Abstract
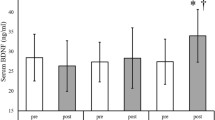
Brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) plays several important roles in nervous system function including neuronal growth and plasticity. The purpose of the present study was to clarify whether neuromuscular electrical stimulation (NMES) and voluntary exercise to the same integrated force as by the NMES-induced exercise would enhance serum BDNF. Eleven healthy male subjects completed three interventions (NMES, voluntary exercise, and resting interventions) for 20 min on different days. In the NMES intervention, NMES was applied to the quadriceps femoris muscles. The stimulus intensity of NMES was progressively increased to the highest tolerated intensity during the experiment. In the voluntary exercise intervention, subjects performed an isometric knee-extension task; in this intervention, the target torque was calculated in accordance with the integrated force of knee extension obtained during the NMES intervention. In the resting intervention, subjects relaxed in a sitting posture. We measured serum BDNF, blood lactate, heart rate, oxygen uptake, respiratory ratio, and blood pressure. Serum BDNF was increased in the NMES (p = 0.003) and voluntary exercise interventions (p = 0.004) after each intervention. At the post-timepoint, serum BDNF in the NMES intervention was highest among all interventions (p = 0.038) and significantly higher than in the voluntary exercise (p = 0.036) and resting (p = 0.037) interventions. Our results showed that NMES was more effective for enhancing serum BDNF than voluntary exercise at least when employing the same method and integrated force.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bax L, Staes F, Verhagen A (2005) Does neuromuscular electrical stimulation strengthen the quadriceps femoris? A systematic review of randomised controlled trials. Sports Med 35:191–212
Brunoni AR, Lopes M, Fregni F (2008) A systematic review and meta-analysis of clinical studies on major depression and BDNF levels: implications for the role of neuroplasticity in depression. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 11:1169–1180. https://doi.org/10.1017/S1461145708009309
Costa A, Peppe A, Carlesimo GA, Zabberoni S, Scalici F, Caltagirone C, Angelucci F (2015) Brain-derived neurotrophic factor serum levels correlate with cognitive performance in Parkinson’s disease patients with mild cognitive impairment. Front Behav Neurosci 9:253. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnbeh.2015.00253
de Oliveira Melo M, Aragao FA, Vaz MA (2013) Neuromuscular electrical stimulation for muscle strengthening in elderly with knee osteoarthritis - a systematic review. Complement Ther Clin Pract 19:27–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ctcp.2012.09.002
Erickson KI, Voss MW, Prakash RS et al (2011) Exercise training increases size of hippocampus and improves memory. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 108:3017–3022. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1015950108
Ferris LT, Williams JS, Shen CL (2007) The effect of acute exercise on serum brain-derived neurotrophic factor levels and cognitive function. Med Sci Sports Exerc 39:728–734. https://doi.org/10.1249/mss.0b013e31802f04c7
Fujimura H, Altar CA, Chen R et al (2002) Brain-derived neurotrophic factor is stored in human platelets and released by agonist stimulation. Thromb Haemost 87:728–734
Hamada T, Kimura T, Moritani T (2004) Selective fatigue of fast motor units after electrically elicited muscle contractions. J Electromyogr Kinesiol 14:531–538. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jelekin.2004.03.008
Hermens HJ, Freriks B, Disselhorst-Klug C, Rau G (2000) Development of recommendations for SEMG sensors and sensor placement procedures. J Electromyogr Kinesiol 10:361–374
Hirsch MA, van Wegen EEH, Newman MA, Heyn PC (2018) Exercise-induced increase in brain-derived neurotrophic factor in human Parkinson’s disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Transl Neurodegener 7:7. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40035-018-0112-1
Huang T, Larsen KT, Ried-Larsen M, Moller NC, Andersen LB (2014) The effects of physical activity and exercise on brain-derived neurotrophic factor in healthy humans: A review. Scand J Med Sci Sports 24:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1111/sms.12069
Kesslak JP, So V, Choi J, Cotman CW, Gomez-Pinilla F (1998) Learning upregulates brain-derived neurotrophic factor messenger ribonucleic acid: a mechanism to facilitate encoding and circuit maintenance? Behav Neurosci 112:1012–1019
Knaepen K, Goekint M, Heyman EM, Meeusen R (2010) Neuroplasticity - exercise-induced response of peripheral brain-derived neurotrophic factor: a systematic review of experimental studies in human subjects. Sports Med 40:765–801. https://doi.org/10.2165/11534530-000000000-00000
Kondo Y, To M, Saruta J, Hayashi T, Sugiyama H, Tsukinoki K (2013) Role of TrkB expression in rat adrenal gland during acute immobilization stress. J Neurochem 124:224–232. https://doi.org/10.1111/jnc.12030
Langeard A, Bigot L, Chastan N, Gauthier A (2017) Does neuromuscular electrical stimulation training of the lower limb have functional effects on the elderly? A systematic review. Exp Gerontol 91:88–98. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.exger.2017.02.070
Maffiuletti NA, Minetto MA, Farina D, Bottinelli R (2011) Electrical stimulation for neuromuscular testing and training: state-of-the art and unresolved issues. Eur J Appl Physiol 111:2391–2397. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-011-2133-7
Miyamoto T, Kou K, Yanamoto H et al (2018) Effect of neuromuscular electrical stimulation on brain-derived neurotrophic factor. Int J Sports Med 39:5–11. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0043-120343
Moreau D, Dubots P, Boggio V, Guilland JC, Cometti G (1995) Effects of electromyostimulation and strength training on muscle soreness, muscle damage and sympathetic activation. J Sports Sci 13:95–100. https://doi.org/10.1080/02640419508732216
Nobrega AC, O’Leary D, Silva BM, Marongiu E, Piepoli MF, Crisafulli A (2014) Neural regulation of cardiovascular response to exercise: role of central command and peripheral afferents. Biomed Res Int 2014:478965. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/478965
Philp A, Macdonald AL, Watt PW (2005) Lactate—a signal coordinating cell and systemic function. J Exp Biol 208:4561–4575. https://doi.org/10.1242/jeb.01961
Scalzo P, Kummer A, Bretas TL, Cardoso F, Teixeira AL (2010) Serum levels of brain-derived neurotrophic factor correlate with motor impairment in Parkinson’s disease. J Neurol 257:540–545. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-009-5357-2
Schiffer T, Schulte S, Sperlich B, Achtzehn S, Fricke H, Struder HK (2011) Lactate infusion at rest increases BDNF blood concentration in humans. Neurosci Lett 488:234–237. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neulet.2010.11.035
Shimada H, Makizako H, Doi T et al (2014) A large, cross-sectional observational study of serum BDNF, cognitive function, and mild cognitive impairment in the elderly. Front Aging Neurosci 6:69. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnagi.2014.00069
Winter B, Breitenstein C, Mooren FC et al (2007) High impact running improves learning. Neurobiol Learn Mem 87:597–609. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nlm.2006.11.003
Wong RA, Jette DU (1984) Changes in sympathetic tone associated with different forms of transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation in healthy subjects. Phys Ther 64:478–482
Yamada K, Mizuno M, Nabeshima T (2002) Role for brain-derived neurotrophic factor in learning and memory. Life Sci 70:735–744
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Grants-in-Aid for Challenging Exploratory Research (24650322. Representative: Fuminari Kaneko). The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kimura, T., Kaneko, F., Iwamoto, E. et al. Neuromuscular electrical stimulation increases serum brain-derived neurotrophic factor in humans. Exp Brain Res 237, 47–56 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-018-5396-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-018-5396-y