Abstract
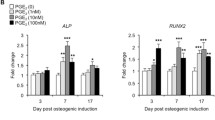
Reports that estrogen treatment modulates arachidonic acid metabolism by bone and bone cells are found in the literature. However, conflicting indications of the relationship that exists between estrogen and arachidonic acid metabolism emerge from the analysis of those reports. The present studies were undertaken to determine if estrogen effected the production of prostaglandins (PG) in human osteoblast-like (hOB) cell cultures derived from adults, under basal or cytokine-stimulated conditions. A 48-hour estrogen pretreatment did not modify hOB cell PG biosynthesis on a qualitative basis, and PGE2 formation predominated under all tested conditions. Estrogen pretreatment did lead to increased PGE2 production in specimens stimulated conjointly with transforming growth factor-β1 and tumor necrosis factor-α (p < 0.001). No changes in PGE2 production were observed in estrogen pretreated specimens stimulated singly with either tested cytokine, nor in samples in which either TGFβ or TNF was replaced by interleukin-1β. Anti-estrogen (ICI 164,384) inclusion prevented the estrogen-dependent increase in PGE2 production in the TGFβ plus TNF-stimulated samples. These results suggest that an estrogen effect on bone cell prostaglandin biosynthesis may be most evident and significant under conditions in which the cells are exposed to multiple osteotropic cytokines, a condition that applies during the bone remodeling process.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Riggs BL (2000) “The mechanism of estrogen regulation of bone resorption.” J Clin Invest 106:1203–1204
Manolagas SC, Kousteni S, Jilka RL (2002) “Sex steroids and bone.” Recent Prog Horm Res 57:385–409
Spelsberg TC, Subramaniam M, Riggs BL, Khosla S (1999) “The actions and interactions of sex steroids and growth factors/cytokines on the skeleton.” Molec Endocrinol 13:819–828
Manolagos SC (2000) “Birth and death of bone cells: basic regulatory mechanisms and implications for the pathogenesis and treatment of osteoporosis.” Endocr Rev 21:115–137
Hughes DE, Dai A, Tiffee JC, Li HH, Mundy GR, Boyce BF (1996) “Estrogen promotes apoptosis of murine osteoclasts mediated by TGF-β.” Nat Med 2:1132–1136
Gohel A, McCarthy M-B, Gronowicz G (1999) “Estrogen prevents glucocorticoid-induced apoptosis in osteoblasts in vivo and in vitro.” Endocrinology 140:5339–5347
Pivirotto LA, Cissel DS, Keeting PE (1995) “Sex hormones mediate interleukin-1β production by human osteoblastic HOBIT cells.” Mol Cell Endocrinol 111:67–74
Jilka RL, Hangoc G, Girasole G, Passeri G, Williams DC, Abrams JS, Boyce B, Broxmeyer H, Manolagos SC (1992) “Increased osteoclast development after estrogen loss: mediation by interleukin-6.” Science 257:88–91
Hofbauer LC, Khosla S, Dunstan CR, Lacey DL, Spelsberg TC, Riggs BL (1999) “Estrogen stimulates gene expression and protein production of osteoprotegerin in human osteoblastic cells.” Endocrinology 140:4367–4370
Oursler MJ, Cortese C, Keeting PE, Anderson M, Bonde S, Riggs BL, Spelsberg TC (1991) “Modulation of transforming growth factor beta production in normal human osteoblast-like cells by 17[β]-estradiol and parathyroid hormone.” Endocrinology 129:3313–3320
Oursler MJ (1998) “Estrogen regulation of gene expression in osteoblasts and osteoclasts.” Clin Rev Eukaryot Gene Expr 8:125–140
Xu JQ, Cissel DS, Varghese S, Whipkey DL, Blaha JD, Graeber GM, Keeting PE (1997) “Cytokine regulation of adult human osteoblast-like cell prostaglandin biosynthesis.” J Cell Biochem 64:618–631
Robey PG, Young MF, Flanders KC, Roche NS, Kondaiah P, Reddi AH, Termine JD, Sporn MB, Roberts AB (1987) “Osteoblasts synthesize and respond to TGFβ in vitro. J Cell Biol 105:457–463
Gowen M, Chapman K, Littlewood A, Hughes D, Evans D, Russell RGG (1990) “Production of tumor necrosis factor by human osteoblasts is modulated by other cytokines, but not by osteotropic hormones.” Endocrinology 126:1250–1255
Keeting PE, Rifas L, Harris SA, Colvard DS, Spelsberg TC, Peck WA, Riggs BL (1991) “Evidence for interleukin-1β production by cultured normal human osteoblast-like cells.” J Bone Miner Res 6:827–833
