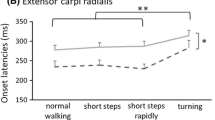
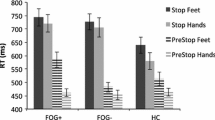
Abstract
Freezing of gait in people with Parkinson’s disease (PwP) is associated with executive dysfunction and motor preparation deficits. We have recently shown that electrophysiological markers of motor preparation, rather than decision-making, differentiate PwP with freezing of gait (FOG +) and without (FOG −) while sitting. To examine the effect of locomotion on these results, we measured behavioural and electrophysiological responses in PwP with and without FOG during a target response time task while sitting (single-task) and stepping-in-place (dual-task). Behavioural and electroencephalographic data were acquired from 18 PwP (eight FOG +) and seven young controls performing the task while sitting and stepping-in-place. FOG + had slower response times while stepping compared with sitting. However, response times were significantly faster while stepping compared with sitting for controls. Electrophysiological responses showed no difference in decision-making potentials (centroparietal positivity) between groups or conditions but there were differences in neurophysiological markers of response inhibition (N2) and motor preparation (lateralized readiness potential, LRP) in FOG + while performing a dual-task. This suggests that the addition of a second complex motor task (stepping-in-place) impacts automatic allocation of resources in FOG +, resulting in delayed response times. The impact of locomotion on the generation of the N2 and LRP potentials, particularly in freezers, indirectly implies that these functions compete with locomotion for resources. In the setting of multiple complex tasks or cognitive impairment, severe motor dysfunction may result, leading to freezing of gait.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amboni M, Cozzolino A, Longo K, Picillo M, Barone P (2008) Freezing of gait and executive functions in patients with Parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord 23:395–400. https://doi.org/10.1002/mds.21850
Beck EN, Ehgoetz Martens KA, Almeida QJ (2015) Freezing of Gait in Parkinson’s disease: an overload problem? PLoS ONE 10:e0144986. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0144986
Benjamini Y, Hochberg Y (1995) Controlling the false discovery rate: a practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. J R Statist Soc Ser B 57:289–300
Bloem BR, Hausdorff JM, Visser JE, Giladi N (2004) Falls and freezing of gait in Parkinson’s disease: a review of two interconnected, episodic phenomena. Mov Disord 19:871–884. https://doi.org/10.1002/mds.20115
Butler JS, Fearon C, Killane I, Waechter SM, Reilly RB, Lynch T (2017) Motor preparation rather than decision-making differentiates Parkinson’s disease patients with and without freezing of gait. Clin Neurophysiol 128:463–471. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clinph.2016.12.019
Camicioli R, Oken BS, Sexton G, Kaye JA, Nutt JG (1998) Verbal fluency task affects gait in Parkinson’s disease with motor freezing. J Geriatr Psychiatry Neurol 11:181–185. https://doi.org/10.1177/089198879901100403
Canu E, Agosta F, Sarasso E et al (2015) Brain structural and functional connectivity in Parkinson’s disease with freezing of gait. Hum Brain Mapp 36:5064–5078. https://doi.org/10.1002/hbm.22994
De Sanctis P, Butler JS, Green JM, Snyder AC, Foxe JJ (2012) Mobile brain/body imaging (MoBI): high-density electrical mapping of inhibitory processes during walking. Conf Proc IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc 2012:1542–1545. https://doi.org/10.1109/EMBC.2012.6346236
De Sanctis P, Butler JS, Malcolm BR, Foxe JJ (2014) Recalibration of inhibitory control systems during walking-related dual-task interference: a mobile brain-body imaging (MOBI) study. Neuroimage 94:55–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2014.03.016
De Vos M, Gandras K, Debener S (2014) Towards a truly mobile auditory brain–computer interface: exploring the P300 to take away. Int J Psychophysiol 91:46–53. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpsycho.2013.08.010
Debener S, Minow F, Emkes R, Gandras K, de Vos M (2012) How about taking a low-cost, small, and wireless EEG for a walk? Psychophysiology 49:1617–1621. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-8986.2012.01471.x
Delorme A, Makeig S (2004) EEGLAB: an open source toolbox for analysis of single-trial EEG dynamics including independent component analysis. J Neurosci Methods 134:9–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jneumeth.2003.10.009
Dienes Z (2016) How Bayes factors change scientific practice. J Math Psychol 72:78
Eimer M (1993) Effects of attention and stimulus probability on Erps in a Go/Nogo task. Biol Psychol 35:123–138
