg.334125025
Maksymowych WP (2016) Imaging in axial spondyloarthritis: evaluation of inflammatory and structural changes. Rheum Dis Clin North Am 42(4):645–662. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rdc.2016.07.003
Berthelot JM, Le Goff B, Maugars Y (2013) Pathogenesis of hyperostosis: a key role for mesenchymatous cells? Joint Bone Spine 80(6):592–596. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbspin.2013.03.013
Machado PM, Baraliakos X, van der Heijde D, Braun J, Landewe R (2016) MRI vertebral corner inflammation followed by fat deposition is the strongest contributor to the development of new bone at the same vertebral corner: a multilevel longitudinal analysis in patients with ankylosing spondylitis. Ann Rheum Dis 75(8):1486–1493. https://doi.org/10.1136/annrheumdis-2015-208011
Maksymowych WP, Wichuk S, Chiowchanwisawakit P, Lambert RG, Pedersen SJ (2017) Fat metaplasia on MRI of the sacroiliac joints increases the propensity for disease progression in the spine of patients with spondyloarthritis. RMD Open 3(1):e000399. https://doi.org/10.1136/rmdopen-2016-000399
Pray C, Feroz NI, Nigil Haroon N (2017) Bone mineral density and fracture risk in ankylosing spondylitis: a meta-analysis. Calcif Tissue Int. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00223-017-0274-3
Machado P, Landewe R, Braun J, Hermann KG, Baker D, van der Heijde D (2010) Both structural damage and inflammation of the spine contribute to impairment of spinal mobility in patients with ankylosing spondylitis. Ann Rheum Dis 69(8):1465–1470. https://doi.org/10.1136/ard.2009.124206
Landewe R, Dougados M, Mielants H, van der Tempel H, van der Heijde D (2009) Physical function in ankylosing spondylitis is independently determined by both disease activity and radiographic damage of the spine. Ann Rheum Dis 68(6):863–867. https://doi.org/10.1136/ard.2008.091793
Poddubnyy D, Fedorova A, Listing J, Haibel H, Baraliakos X, Braun J, Sieper J (2016) physical function and spinal mobility remain stable despite radiographic spinal progression in patients with ankylosing spondylitis treated with TNF-alpha inhibitors for Up to 10 years. J Rheumatol 43(12):2142–2148. https://doi.org/10.3899/jrheum.160594
Hauser B, Zhao S, Visconti MR, Riches PL, Fraser WD, Piec I, Goodson NJ, Ralston SH (2017) Autoantibodies to osteoprotegerin are associated with low hip bone mineral density and history of fractures in axial spondyloarthritis: a cross-sectional observational study. Calcif Tissue Int. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00223-017-0291-2
Leone A, Marino M, Dell’Atti C, Zecchi V, Magarelli N, Colosimo C (2016) Spinal fractures in patients with ankylosing spondylitis. Rheumatol Int 36(10):1335–1346. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00296-016-3524-1
Mandl P, Navarro-Compan V, Terslev L, Aegerter P, van der Heijde D, D’Agostino MA, Baraliakos X, Pedersen SJ, Jurik AG, Naredo E, Schueller-Weidekamm C, Weber U, Wick MC, Bakker PA, Filippucci E, Conaghan PG, Rudwaleit M, Schett G, Sieper J, Tarp S, Marzo-Ortega H, Ostergaard M, European League Against R (2015) EULAR recommendations for the use of imaging in the diagnosis and management of spondyloarthritis in clinical practice. Ann Rheum Dis 74(7):1327–1339. https://doi.org/10.1136/annrheumdis-2014-206971
Kanis JA, McCloskey E, Johansson H, Oden A, Leslie WD (2012) FRAX((R)) with and without bone mineral density. Calcif Tissue Int 90(1):1–13. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00223-011-9544-7
Lefebvre V, Bhattaram P (2010) Vertebrate skeletogenesis. Curr Top Dev Biol 90:291–317. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0070-2153(10)90008-2
Zhou X, von der Mark K, Henry S, Norton W, Adams H, de Crombrugghe B (2014) Chondrocytes transdifferentiate into osteoblasts in endochondral bone during development, postnatal growth and fracture healing in mice. PLoS Genet 10(12):e1004820. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.1004820
Lories RJ, Schett G (2012) Pathophysiology of new bone formation and ankylosis in spondyloarthritis. Rheum Dis Clin North Am 38(3):555–567. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rdc.2012.08.003
Lories R (2011) The balance of tissue repair and remodeling in chronic arthritis. Nat Rev Rheumatol 7(12):700–707. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrrheum.2011.156
