Abstract.
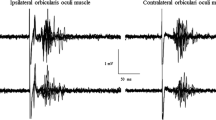
This study characterizes trigeminal blinks in normal human subjects between 20 and 80 years of age, 60-year-old Parkinson's disease patients, and young and old guinea pigs. In normal humans over 60 years of age, lid-closing duration, and the excitability and latency of the trigeminal reflex blink increase significantly relative to younger subjects. Aged guinea pigs appear to display similar increases in reflex blink duration and latency. Reflex blink amplitude, however, does not change consistently with age. For subjects less than 70 years of age, a unilateral trigeminal stimulus evokes a 37% larger blink in the eyelid ipsilateral to the stimulus than in the contralateral eyelid, but 70-year-olds exhibit blinks of equal amplitude. In all cases, blink duration is identical for the two eyelids. If normal, age-related loss of dopamine neurons explains these trigeminal blink modifications, then Parkinson's disease should exaggerate age-related changes in these blink parameters. Preliminary data show that Parkinson's disease increases blink duration and excitability relative to age-matched control subjects. Thus, it seems likely that normal, age-related loss of dopamine neurons accounts for increases in trigeminal blink excitability and duration. A previously uncharacterized type of trigeminally evoked blink appears after age 40 in humans and in aged guinea pigs. In subjects less than 40 years old, a single trigeminal stimulus elicits a single reflex blink. In subjects over age 40, however, a single stimulus frequently evokes a reflex blink and additional blinks that occur at a fixed interval relative to the preceding blink. These "blink oscillations" may arise from oscillatory processes within trigeminal reflex blink circuits. The presence of exaggerated blink oscillations in subjects with dry eye and benign essential blepharospasm suggests that an alteration of blink oscillation mechanisms plays a critical role in these disorders.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Peshori, K., Schicatano, E., Gopalaswamy, R. et al. Aging of the trigeminal blink system. Exp Brain Res 136, 351–363 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002210000585
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002210000585