Abstract
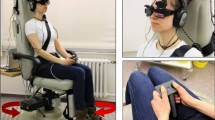
Most prior studies of the subjective visual vertical (SVV) focus on inaccuracy of subjects’ SVV responses with the head in an upright position. Here we investigated SVV imprecision during lateral head tilt in patients with chronic dizziness compared to healthy controls. Forty-five dizzy patients and 45 healthy controls underwent SVV testing wearing virtual reality (VR) goggles, sitting upright (0°) and during head tilt in the roll plane (± 30°). Ten trials were completed in each of three static head positions. The SVV inaccuracy and SVV imprecision were analyzed and compared between groups, along with systematic errors during head tilt, i.e., A-effect and E-effect (E-effect is a typical SVV response during head tilts of ± 30°). The SVV imprecision was found to be affected by head position (upright/right head tilt/left head tilt, p < 0.001) and underlying dizziness (dizzy patients/healthy controls, p = 0.005). The SVV imprecision during left head tilt was greater in dizzy patients compared to healthy controls (p = 0.04). With right head tilt, there was a trend towards greater SVV imprecision in dizzy patients (p = 0.08). Dizzy patients were more likely to have bilateral (6.7%) or unilateral (22.2%) A-effect during lateral head tilt than healthy controls (bilateral (0%) or unilateral (6.7%) A-effect, p < 0.01). Greater SVV imprecision in chronically dizzy patients during head tilts may be attributable to increased noise of vestibular sensory afferents or disturbances of multisensory integration. Our findings suggest that SVV imprecision may be a useful clinical parameter of underlying dizziness measurable with bedside SVV testing in VR.



Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
Requests for study data may be addressed to the corresponding author.
Code availability
N/A.
References
Alberts BBGT, Selen LPJ, Bertolini G et al (2016) Dissociating vestibular and somatosensory contributions to spatial orientation. J Neurophysiol 116:30–40. https://doi.org/10.1152/jn.00056.2016
Anastasopoulos D, Bronstein AM (1999) A case of thalamic syndrome: somatosensory influences on visual orientation. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 67:390–394. https://doi.org/10.1136/jnnp.67.3.390
Angelaki DE, Cullen KE (2008) Vestibular system: the many facets of a multimodal sense. Annu Rev Neurosci 31:125–150. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.neuro.31.060407.125555
Barra J, Marquer A, Joassin R et al (2010) Humans use internal models to construct and update a sense of verticality. Brain J Neurol 133:3552–3563. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/awq311
Böhmer A, Rickenmann J (1995) The subjective visual vertical as a clinical parameter of vestibular function in peripheral vestibular diseases. J Vestib Res Equilib Orientat 5:35–45
Brandt T, Dieterich M (2019) Thalamocortical network: a core structure for integrative multimodal vestibular functions. Curr Opin Neurol 32:154–164. https://doi.org/10.1097/WCO.0000000000000638
Brandt T, Strupp M (2005) General vestibular testing. Clin Neurophysiol off J Int Fed Clin Neurophysiol 116:406–426. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clinph.2004.08.009
Bremova T, Caushaj A, Ertl M et al (2016) Comparison of linear motion perception thresholds in vestibular migraine and Menière’s disease. Eur Arch Oto-Rhino-Laryngol off J Eur Fed Oto-Rhino-Laryngol Soc EUFOS Affil Ger Soc Oto-Rhino-Laryngol—Head Neck Surg 273:2931–2939. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-015-3835-y
Bronstein AM, Yardley L, Moore AP, Cleeves L (1996) Visually and posturally mediated tilt illusion in Parkinson’s disease and in labyrinthine defective subjects. Neurology 47:651–656. https://doi.org/10.1212/wnl.47.3.651
Bürgin A, Bockisch CJ, Tarnutzer AA (2018) Precision of perceived direction of gravity in partial bilateral vestibulopathy correlates with residual utricular function. Clin Neurophysiol off J Int Fed Clin Neurophysiol 129:934–945. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clinph.2018.02.121
Carriot J, Jamali M, Cullen KE (2015) Rapid adaptation of multisensory integration in vestibular pathways. Front Syst Neurosci 9:59. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnsys.2015.00059
Cha Y-H, Lee H, Santell L, Baloh R (2009) Association of benign recurrent vertigo and migraine in 208 patients. Cephalalgia 29:550–555. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1468-2982.2008.01770.x