Gonzalez-Chavez SA, Quinonez-Flores CM, Pacheco-Tena C (2016) Molecular mechanisms of bone formation in spondyloarthritis. Joint Bone Spine 83(4):394–400. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbspin.2015.07.008
Lories RJ, Derese I, Luyten FP (2005) Modulation of bone morphogenetic protein signaling inhibits the onset and progression of ankylosing enthesitis. J Clin Invest 115(6):1571–1579. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI23738
Lories RJ, Matthys P, de Vlam K, Derese I, Luyten FP (2004) Ankylosing enthesitis, dactylitis, and onychoperiostitis in male DBA/1 mice: a model of psoriatic arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 63(5):595–598. https://doi.org/10.1136/ard.2003.013599
Braem K, Luyten FP, Lories RJ (2012) Blocking p38 signalling inhibits chondrogenesis in vitro but not ankylosis in a model of ankylosing spondylitis in vivo. Ann Rheum Dis 71(5):722–728. https://doi.org/10.1136/annrheumdis-2011-200377
Joo YB, Bang SY, Kim TH, Shim SC, Lee S, Joo KB, Kim JH, Min HJ, Rahman P, Inman RD (2014) Bone morphogenetic protein 6 polymorphisms are associated with radiographic progression in ankylosing spondylitis. PLoS ONE 9(8):e104966. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0104966
Xie Z, Wang P, Li Y, Deng W, Zhang X, Su H, Li D, Wu Y, Shen H (2016) Imbalance between bone morphogenetic protein 2 and noggin induces abnormal osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells in ankylosing spondylitis. Arthritis Rheumatol 68(2):430–440. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.39433
Tsui FW, Tsui HW, Las Heras F, Pritzker KP, Inman RD (2014) Serum levels of novel noggin and sclerostin-immune complexes are elevated in ankylosing spondylitis. Ann Rheum Dis 73(10):1873–1879. https://doi.org/10.1136/annrheumdis-2013-203630
Nusse R, Clevers H (2017) Wnt/beta-catenin signaling, disease, and emerging therapeutic modalities. Cell 169(6):985–999. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2017.05.016
Diarra D, Stolina M, Polzer K, Zwerina J, Ominsky MS, Dwyer D, Korb A, Smolen J, Hoffmann M, Scheinecker C, van der Heide D, Landewe R, Lacey D, Richards WG, Schett G (2007) Dickkopf-1 is a master regulator of joint remodeling. Nat Med 13(2):156–163. https://doi.org/10.1038/nm1538
Uderhardt S, Diarra D, Katzenbeisser J, David JP, Zwerina J, Richards W, Kronke G, Schett G (2010) Blockade of Dickkopf (DKK)-1 induces fusion of sacroiliac joints. Ann Rheum Dis 69(3):592–597. https://doi.org/10.1136/ard.2008.102046
Heiland GR, Appel H, Poddubnyy D, Zwerina J, Hueber A, Haibel H, Baraliakos X, Listing J, Rudwaleit M, Schett G, Sieper J (2012) High level of functional dickkopf-1 predicts protection from syndesmophyte formation in patients with ankylosing spondylitis. Ann Rheum Dis 71(4):572–574. https://doi.org/10.1136/annrheumdis-2011-200216
Ruiz-Heiland G, Horn A, Zerr P, Hofstetter W, Baum W, Stock M, Distler JH, Nimmerjahn F, Schett G, Zwerina J (2012) Blockade of the hedgehog pathway inhibits osteophyte formation in arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 71(3):400–407. https://doi.org/10.1136/ard.2010.148262
Haroon NN, Sriganthan J, Al Ghanim N, Inman RD, Cheung AM (2014) Effect of TNF-alpha inhibitor treatment on bone mineral density in patients with ankylosing spondylitis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Semin Arthritis Rheum 44(2):155–161. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.semarthrit.2014.05.008
Yago T, Nanke Y, Ichikawa N, Kobashigawa T, Mogi M, Kamatani N, Kotake S (2009) IL-17 induces osteoclastogenesis from human monocytes alone in the absence of osteoblasts, which is potently inhibited by anti-TNF-alpha antibody: a novel mechanism of osteoclastogenesis by IL-17. J Cell Biochem 108(4):947–955. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcb.22326
Osta B, Benedetti G, Miossec P (2014) Classical and paradoxical effects of TNF-alpha on bone homeostasis. Front Immunol 5:48. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2014.00048
Jacques P, Lambrecht S, Verheugen E, Pauwels E, Kollias G, Armaka M, Verhoye M, Van der Linden A, Achten R, Lories RJ, Elewaut D (2014) Proof of concept: enthesitis and new bone formation in spondyloarthritis are driven by mechanical strain and stromal cells. Ann Rheum Dis 73(2):437–445. https://doi.org/10.1136/annrheumdis-2013-203643
Lories RJ, Derese I, de Bari C, Luyten FP (2007) Evidence for uncoupling of inflammation and joint remodeling in a mouse model of spondylarthritis. Arthritis Rheum 56(2):489–497. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.22372
