Abstract
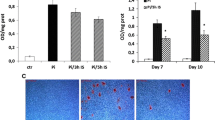
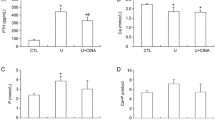
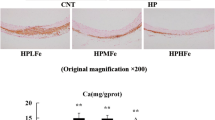
Clinical and experimental studies have reported that phosphate overload plays a central role in the pathogenesis of vascular calcification in chronic kidney disease. However, it remains undetermined whether phosphate induces cellular senescence during vascular calcification. We established a modified uremic rat model induced by a diet containing 0.3 % adenine that showed more slowly progressive kidney failure, more robust vascular calcification, and longer survival than the conventional model (0.75 % adenine). To determine the effect of phosphate on senescence of vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMCs) and the protective effect of phosphate binders, rats were divided into four groups: (1) normal control rats; (2) rats fed with the modified adenine-based diet (CKD); (3) CKD rats treated with 6 % lanthanum carbonate (CKD-LaC); and (4) CKD rats treated with 6 % calcium carbonate (CKD-CaC). After 8 weeks, CKD rats showed circumferential arterial medial calcification, which was inhibited in CKD-LaC and CKD-CaC rats. CKD rats showed increased protein expression of senescence-associated β-galactosidase, bone-related proteins, p16 and p21, and increased oxidative stress levels in the calcified area, which were inhibited by both phosphate binders. However, serum levels of oxidative stress and inflammatory markers, serum fibroblast growth factor 23, and aortic calcium content in CKD-CaC rats were higher than those in CKD-LaC rats. In conclusion, phosphate induces cellular senescence of VSMCs in the modified uremic rat model, and phosphate binders can prevent both cellular senescence and calcification of VSMCs via phosphate unloading. Our modified adenine-based uremic rat model is useful for evaluating uremia-related complications, including vascular calcification.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Campisi J, d’Adda di Fagagna F (2007) Cellular senescence: when bad things happen to good cells. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 8:729–740
Ben-Porath I, Weinberg RA (2005) The signals and pathways activating cellular senescence. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 37:961–976
Yang H, Fogo AB (2010) Cell senescence in the aging kidney. J Am Soc Nephrol 21:1436–1439
Kooman JP, Broers NJ, Usvyat L, Thijssen S, van der Sande FM, Cornelis T, Levin NW, Leunissen KM, Kotanko P (2013) Out of control: accelerated aging in uremia. Nephrol Dial Transplant 28:48–54
Nakano-Kurimoto R, Ikeda K, Uraoka M, Nakagawa Y, Yutaka K, Koide M, Takahashi T, Matoba S, Yamada H, Okigaki M, Matsubara H (2009) Replicative senescence of vascular smooth muscle cells enhances the calcification through initiating the osteoblastic transition. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 297:H1673–H1684
Shanahan CM, Crouthamel MH, Kapustin A, Giachelli CM (2011) Arterial calcification in chronic kidney disease: key roles for calcium and phosphate. Circ Res 109:697–711
Qunibi W, Moustafa M, Muenz LR, He DY, Kessler PD, Diaz-Buxo JA, Budoff M, CARE-2 Investigators (2008) A 1-year randomized trial of calcium acetate versus sevelamer on progression of coronary artery calcification in hemodialysis patients with comparable lipid control: the Calcium Acetate Renagel Evaluation-2 (CARE-2) study. Am J Kidney Dis 51:952–965
Di Iorio B, Bellasi A, Russo D, INDEPENDENT Study Investigators (2012) Mortality in kidney disease patients treated with phosphate binders: a randomized study. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 7:487–493
Shobeiri N, Adams MA, Holden RM (2010) Vascular calcification in animal models of CKD: a review. Am J Nephrol 31:471–481
Atkinson J (2008) Age-related medial elastocalcinosis in arteries: mechanisms, animal models, and physiological consequences. J Appl Physiol 105:1643–1651
Yokozawa T, Zheng PD, Oura H, Koizumi F (1986) Animal model of adenine-induced chronic renal failure in rats. Nephron 44:230–234
Katsumata K, Kusano K, Hirata M, Tsunemi K, Nagano N, Burke SK, Fukushima N (2003) Sevelamer hydrochloride prevents ectopic calcification and renal osteodystrophy in chronic renal failure rats. Kidney Int 64:441–450
