Abstract.
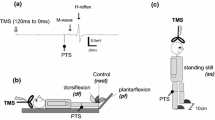
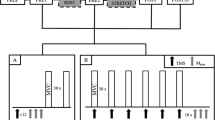
Post-exercise facilitation (PEF) of motor evoked potentials (MEPs) was studied by transcranial magnetic stimulation in 15 healthy subjects following standardized and controlled isometric contraction of the biceps brachii muscle. PEF was highly dependent on the time delay (TD) from muscle relaxation to delivery of the magnetic stimulus and only to a minor degree on the duration of the maintained muscular contraction of 2, 4, and 6 s. In addition, PEF was unaffected by the contraction levels of 25%, 50%, and 100% of maximal voluntary contraction (MVC). There was a linear relationship between the log amplitude of the post-exercise MEPs and the TD. The time point at which PEF had vanished was calculated to be 15.2 s. In order to challenge the question whether segmental and/or suprasegmental mechanisms are primarily responsible for PEF, MEPs and H-reflexes were recorded from the soleus muscle following a sustained plantar flexion at the ankle joint in three healthy subjects. PEF of MEPs was present at a TD of 1000 ms following a sustained contraction of 6 s at a level of 50% of MVC. It was accompanied by a pronounced decrease in the soleus H-reflex amplitude at a TD of 1000 ms.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nørgaard, P., Feldbæk Nielsen, J. & Andersen, H. Post-exercise facilitation of compound muscle action potentials evoked by transcranial magnetic stimulation in healthy subjects. Exp Brain Res 132, 517–522 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002219900318
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002219900318