Fearon C, Butler JS, Newman L, Lynch T, Reilly RB (2015) Audiovisual processing is abnormal in Parkinson’s disease and correlates with freezing of gait and disease duration. J Parkinsons Dis 5:925–936. https://doi.org/10.3233/JPD-150655
Fling BW, Cohen RG, Mancini M, Carpenter SD, Fair DA, Nutt JG, Horak FB (2014) Functional reorganization of the locomotor network in Parkinson patients with freezing of gait. PLoS ONE 9:e100291. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0100291
Friend DM, Kravitz AV (2014) Working together: basal ganglia pathways in action selection. Trends Neurosci 37:301–303. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tins.2014.04.004
Gramann K, Gwin JT, Bigdely-Shamlo N, Ferris DP, Makeig S (2010) Visual evoked responses during standing and walking. Front Hum Neurosci 4:202. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnhum.2010.00202
Guthrie D, Buchwald JS (1991) Significance testing of difference potentials. Psychophysiology 28:240–244
Gwin JT, Gramann K, Makeig S, Ferris DP (2010) Removal of movement artifact from high-density EEG recorded during walking and running. J Neurophysiol 103:3526–3534. https://doi.org/10.1152/jn.00105.2010
Handojoseno AM, Shine JM, Nguyen TN, Tran Y, Lewis SJ, Nguyen HT (2012) The detection of freezing of Gait in Parkinson’s disease patients using EEG signals based on Wavelet decomposition. Conf Proc IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc 2012:69–72. https://doi.org/10.1109/EMBC.2012.6345873
Handojoseno AM, Shine JM, Nguyen TN, Tran Y, Lewis SJ, Nguyen HT (2013) Using EEG spatial correlation, cross frequency energy, and wavelet coefficients for the prediction of Freezing of Gait in Parkinson’s disease patients. Conf Proc IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc 2013:4263–4266. https://doi.org/10.1109/EMBC.2013.6610487
Handojoseno AM, Shine JM, Nguyen TN, Tran Y, Lewis SJ, Nguyen HT (2015) Analysis and prediction of the freezing of gait using EEG brain dynamics. IEEE Trans Neural Syst Rehabil Eng 23:887–896. https://doi.org/10.1109/TNSRE.2014.2381254
Hausdorff JM, Balash J, Giladi N (2003) Effects of cognitive challenge on gait variability in patients with Parkinson’s disease. J Geriatr Psychiatry Neurol 16:53–58. https://doi.org/10.1177/0891988702250580
Heinzel S, Maechtel M, Hasmann SE, Hobert MA, Heger T, Berg D, Maetzler W (2016) Motor dual-tasking deficits predict falls in Parkinson’s disease: a prospective study. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 26:73–77. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.parkreldis.2016.03.007
Herath P, Klingberg T, Young J, Amunts K, Roland P (2001) Neural correlates of dual task interference can be dissociated from those of divided attention: an fMRI study. Cereb Cortex 11:796–805
Hughes AJ, Daniel SE, Kilford L, Lees AJ (1992) Accuracy of clinical diagnosis of idiopathic Parkinson’s disease: a clinico-pathological study of 100 cases. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 55:181–184
Jacobs JV, Nutt JG, Carlson-Kuhta P, Stephens M, Horak FB (2009) Knee trembling during freezing of gait represents multiple anticipatory postural adjustments. Exp Neurol 215:334–341. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.expneurol.2008.10.019
Kayser J, Tenke CE (2006a) Principal components analysis of Laplacian waveforms as a generic method for identifying ERP generator patterns: I. Evaluation with auditory oddball tasks. Clin Neurophysiol 117:348–368. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clinph.2005.08.034
Kayser J, Tenke CE (2006b) Principal components analysis of Laplacian waveforms as a generic method for identifying ERP generator patterns: II Adequacy of low-density estimates. Clin Neurophysiol 117:369–380. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clinph.2005.08.033
Kelly SP, O’Connell RG (2013) Internal and external influences on the rate of sensory evidence accumulation in the human brain. J Neurosci 33:19434–19441. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3355-13.2013
Killane I, Fearon C, Newman L et al (2015) Dual motor-cognitive virtual reality training impacts dual-task performance in freezing of gait. IEEE J Biomed Health Inform 19:1855–1861. https://doi.org/10.1109/JBHI.2015.2479625
Kindermann SS, Kalayam B, Brown GG, Burdick KE, Alexopoulos GS (2000) Executive functions and P300 latency in elderly depressed patients and control subjects. Am J Geriatr Psychiatry 8:57–65
Knobl P, Kielstra L, Almeida Q (2012) The relationship between motor planning and freezing of gait in Parkinson’s disease. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 83:98–101. https://doi.org/10.1136/jnnp-2011-300869