Lories RJ, Luyten FP, de Vlam K (2009) Progress in spondylarthritis. Mechanisms of new bone formation in spondyloarthritis. Arthritis Res Ther 11(2):221. https://doi.org/10.1186/ar2642
Maksymowych WP, Chiowchanwisawakit P, Clare T, Pedersen SJ, Ostergaard M, Lambert RG (2009) Inflammatory lesions of the spine on magnetic resonance imaging predict the development of new syndesmophytes in ankylosing spondylitis: evidence of a relationship between inflammation and new bone formation. Arthritis Rheum 60(1):93–102. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.24132
Baraliakos X, Haibel H, Listing J, Sieper J, Braun J (2014) Continuous long-term anti-TNF therapy does not lead to an increase in the rate of new bone formation over 8 years in patients with ankylosing spondylitis. Ann Rheum Dis 73(4):710–715. https://doi.org/10.1136/annrheumdis-2012-202698
van der Heijde D, Salonen D, Weissman BN, Landewe R, Maksymowych WP, Kupper H, Ballal S, Gibson E, Wong R, Canadian study g, group As (2009) Assessment of radiographic progression in the spines of patients with ankylosing spondylitis treated with adalimumab for up to 2 years. Arthritis Res Ther 11(4):R127. https://doi.org/10.1186/ar2794
van der Heijde D, Landewe R, Baraliakos X, Houben H, van Tubergen A, Williamson P, Xu W, Baker D, Goldstein N, Braun J, Ankylosing Spondylitis Study for the Evaluation of Recombinant Infliximab Therapy Study G (2008) Radiographic findings following two years of infliximab therapy in patients with ankylosing spondylitis. Arthritis Rheum 58(10):3063–3070. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.23901
van der Heijde D, Landewe R, Einstein S, Ory P, Vosse D, Ni L, Lin SL, Tsuji W, Davis JC Jr (2008) Radiographic progression of ankylosing spondylitis after up to two years of treatment with etanercept. Arthritis Rheum 58(5):1324–1331. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.23471
Haroon N, Inman RD, Learch TJ, Weisman MH, Lee M, Rahbar MH, Ward MM, Reveille JD, Gensler LS (2013) The impact of tumor necrosis factor alpha inhibitors on radiographic progression in ankylosing spondylitis. Arthritis Rheum 65(10):2645–2654. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.38070
Maas F, Arends S, Brouwer E, Essers I, van der Veer E, Efde M, van Ooijen PM, Wolf R, Veeger NJ, Bootsma H, Wink FR, Spoorenberg A (2016) Reduction in spinal radiographic progression in ankylosing spondylitis patients receiving prolonged treatment with TNF-alpha inhibitors. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). https://doi.org/10.1002/acr.23097
Guillot X, Prati C, Sondag M, Wendling D (2017) Etanercept for treating axial spondyloarthritis. Expert Opin Biol Ther 17(9):1173–1181. https://doi.org/10.1080/14712598.2017.1347156
Van Mechelen M, Lories RJ (2016) Microtrauma: no longer to be ignored in spondyloarthritis? Curr Opin Rheumatol 28(2):176–180. https://doi.org/10.1097/BOR.0000000000000254
Cheung PP (2017) Anti-IL17A in axial spondyloarthritis-where are we at? Front Med (Lausanne) 4:1. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmed.2017.00001
Baeten D, Sieper J, Braun J, Baraliakos X, Dougados M, Emery P, Deodhar A, Porter B, Martin R, Andersson M, Mpofu S, Richards HB, Group MS, Group MS (2015) Secukinumab, an Interleukin-17A Inhibitor, in Ankylosing Spondylitis. N Engl J Med 373(26):2534–2548. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1505066
Croes M, Oner FC, van Neerven D, Sabir E, Kruyt MC, Blokhuis TJ, Dhert WJ, Alblas J (2016) Proinflammatory T cells and IL-17 stimulate osteoblast differentiation. Bone 84:262–270. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bone.2016.01.010
Uluckan O, Jimenez M, Karbach S, Jeschke A, Grana O, Keller J, Busse B, Croxford AL, Finzel S, Koenders M, van den Berg W, Schinke T, Amling M, Waisman A, Schett G, Wagner EF (2016) Chronic skin inflammation leads to bone loss by IL-17-mediated inhibition of Wnt signaling in osteoblasts. Sci Transl Med 8(330):330ra337. https://doi.org/10.1126/scitranslmed.aad8996
Uluckan O, Wagner EF (2016) Role of IL-17A signalling in psoriasis and associated bone loss. Clin Exp Rheumatol 34(4 Suppl 98):17–20
Miossec P (2017) Update on interleukin-17: a role in the pathogenesis of inflammatory arthritis and implication for clinical practice. RMD Open 3(1):e000284. https://doi.org/10.1136/rmdopen-2016-000284
