Abstract
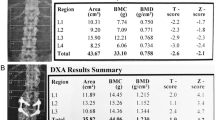
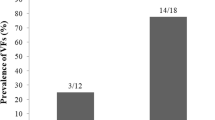
Due to the increasing survival of thalassemic patients, osteopathy is a mounting clinical problem. Low bone mass alone cannot account for the high fracture risk described; impaired bone quality has been speculated but so far it cannot be demonstrated noninvasively. We studied bone quality in thalassemia major using trabecular bone score (TBS), a novel texture measurement extracted from spine dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA), proposed in postmenopausal and secondary osteoporosis as an indirect index of microarchitecture. TBS was evaluated in 124 adult thalassemics (age range 19–56 years), followed-up with optimal transfusional and therapeutical regimens, and in 65 non-thalassemic patients (22–52 years) undergoing DXA for different bone diseases. TBS was lower in thalassemic patients (1.04 ± 0.12 [range 0.80–1.30]) versus controls (1.34 ± 0.11 [1.06–1.52]) (p < 0.001), and correlated with BMD. TBS and BMD values correlated with age, indicating that thalassemia negatively affects both bone quality and quantity, especially as the patient gets older. TBS was 1.02 ± 0.11 [0.80–1.28] in the osteoporotic thalassemic patients, 1.08 ± 0.12 [0.82–1.30] in the osteopenic ones and 1.15 ± 0.10 [0.96–1.26] in those with normal BMD. No gender differences were found (males: 1.02 ± 0.13 [0.80–1.30], females 1.05 ± 0.11 [0.80–1.30]), nor between patients with and without endocrine–metabolic disorders affecting bone metabolism. Our findings from a large population with thalassemia major show that TBS is a valuable tool to assess noninvasively bone quality, and it may be related to fragility fracture risk in thalassemic osteopathy.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chatterjee R, Shah FT, Davis BA, Byers M, Sooranna D, Bajoria R, Pringle J, Porter JB (2012) Prospective study of histomorphometry, biochemical bone markers and bone densitometric response to pamidronate in beta-thalassaemia presenting with osteopenia–osteoporosis syndrome. Br J Haematol 159:462–471
Haidar R, Musallam KM, Taher AT (2011) Bone disease and skeletal complications in patients with beta thalassemia major. Bone 48:425–432
Mylona M, Leotsinides M, Alexandrides T, Zoumbos N, Dimopoulos PA (2005) Comparison of DXA, QCT and trabecular structure in beta-thalassaemia. Eur J Haematol 74:430–437
Ulivieri FM, Silva BC, Sardanelli F, Hans D, Bilezikian JP, Caudarella R (2014) Utility of the trabecular bone score (TBS) in secondary osteoporosis. Endocrine (in press)
Hans D, Barthe N, Boutroy S, Pothuaud L, Winzenrieth R, Krieg MA (2011) Correlations between trabecular bone score, measured using anteroposterior dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry acquisition, and 3-dimensional parameters of bone microarchitecture: an experimental study on human cadaver vertebrae. J Clin Densitom 14:302–312
Rabier B, Heraud A, Grand-Lenoir C, Winzenrieth R, Hans D (2010) A multicentre, retrospective case–control study assessing the role of trabecular bone score (TBS) in menopausal Caucasian women with low areal bone mineral density (BMDa): analysing the odds of vertebral fracture. Bone 46:176–181
Pothuaud L, Barthe N, Krieg MA, Mehsen N, Carceller P, Hans D (2009) Evaluation of the potential use of trabecular bone score to complement bone mineral density in the diagnosis of osteoporosis: a preliminary spine BMD-matched, case–control study. J Clin Densitom 12:170–176
Pothuaud L, Carceller P, Hans D (2008) Correlations between grey-level variations in 2D projection images (TBS) and 3D microarchitecture: applications in the study of human trabecular bone microarchitecture. Bone 42:775–787