Kostic VS, Agosta F, Pievani M et al (2012) Pattern of brain tissue loss associated with freezing of gait in Parkinson disease. Neurology 78:409–416. https://doi.org/10.1212/WNL.0b013e318245d23c
Lewis SJ, Shine JM (2016) The next step: a common neural mechanism for freezing of gait. Neuroscientist 22:72–82. https://doi.org/10.1177/1073858414559101
Loughnane GM, Newman DP, Bellgrove MA, Lalor EC, Kelly SP, O’Connell RG (2016) Target selection signals influence perceptual decisions by modulating the onset and rate of evidence accumulation. Curr Biol 26:496–502. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2015.12.049
Ly QT, Handojoseno AM, Gilat M et al (2017) Detection of turning freeze in Parkinson’s disease based on S-transform decomposition of EEG signals. Conf Proc IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc 2017:3044–3047
Maidan I, Fahoum F, Shustak S et al (2019) Changes in event-related potentials during dual task walking in aging and Parkinson’s disease. Clin Neurophysiol 130:224–230. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clinph.2018.11.019
Malcolm BR, Foxe JJ, Butler JS, De Sanctis P (2015) The aging brain shows less flexible reallocation of cognitive resources during dual-task walking: a mobile brain/body imaging (MoBI) study. Neuroimage 117:230–242. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2015.05.028
Malcolm BR, Foxe JJ, Butler JS, Mowrey WB, Molholm S, De Sanctis P (2017) Long-term test–retest reliability of event-related potential (ERP) recordings during treadmill walking using the mobile brain/body imaging (MoBI) approach. Brain Res. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainres.2017.05.021
Malcolm BR, Foxe JJ, Butler JS, Molholm S, De Sanctis P (2018) Cognitive load reduces the effects of optic flow on gait and electrocortical dynamics during treadmill walking. J Neurophysiol 120:2246–2259
Mazza V, Turatto M, Caramazza A (2009) Attention selection, distractor suppression and N2pc. Cortex 45:879–890. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cortex.2008.10.009
Nieuwboer A, Rochester L, Herman T, Vandenberghe W, Emil GE, Thomaes T, Giladi N (2009) Reliability of the new freezing of gait questionnaire: agreement between patients with Parkinson’s disease and their carers. Gait Posture 30:459–463. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gaitpost.2009.07.108
Nutt JG, Bloem BR, Giladi N, Hallett M, Horak FB, Nieuwboer A (2011) Freezing of gait: moving forward on a mysterious clinical phenomenon. Lancet Neurol 10:734–744. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1474-4422(11)70143-0
O’Connell RG, Dockree PM, Kelly SP (2012) A supramodal accumulation-to-bound signal that determines perceptual decisions in humans. Nat Neurosci 15:1729–1735. https://doi.org/10.1038/nn.3248
Perrin F, Pernier J, Bertrand O, Echallier JF (1989) Spherical splines for scalp potential and current-density mapping. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 72:184–187
Peterson DS, Fling BW, Mancini M, Cohen RG, Nutt JG, Horak FB (2015) Dual-task interference and brain structural connectivity in people with Parkinson’s disease who freeze. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 86:786–792. https://doi.org/10.1136/jnnp-2014-308840
Pieruccini-Faria F, Jones JA, Almeida QJ (2014) Motor planning in Parkinson’s disease patients experiencing freezing of gait: the influence of cognitive load when approaching obstacles. Brain Cogn 87:76–85. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bandc.2014.03.005
Piramide N, Agosta F, Sarasso E, Canu E, Volontè MA, Filippi M (2020) Brain activity during lower limb movements in Parkinson’s disease patients with and without freezing of gait. J Neurol. 267:1116–1126
Potvin-Desrochers A, Mitchell T, Gisiger T, Paquette C (2019) Changes in resting-state functional connectivity related to freezing of gait in Parkinson’s disease. Neuroscience 418:311–317
R Development Core Team (2017) R: a language and environment for statistical computing. vol 2017
Redgrave P, Rodriguez M, Smith Y et al (2010) Goal-directed and habitual control in the basal ganglia: implications for Parkinson’s disease. Nat Rev Neurosci 11:760–772. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrn2915
Rouder JN, Speckman PL, Sun D, Morey RD, Iverson G (2009) Bayesian t tests for accepting and rejecting the null hypothesis. Psychon Bull Rev 16:225–237. https://doi.org/10.3758/PBR.16.2.225
Rstudio (2016) RStudio: integrated development environment for R. RStudio, Inc
Salisbury DF, Rutherford B, Shenton ME, McCarley RW (2001) Button-pressing affects P300 amplitude and scalp topography. Clin Neurophysiol 112:1676–1684