Dodds RA, Merry K, Littlewood A, Gowen M (1994) “Expression of mRNA for IL1 beta, IL6 and TGFbeta 1 in developing human bone and cartilage.” Histochem Cytochem 42:733–744
Kawaguchi H, Pilbeam CC, Harrison JR, Raisz LG (1995) “The role of prostaglandins in the regulation of bone metabolism.” Clin Orthop Rel Res 313:36–46
Robey PG, Termine JD (1985) “Human bone cells in vitro.” Calcif Tissue Int 37:453–460
Cissel DS, Murty M, Whipkey DL, Blaha JD, Graeber GM, Keeting PE (1996) “Estrogen pretreatment increases arachidonic acid release by bradykinin-stimulated normal human osteoblast-like cells.” J Cell Biochem 60:260–270
Borke JL, Eriksen EF, Minami J, Keeting P, Mann KG, Penniston JT, Riggs BL, Kumar R (1988) “Epitopes of the human erythrocyte Ca2+-Mg2+ ATPase pump in human osteoblast-like cell plasma membranes.” J Clin Endocrinol Metab 67:1299–1304
Marie PJ (1994) “Human osteoblast-like cells: a potential tool to assess the etiology of pathologic bone formation.” J Bone Miner Res 9:1847–1850
Klinge CM (2001) “Estrogen receptor interaction with estrogen response elements.” Nucl Acids Res 29:2905–2919
Cissel DS, Birkle DL, Whipkey DL, Blaha JD, Graeber GM, Keeting PE (1995) “1,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D3 or dexamethasone modulate arachidonic acid uptake and distribution into glycerophospholipids by normal adult human osteoblast-like cells.” J Cell Biochem 57:599–609
Clark JD, Lin L, Kriz RW, Ramesha CS, Sultzman LA, Lin AY, Milona N, Knopf JL (1991) “A novel arachidonic acid-selective cytosolic phospholipase A2 contains a Ca2+ -dependent translocation domain with homology to PKC and GAP.” Cell 65:1043–1051
Keeting PE, Li CH, Murty M, Xu J, Cissel DS, Whipkey DL, Graeber GM, Blaha JD (1998) “Arachidonic acid metabolism by adult human osteoblast-like cells exhibits sexually dimorphic characteristics.” J Cell Biochem 71:74–81
Feyen JHM, Raisz LG (1987) “Prostaglandin production from sham-operated and ovariectomized rats: effects of 17β-estradiol in vivo.” Endocrinology 121:819–821
Pilbeam CC, Klein-Nulend J, Raisz LG (1989) “Inhibition by 17β-estradiol of PTH-stimulated resorption and prostaglandin production in cultured neonatal mouse calvariae.” Biochem Biophys Res Commun 163:1319–1324
Lane N, Coble T, Kimmel DB (1990) “Effects of naproxen on cancellous bone in ovariectomized rats.” J Bone Miner Res 5:1029–1035
Raisz LG (1995) “Physiologic and pathologic roles of prostaglandins and other eicosanoids in bone metabolism.” J Nutr 125:2024S–2027S
Jee WSS, Ueno K, Deng YP, Woodbury DM (1985) “The effects of prostaglandin E2 in growing rats: increased metaphyseal hard tissue and cortico-endosteal bone formation.” Calcif Tissue Int 37:148–157
Jee WSS, Mori S, Li XJ, Chan S (1990) “Prostaglandin E2 enhances cortical bone mass and activates intracortical bone remodeling in intact and ovariectomized female rats.” Bone 11:253–266
Kimmel DB, Slovik DM, Lane NE (1994) “Current and investigational approaches for reversing established osteoporosis.” Rheum Dis Clin North America 20:735–758
Mori S, Jee WSS, Li XJ (1992) “Production of new trabecular bone in osteopenic ovariectomized rats by prostaglandin E2.” Calcif Tissue Int 50:80–87
Welch RD, Johnston CE, Waldron MJ, Poteet B (1993) “Intraosseous infusion of PGE2 in the caprine tibia.” J Orthop Res 11:110–121
Sibonga JD, Bell NH, Turner RT (1998) “Evidence that ibuprofen antagonizes selective actions of estrogen and tamoxifen on rat bone.” J Bone Miner Res 13:863–870
Samuels A, Perry MJ, Tobias JH (1999) “High-dose estrogen-induced osteogenesis in the mouse is partially suppressed by indomethacin.” Bone 25:675–680
Kopp E, Ghosh S (1994) “Inhibition of NKκB by sodium salicylate and aspirin.” Science 265:956–959
Lehmann JM, Lenhard JM, Oliver BB, Ringold GM, Kliewer SA (1997) “Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors are activated by indomethacin and other non-steroidal antiinflammatory drugs.” J Biol Chem 272:3406–3410