Clemens IAH, De Vrijer M, Selen LPJ et al (2011) Multisensory processing in spatial orientation: an inverse probabilistic approach. J Neurosci 31:5365–5377. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.6472-10.2011
Cnyrim CD, Rettinger N, Mansmann U et al (2007) Central compensation of deviated subjective visual vertical in Wallenberg’s syndrome. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 78:527–528. https://doi.org/10.1136/jnnp.2006.100727
Cousins S, Kaski D, Cutfield N et al (2013) Vestibular perception following acute unilateral vestibular lesions. PLoS ONE 8:e61862. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0061862
Di Fabio RP (1995) Sensitivity and specificity of platform posturography for identifying patients with vestibular dysfunction. Phys Ther 75:290–305. https://doi.org/10.1093/ptj/75.4.290
Diaz-Artiles A, Karmali F (2021) Vestibular precision at the level of perception, eye movements, posture, and neurons. Neuroscience. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2021.05.028
Dieterich M, Brandt T (2019) Perception of verticality and vestibular disorders of balance and falls. Front Neurol 10:172. https://doi.org/10.3389/fneur.2019.00172
El-Kashlan HK, Shepard NT, Asher AM et al (1998) Evaluation of clinical measures of equilibrium. Laryngoscope 108:311–319. https://doi.org/10.1097/00005537-199803000-00002
Espinosa-Sanchez JM, Lopez-Escamez JA (2015) New insights into pathophysiology of vestibular migraine. Front Neurol 6:12. https://doi.org/10.3389/fneur.2015.00012
Faisal AA, Selen LPJ, Wolpert DM (2008) Noise in the nervous system. Nat Rev Neurosci 9:292–303. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrn2258
Fife TD, Colebatch JG, Kerber KA et al (2017) Practice guideline: cervical and ocular vestibular evoked myogenic potential testing: report of the guideline development, dissemination, and implementation subcommittee of the American Academy of Neurology. Neurology 89:2288–2296. https://doi.org/10.1212/WNL.0000000000004690
Friedmann G (1970) The judgement of the visual vertical and horizontal with peripheral and central vestibular lesions. Brain 93:313–328. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/93.2.313
Halmagyi GM, Chen L, MacDougall HG et al (2017) The video head impulse test. Front Neurol 8:258. https://doi.org/10.3389/fneur.2017.00258
Howard IP (1982) Human visual orientation. Wiley, New York
Jacobson GP, Newman CW (1990) The development of the dizziness handicap inventory. Arch Otolaryngol Neck Surg 116:424–427. https://doi.org/10.1001/archotol.1990.01870040046011
Kheradmand A, Winnick A (2017) Perception of upright: multisensory convergence and the role of temporo-parietal cortex. Front Neurol 8:552. https://doi.org/10.3389/fneur.2017.00552
King S, Priesol AJ, Davidi SE et al (2019) Self-motion perception is sensitized in vestibular migraine: pathophysiologic and clinical implications. Sci Rep 9:14323. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-50803-y
Lempert T, Olesen J, Furman J et al (2012) Vestibular migraine: diagnostic criteria. J Vestib Res Equilib Orientat 22:167–172. https://doi.org/10.3233/VES-2012-0453
Lewis RF, Priesol AJ, Nicoucar K et al (2011) Abnormal motion perception in vestibular migraine. Laryngoscope 121:1124–1125. https://doi.org/10.1002/lary.21723
Lopez-Escamez JA, Carey J, Chung W-H et al (2015) Diagnostic criteria for Menière’s disease. J Vestib Res Equilib Orientat 25:1–7. https://doi.org/10.3233/VES-150549
Medendorp WP, Alberts BBGT, Verhagen WIM et al (2018) Psychophysical evaluation of sensory reweighting in bilateral vestibulopathy. Front Neurol 9:377. https://doi.org/10.3389/fneur.2018.00377
Mittelstaedt H (1983) A new solution to the problem of the subjective vertical. Naturwissenschaften 70:272–281. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00404833
Müller JA, Bockisch CJ, Tarnutzer AA (2016) Spatial orientation in patients with chronic unilateral vestibular hypofunction is ipsilesionally distorted. Clin Neurophysiol 127:3243–3251. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clinph.2016.07.010
Negrillo-Cárdenas J, Rueda-Ruiz AJ, Ogayar-Anguita CJ et al (2018) A system for the measurement of the subjective visual vertical using a virtual reality device. J Med Syst 42:124. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10916-018-0981-y
Otero-Millan J, Kheradmand A (2016) Upright perception and ocular torsion change independently during head tilt. Front Hum Neurosci 10:573. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnhum.2016.00573