Savier EL, Chen H, Cang J (2019) Effects of locomotion on visual responses in the mouse superior colliculus. J Neurosci 39(47):9360–9368
Shibasaki H, Hallett M (2006) What is the bereitschaftspotential? Clin Neurophysiol 117:2341–2356. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clinph.2006.04.025
Shine JM, Matar E, Ward PB et al (2013) Exploring the cortical and subcortical functional magnetic resonance imaging changes associated with freezing in Parkinson’s disease. Brain 136:1204–1215. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/awt049
Shine JM, Matar E, Ward PB, Bolitho SJ, Pearson M, Naismith SL, Lewis SJ (2013) Differential neural activation patterns in patients with Parkinson’s disease and freezing of gait in response to concurrent cognitive and motor load. PLoS ONE 8:e52602. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0052602
Shine JM, Moustafa AA, Matar E, Frank MJ, Lewis SJ (2013) The role of frontostriatal impairment in freezing of gait in Parkinson’s disease. Front Syst Neurosci 7:61. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnsys.2013.00061
Shine JM, Handojoseno AM, Nguyen TN, Tran Y, Naismith SL, Nguyen H, Lewis SJ (2014) Abnormal patterns of theta frequency oscillations during the temporal evolution of freezing of gait in Parkinson’s disease. Clin Neurophysiol 125:569–576. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clinph.2013.09.006
Spildooren J, Vercruysse S, Desloovere K, Vandenberghe W, Kerckhofs E, Nieuwboer A (2010) Freezing of gait in Parkinson’s disease: the impact of dual-tasking and turning. Mov Disord 25:2563–2570. https://doi.org/10.1002/mds.23327
Stuart S, Vitorio R, Morris R et al (2018) Cortical activity during walking and balance tasks in older adults and in people with Parkinson’s disease: a structured review. Maturitas 113:53–72
Tard C, Dujardin K, Bourriez JL, Destee A, Derambure P, Defebvre L, Delval A (2014) Attention modulates step initiation postural adjustments in Parkinson freezers. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 20:284–289. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.parkreldis.2013.11.016
Toledo JB, López-Azcárate J, Garcia-Garcia D et al (2014) High beta activity in the subthalamic nucleus and freezing of gait in Parkinson’s disease. Neurobiol Dis 64:60–65
Twomey DM, Murphy PR, Kelly SP, O’Connell RG (2015) The classic P300 encodes a build-to-threshold decision variable. Eur J Neurosci 42:1636–1643. https://doi.org/10.1111/ejn.12936
Vandenbossche J, Deroost N, Soetens E, Spildooren J, Vercruysse S, Nieuwboer A, Kerckhofs E (2011) Freezing of gait in Parkinson disease is associated with impaired conflict resolution. Neurorehabil Neural Repair 25:765–773. https://doi.org/10.1177/1545968311403493
Vandenbossche J, Deroost N, Soetens E et al (2012) Conflict and freezing of gait in Parkinson’s disease: support for a response control deficit. Neuroscience 206:144–154. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2011.12.048
Velu PD, Mullen T, Noh E et al (2014) Effect of visual feedback on the occipital-parietal-motor network in Parkinson’s disease with freezing of gait. Front Neurol 9(4):209
Vervoort G, Heremans E, Bengevoord A, Strouwen C, Nackaerts E, Vandenberghe W, Nieuwboer A (2016) Dual-task-related neural connectivity changes in patients with Parkinson’ disease. Neuroscience 317:36–46. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2015.12.056
Vo A, Seergobin KN, MacDonald PA (2017) Effects of levodopa on stimulus–response learning versus response selection in healthy young adults. Behav Brain Res 317:553–561. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbr.2016.10.019
Waechter S, Fearon C, McDonnell C, et al. (2015) The impact of dual tasking on cognitive performance in a Parkinson’s disease cohort with and without freezing of gait: an EEG and behavioral based approach. In: Neural Engineering (NER)In: 7th International IEEE/EMBS Conference on. IEEE, pp 1072–1075
Wu T, Hallett M (2008) Neural correlates of dual task performance in patients with Parkinson’s disease. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 79:760–766. https://doi.org/10.1136/jnnp.2007.126599
Wu T, Hallett M, Chan P (2015) Motor automaticity in Parkinson’s disease. Neurobiol Dis 82:226–234. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nbd.2015.06.014
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Communicated by Winston D Byblow.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fearon, C., Butler, J.S., Waechter, S.M. et al. Neurophysiological correlates of dual tasking in people with Parkinson’s disease and freezing of gait. Exp Brain Res 239, 175–187 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-020-05968-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-020-05968-8