Paik JH, Ju JH, Lee JY, Boudreau MD, Hwang DH (2000) “Two opposing effects of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs on the expression of the inducible cyclooxygenase.” J Biol Chem 275:28173–28179
Raisz LG (1999) “Physiology and pathophysiology of bone remodeling.” Clin Chem 45:1353–1358
Smith WL, DeWitt DL (1996) “Prostaglandin endoperoxide H synthases-1 and -2.” Adv Immunol 62:167–215
Murakami M, Kambe T, Shimbara S, Kudo I (1999) “Functional coupling between various phospholipase A2’s and cyclooxygenases in immediate and delayed prostanoid biosynthetic pathways.” J Biol Chem 274:3103–3115
Fujishima H, Sanchez Mejia RO, Bingham CO III, Lam BK, Sapirstein A, Bonventre JV, Austen KF, Arm JP (1999) “Cytosolic phospholipase A2 is essential for both the immediate and the delayed phases of eicosanoid generation in mouse bone-derived mast cells.” Proc Natl Acad Sci 96:4803–4807
Breton M, Colyard O (1991) “Protein kinase C promotes arachidonate mobilization through enhancement of Co-A-independent transacylase activity in platelets.” Biochem J 280:93–98
O’Doherty PJA (1978) “1,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D3 increases the activity of the intestinal phosphatidylcholine deacylation-reacylation cycle.” Lipids 14:75–77
Keeting PE, Li CH, Whipkey DL, Thweatt R, Xu JQ, Murty M, Blaha JD, Graeber GM (1998) 1,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D3 pretreatment limits prostaglandin biosynthesis by cytokine-stimulated adult human osteoblast-like cells. J Cell Biochem 68:237–246
Jun SS, Chen Z, Pace MC, Shaul PW (1998) “Estrogen upregulates cyclooxygenase-1 gene expression in ovine fetal pulmonary artery endothelium.” J Clin Invest 102:176–183
Sato T, Michizu H, Hashizume K, Ito A (2001) “Hormonal regulation of PGE2 and COX-2 production in rabbit uterine cervical fibroblasts.” J Appl Physiol 90:1227–1231
Akarasereenont P, Techatraisak K, Thaworn A, Chotewuttakorn S (2000) “The induction of cyclooxygenase-2 by 17β-estradiol in endothelial cells is mediated through protein kinase C.” Inflamm Res 49:460–465
Turner RT, Evans GL, Wakley GK (1993) “Mechanism of action of estrogen on cancellous bone balance in tibiae of ovariectomized growing rats: inhibition of indices of formation and resorption.” J Bone Miner Res 8:359–365
Turner RT, Riggs BL, Spelsberg TC (1994) “Skeletal effects of estrogen.” Endocr Rev 15:275–300
Lindsay R (1987) “The menopause: sex steroids and osteoporosis.” Clin Obstet Gynecol 30:847–858
Keeting PE, Scott RE, Colvard DS, Han IK, Spelsberg TC, Riggs BL (1991) “Lack of a direct effect of estrogen on proliferation and differentiation of normal human osteoblast-like cells.” J Bone Miner Res 6:827–833
Robinson JA, Harris SA, Riggs BL, Spelsberg TC (1997) “Estrogen regulation of human osteoblastic cell proliferation and differentiation.” Endocrinology 138:2919–2927
Oursler MJ, Cortese C, Keeting PE, Anderson M, Bonde S, Riggs BL, Spelsberg TC (1991) “Modulation of TGFβ production in normal human osteoblast-like cells by 17β-estradiol and parathyroid hormone.” Endocrinology 129:3313–3320
Girasole G, Jilka RL, Passeri G, Bowell S, Boder G, Williams DS, Manolagas SC (1992) “17β-Estradiol inhibits interleukin-6 production by bone marrow-derived stromal cells and osteoblasts in vitro: a potential mechanism for the antiosteoporotic effect of estrogens.” J Clin Invest 89:883–891
Kassem M, Harris SA, Spelsberg TC, Riggs BL (1996) “Estrogen inhibits interleukin-6 production and gene expression in a human osteoblastic cell line with high levels of estrogen receptors.” J Bone Miner Res 11:193–199
Acknowledgements
This work was supported in part by grants AR41769 and AG16656 from the National Institutes of Health, United States Public Health Service.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Secreto, F.J., Grover, A., Pacurari, M. et al. Estrogen Potentiates the Combined Effects of Transforming Growth Factor-β and Tumor Necrosis Factor-α on Adult Human Osteoblast-like Cell Prostaglandin E2 Biosynthesis. Calcif Tissue Int 73, 565–574 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00223-002-0023-z
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00223-002-0023-z