Tamagaki K, Yuan Q, Ohkawa H, Imazeki I, Moriguchi Y, Imai N, Sasaki S, Takeda K, Fukagawa M (2006) Severe hyperparathyroidism with bone abnormalities and metastatic calcification in rats with adenine-induced uraemia. Nephrol Dial Transplant 21:651–659
Price PA, Roublick AM, Williamson MK (2006) Artery calcification in uremic rats is increased by a low protein diet and prevented by treatment with ibandronate. Kidney Int 70:1577–1583
Aoshima Y, Mizobuchi M, Ogata H, Kumata C, Nakazawa A, Kondo F, Ono N, Koiwa F, Kinugasa E, Akizawa T (2012) Vitamin D receptor activators inhibit vascular smooth muscle cell mineralization induced by phosphate and TNF-α. Nephrol Dial Transplant 27:1800–1806
Zhao G, Xu MJ, Zhao MM, Dai XY, Kong W, Wilson GM, Guan Y, Wang CY, Wang X (2012) Activation of nuclear factor-kappa B accelerates vascular calcification by inhibiting ankylosis protein homolog expression. Kidney Int 82:34–44
Yu C, Chen B, Zhao T, Wang R, Akhtar J, Wang H, Zhang H (2013) High phosphate feeding induced arterial medial calcification in uremic rats: roles of Lanthanum carbonate on protecting vasculature. Life Sci 93:646–653
Yamada S, Taniguchi M, Tokumoto M, Toyonaga J, Fujisaki K, Suehiro T, Noguchi H, Iida M, Tsuruya K, Kitazono T (2012) The antioxidant tempol ameliorates arterial medial calcification in uremic rats: important role of oxidative stress in the pathogenesis of vascular calcification in chronic kidney disease. J Bone Miner Res 27:474–485
Gruber HE, Ingram JA, Norton HJ, Hanley EN Jr (2007) Senescence in cells of the aging and degenerating intervertebral disc: immunolocalization of senescence-associated beta-galactosidase in human and sand rat discs. Spine 32:321–327
Moe SM, Chen NX, Seifert MF, Sinders RM, Duan D, Chen X, Liang Y, Radcliff JS, White KE, Gattone VH 2nd (2009) A rat model of chronic kidney disease-mineral bone disorder. Kidney Int 75:176–184
Kawata T, Nagano N, Obi M, Miyata S, Koyama C, Kobayashi N, Wakita S, Wada M (2008) Cinacalcet suppresses calcification of the aorta and heart in uremic rats. Kidney Int 74:1270–1277
Burton DG, Matsubara H, Ikeda K (2010) Pathophysiology of vascular calcification: pivotal role of cellular senescence in vascular smooth muscle cells. Exp Gerontol 45:819–824
Burton DG, Giles PJ, Sheerin AN, Smith SK, Lawton JJ, Ostler EL, Rhys-Williams W, Kipling D, Faragher RG (2009) Microarray analysis of senescent vascular smooth muscle cells: a link to atherosclerosis and vascular calcification. Exp Gerontol 44:659–665
Adijiang A, Higuchi Y, Nishijima F, Shimizu H, Niwa T (2010) Indoxyl sulfate, a uremic toxin, promotes cell senescence in aorta of hypertensive rats. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 399:637–641
Takemura A, Iijima K, Ota H, Son BK, Ito Y, Ogawa S, Eto M, Akishita M, Ouchi Y (2011) Sirtuin A retards hyperphosphatemia-induced calcification of vascular smooth muscle cells. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 31:2054–2062
Zhao MM, Xu MJ, Cai Y, Zhao G, Guan Y, Kong W, Tang C, Wang W (2011) Mitochondrial reactive oxygen species promote p65 nuclear translocation mediating high-phosphate-induced vascular calcification in vitro and in vivo. Kidney Int 79:1071–1079
Zhou RH, Vendrov AE, Tchivilev I, Niu XL, Molnar KC, Rojas M, Carter JD, Tong H, Stouffer GA, Madamanchi NR, Runge MS (2012) Mitochondrial oxidative stress in aortic stiffening with age: the role of smooth muscle cell function. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 32:745–755
Neven E, Dams G, Postnov A, Chen B, De Clerck N, De Broe ME, D’Haese PC, Persy V (2009) Adequate phosphate binding with lanthanum carbonate attenuates arterial calcification in chronic kidney disease. Nephrol Dial Transplant 24:1790–1799
De Schutter TM, Behets GJ, Geryl H, Peter ME, Steppan S, Gundlach K, Passlick-Deetjen J, D’Haese PC, Neven E (2013) Effect of a magnesium-based phosphate binder on medial calcification in a rat model of uremia. Kidney Int 83:1109–1117
Jahnen-Dechent W, Heiss A, Schäfer C, Ketteler M (2011) Fetuin-A regulation of calcified matrix metabolism. Circ Res 108:1494–1509