Osta B, Lavocat F, Eljaafari A, Miossec P (2014) Effects of interleukin-17A on osteogenic differentiation of isolated human mesenchymal stem cells. Front Immunol 5:425. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2014.00425
Lavocat F, Osta B, Miossec P (2016) Increased sensitivity of rheumatoid synoviocytes to Schnurri-3 expression in TNF-alpha and IL-17A induced osteoblastic differentiation. Bone 87:89–96. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bone.2016.04.008
Wein MN, Jones DC, Shim JH, Aliprantis AO, Sulyanto R, Lazarevic V, Poliachik SL, Gross TS, Glimcher LH (2012) Control of bone resorption in mice by Schnurri-3. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 109(21):8173–8178. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1205848109
Braun J, Baraliakos X, Deodhar A, Baeten D, Sieper J, Emery P, Readie A, Martin R, Mpofu S, Richards HB, group Ms (2016) Effect of secukinumab on clinical and radiographic outcomes in ankylosing spondylitis: 2-year results from the randomised phase III MEASURE 1 study. Ann Rheum Dis. https://doi.org/10.1136/annrheumdis-2016-209730
Ebihara S, Date F, Dong Y, Ono M (2015) Interleukin-17 is a critical target for the treatment of ankylosing enthesitis and psoriasis-like dermatitis in mice. Autoimmunity 48(4):259–266. https://doi.org/10.3109/08916934.2014.976630
Ono T, Okamoto K, Nakashima T, Nitta T, Hori S, Iwakura Y, Takayanagi H (2016) IL-17-producing gammadelta T cells enhance bone regeneration. Nat Commun 7:10928. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms10928
Sieper J, Listing J, Poddubnyy D, Song IH, Hermann KG, Callhoff J, Syrbe U, Braun J, Rudwaleit M (2016) Effect of continuous versus on-demand treatment of ankylosing spondylitis with diclofenac over 2 years on radiographic progression of the spine: results from a randomised multicentre trial (ENRADAS). Ann Rheum Dis 75(8):1438–1443. https://doi.org/10.1136/annrheumdis-2015-207897
Boersma JW (1976) Retardation of ossification of the lumbar vertebral column in ankylosing spondylitis by means of phenylbutazone. Scand J Rheumatol 5(1):60–64
Proft F, Muche B, Listing J, Rios-Rodriguez V, Sieper J, Poddubnyy D (2017) Study protocol: COmparison of the effect of treatment with Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs added to anti-tumour necrosis factor a therapy versus anti-tumour necrosis factor a therapy alone on progression of StrUctural damage in the spine over two years in patients with ankyLosing spondylitis (CONSUL) - an open-label randomized controlled multicenter trial. BMJ Open 7(6):e014591. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjopen-2016-014591
Sherlock JP, Joyce-Shaikh B, Turner SP, Chao CC, Sathe M, Grein J, Gorman DM, Bowman EP, McClanahan TK, Yearley JH, Eberl G, Buckley CD, Kastelein RA, Pierce RH, Laface DM, Cua DJ (2012) IL-23 induces spondyloarthropathy by acting on ROR-gammat + CD3 + CD4-CD8- entheseal resident T cells. Nat Med 18(7):1069–1076. https://doi.org/10.1038/nm.2817
Cuthbert RJ, Fragkakis EM, Dunsmuir R, Li Z, Coles M, Marzo-Ortega H, Giannoudis P, Jones E, El-Sherbiny YM, McGonagle D (2017) Human enthesis group 3 innate lymphoid cells. Arthritis Rheumatol. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.40150
Neerinckx B, Lories R (2017) Mechanisms, impact and prevention of pathological bone regeneration in spondyloarthritis. Curr Opin Rheumatol. https://doi.org/10.1097/BOR.0000000000000404
Acknowledgements
MVM is the recipient of an Aspirant fellowship and GRG is the recipient of a post-doctoral fellowship from the Flanders Research Foundation (FWO-Vlaanderen). Research on the topic of the review is supported by FWO Grants G094614 and G095916 N.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Leuven Research and Development, the technology transfer office of KU Leuven, has received speaker’s and consultancy fees on behalf of R.L. from Abbvie, Boehringer-Ingelheim, Celgene, Janssen, Novartis, Merck, Pfizer, and UCB, and research grants from Boehringer-Ingelheim, Celgene, and Pfizer. KDV reports speaker’s and consultancy fees from Abbvie, Celgene, Johnson & Johnson, Merck, Novartis, Pfizer, and UCB.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Van Mechelen, M., Gulino, G.R., de Vlam, K. et al. Bone Disease in Axial Spondyloarthritis. Calcif Tissue Int 102, 547–558 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00223-017-0356-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00223-017-0356-2