Shayman CS, Seo J-H, Oh Y et al (2018) Relationship between vestibular sensitivity and multisensory temporal integration. J Neurophysiol 120:1572–1577. https://doi.org/10.1152/jn.00379.2018
Staab JP, Eckhardt-Henn A, Horii A et al (2017) Diagnostic criteria for persistent postural-perceptual dizziness (PPPD): Consensus document of the committee for the Classification of Vestibular Disorders of the Bárány Society. J Vestib Res Equilib Orientat 27:191–208. https://doi.org/10.3233/VES-170622
Strupp M, Magnusson M (2015) Acute unilateral vestibulopathy. Neurol Clin 33:669–685. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ncl.2015.04.012
Strupp M, Kim J-S, Murofushi T et al (2017) Bilateral vestibulopathy: diagnostic criteria consensus document of the classification committee of the Bárány Society. J Vestib Res Equilib Orientat 27:177–189. https://doi.org/10.3233/VES-170619
Tarnutzer AA, Bockisch C, Straumann D, Olasagasti I (2009) Gravity dependence of subjective visual vertical variability. J Neurophysiol 102:1657–1671. https://doi.org/10.1152/jn.00007.2008
Totilienė M, Uloza V, Lesauskaitė V et al (2021) Impaired subjective visual vertical and increased visual dependence in older adults with falls. Front Aging Neurosci 13:667608. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnagi.2021.667608
Trousselard M, Cian C, Nougier V et al (2003) Contribution of somesthetic cues to the perception of body orientation and subjective visual vertical. Percept Psychophys 65:1179–1187. https://doi.org/10.3758/bf03194843
Ulozienė I, Totilienė M, Paulauskas A et al (2017) Subjective visual vertical assessment with mobile virtual reality system. Med Kaunas Lith 53:394–402. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.medici.2018.02.002
Ulozienė I, Totilienė M, Balnytė R et al (2020) Subjective visual vertical and visual dependency in patients with multiple sclerosis. Mult Scler Relat Disord 44:102255. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msard.2020.102255
Van Beuzekom AD, Medendorp WP, Van Gisbergen JA (2001) The subjective vertical and the sense of self orientation during active body tilt. Vision Res 41:3229–3242. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0042-6989(01)00144-4
Vrijer MD, Medendorp WP, Gisbergen JAMV (2009) Accuracy-precision trade-off in visual orientation constancy. J vis 9:9–9. https://doi.org/10.1167/9.2.9
Wade NJ (1968) Visual orientation during and after lateral head, body, and trunk tilt. Percept Psychophys 3:215–219. https://doi.org/10.3758/BF03212730
Wang C-H, Winnick A, Ko Y-H et al (2021) Test-retest reliability of subjective visual vertical measurements with lateral head tilt in virtual reality goggles. Tzu Chi Med J 33:294. https://doi.org/10.4103/tcmj.tcmj_207_20
Winnick A, Sadeghpour S, Otero-Millan J et al (2018) Errors of upright perception in patients with vestibular migraine. Front Neurol 9:892. https://doi.org/10.3389/fneur.2018.00892
Yardley L, Masson E, Verschuur C et al (1992) Symptoms, anxiety and handicap in dizzy patients: development of the vertigo symptom scale. J Psychosom Res 36:731–741. https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-3999(92)90131-k
Zwergal A, Rettinger N, Frenzel C et al (2009) A bucket of static vestibular function. Neurology 72:1689–1692. https://doi.org/10.1212/WNL.0b013e3181a55ecf
Funding
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization: AW, CHW, YHK, and TPC; methodology: AW, CHW, YHK, and TPC; data collection: CHW and TPC; data analysis: AW, CHW, YHK, and TPC; manuscript drafting and revisions: AW, CHW, YHK, and TPC. All authors have read and agreed to the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
None to disclose.
Ethics approval
Ethical approval for this study (REC-109-06) was provided by the Research Ethics Committee of Taichung Tzu Chi Hospital. The study was performed in accordance with the guidelines of the Declaration of Helsinki, and written informed consent was obtained from all subjects prior to participation.
Additional information
Communicated by Francesco Lacquaniti.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Winnick, A.A., Wang, CH., Ko, YH. et al. Subjective visual vertical imprecision during lateral head tilt in patients with chronic dizziness. Exp Brain Res 240, 199–206 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-021-06247-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-021-06247-w