Pazár B, Ea HK, Narayan S, Kolly L, Bagnoud N, Chobaz V, Roger T, Lioté F, So A, Busso N (2011) Basic calcium phosphate crystals induce monocyte/macrophage IL-1β secretion through the NLRP3 inflammasome in vitro. J Immunol 186:2495–2502
New SE, Goettsch C, Aikawa M, Marchini JF, Shibasaki M, Yabusaki K, Libby P, Shanahan CM, Croce K, Aikawa E (2013) Macrophage-derived matrix vesicles: an alternative novel mechanism for microcalcification in atherosclerotic plaques. Circ Res 113:72–77
Shroff RC, McNair R, Skepper JN, Figg N, Schurgers LJ, Deanfield J, Rees L, Shanahan CM (2010) Chronic mineral dysregulation promotes vascular smooth muscle cell adaptation and extracellular matrix calcification. J Am Soc Nephrol 21:103–112
Cozzolino M, Staniforth ME, Liapis H, Finch J, Burke SK, Dusso AS, Slatopolsky E (2003) Sevelamer hydrochloride attenuates kidney and cardiovascular calcifications in long-term experimental uremia. Kidney Int 64:1653–1661
Moe SM, Chen NX, Newman CL, Gattone VH 2nd, Organ JM, Chen X, Allen MR (2014) A Comparison of calcium to zoledronic acid for improvement of cortical bone in an animal model of CKD. J Bone Miner Res 29:902–910
Jimbo R, Kawakami-Mori F, Mu S, Hirohama D, Majtan B, Shimizu Y, Yatomi Y, Fukumoto S, Fujita T, Shimosawa T (2014) Fibroblast growth factor 23 accelerates phosphate-induced vascular calcification in the absence of Klotho deficiency. Kidney Int 85:1103–1111
Six I, Okazaki H, Gross P, Cagnard J, Boudot C, Maizel J, Drueke TB, Massy ZA (2014) Direct, acute effects of Klotho and FGF23 on vascular smooth muscle and endothelium. PLoS One 9:e93423
Rodriguez-Ortiz ME, Lopez I, Muñoz-Castañeda JR, Martinez-Moreno JM, Ramírez AP, Pineda C, Canalejo A, Jaeger P, Aguilera-Tejero E, Rodriguez M, Felsenfeld A, Almaden Y (2012) Calcium deficiency reduces circulating levels of FGF23. J Am Soc Nephrol 23:1190–1197
Vlassara H, Uribarri J, Cai W, Goodman S, Pyzik R, Post J, Grosjean F, Woodward M, Striker GE (2012) Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 7:934–942
Sun PP, Perianayagam MC, Jaber BL (2009) Endotoxin-binding affinity of sevelamer: a potential novel anti-inflammatory mechanism. Kidney Int Suppl 114:S20–S25
Hauser AB, Azevedo IR, Gonçalves S, Stinghen A, Aita C, Pecoits-Filho R (2010) Sevelamer carbonate reduces inflammation and endotoxemia in an animal model of uremia. Blood Purif 30:153–158
Hutchison AJ, Maes B, Vanwalleghem J, Asmus G, Mohamed E, Schmieder R, Backs W, Jamar R, Vosskuhler A (2005) Efficacy, tolerability, and safety of lanthanum carbonate in hyperphosphatemia: a 6-month, randomized, comparative trial versus calcium carbonate. Nephron Clin Pract 100:c8–c19
Shigematsu T, Lanthanum Carbonate Group (2008) Multicenter prospective randomized, double-blind comparative study between lanthanum carbonate and calcium carbonate as phosphate binders in Japanese hemodialysis patients with hyperphosphatemia. Clin Nephrol 70:404–410
Daugirdas JT, Finn WF, Emmett M, Chertow GM (2011) The phosphate binder equivalent dose. Semin Dial 24:41–49
Takashima T, Sanai T, Miyazono M, Fukuda M, Kishi T, Nonaka Y, Yoshizaki M, Sato S, Ikeda Y (2014) A comparison of the long-term effects of lanthanum carbonate and calcium carbonate on the course of chronic renal failure in rats with adriamycin-induced nephropathy. PLoS One 9:e97859
Conflict of interest
Shunsuke Yamada, Narihito Tatsumoto, Masanori Tokumoto, Hideko Noguchi, Hiroaki Ooboshi, Takanari Kitazono, and Kazuhiko Tsuruya have nothing to disclose.
Human and Animal Rights and Informed Consent
All experimental protocols were reviewed and approved by the Committee on Ethics of Animal Experimentation at Kyushu University Faculty of Medicine (A25-073-1).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yamada, S., Tatsumoto, N., Tokumoto, M. et al. Phosphate Binders Prevent Phosphate-Induced Cellular Senescence of Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells and Vascular Calcification in a Modified, Adenine-Based Uremic Rat Model. Calcif Tissue Int 96, 347–358 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00223-014-9929-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00223-014-9929-5