Silva BC, Leslie WD, Resch H, Lamy O, Lesnyak O, Binkley N, McCloskey EV, Kanis JA, Bilezikian JP (2014) Trabecular bone score: a non-invasive analytical method based upon the DXA image. J Bone Miner Res 29:518–530
Wood JC, Enriquez C, Ghugre N, Tyzka JM et al (2005) MRI R2 and R2* mapping accurately estimates hepatic iron concentration in transfusion-dependent thalassemia and sickle-cells disease patients. Blood 106:1460–1465
Angastiniotis M, Eleftheriou A (2008) Thalassaemic bone disease. An overview. Pediatr Endocrinol Rev 6(Suppl 1):73–80
Toumba M, Skordis N (2010) Osteoporosis syndrome in thalassaemia major: an overview. J Osteoporos 2010:537673
Baldini M, Forti S, Orsatti A, Ulivieri FM, Airaghi L, Zanaboni L, Cappellini MD (2011) Bone disease in adult patients with beta-thalassaemia major: a case–control study. Intern Emerg Med 9:59–63
Baldini M, Forti S, Marcon A, Ulivieri FM, Orsatti A, Tampieri B, Airaghi L, Zanaboni L, Cappellini MD (2010) Endocrine and bone disease in appropriately treated adult patients with beta-thalassemia major. Ann Hematol 89:1207–1213
Chatterjee R, Katz M, Bajoria R (2011) Use of hormone replacement therapy for correction of high turnover bone disease in hypogonadal beta-thalassemia major patients presenting with osteoporosis: comparison with idiopathic premature ovarian failure. Hemoglobin 35:653–658
Hans D, Goertzen AL, Krieg MA, Leslie WD (2011) Bone microarchitecture assessed by TBS predicts osteoporotic fractures independent of bone density: the Manitoba study. J Bone Miner Res 26:2762–2769
Origa R, Fiumana E, Gamberini MR, Armari S, Mottes M, Sangalli A, Paglietti E, Galanello R, Borgna-Pignatti C (2005) Osteoporosis in beta-thalassemia: clinical and genetic aspects. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1054:451–456
Gaudio A, Morabito N, Xourafa A, Macri I, Meo A, Morgante S, Trifiletti A, Lasco A, Frisina N (2008) Bisphosphonates in the treatment of thalassemia-associated osteoporosis. J Endocrinol Invest 31:181–184
Skordis N, Toumba M (2011) Bone disease in thalassaemia major: recent advances in pathogenesis and clinical aspects. Pediatr Endocrinol Rev 8(Suppl 2):300–306
Leslie WD, Krieg MA, Hans D, Manitoba Bone Density Program (2013) Clinical factors associated with trabecular bone score. J Clin Densitom 16:374–379
Boutroy S, Hans D, Sornay-Rendu E, Vilayphiou N, Winzenrieth R, Chapurlat R (2013) Trabecular bone score improves fracture risk prediction in non-osteoporotic women: the OFELY study. Osteoporos Int 24:77–85
Breban S, Briot K, Kolta S, Paternotte S, Ghazi M, Fechtenbaum J, Roux C (2012) Identification of rheumatoid arthritis patients with vertebral fractures using bone mineral density and trabecular bone score. J Clin Densitom 15:260–266
Conflict of Interest
Didier Hans is co-owner of the TBS patent and has corresponding ownership shares in Medimaps group. Marina Baldini, Fabio Massimo Ulivieri, Stella Forti, Serena Serafino, Sonia Seghezzi, Alessia Marcon, Federico Giarda, Carmelo Messina, Elena Cassinerio, Bérengère Aubry-Rozier, and Maria Domenica Cappellini declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Human and Animal Rights and Informed Consent
All procedures performed were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. For this type of study (retrospective) formal consent is not required.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Baldini, M., Ulivieri, F.M., Forti, S. et al. Spine Bone Texture Assessed by Trabecular Bone Score (TBS) to Evaluate Bone Health in Thalassemia Major. Calcif Tissue Int 95, 540–546 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00223-014-9919-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00223-014-9919-7