Abstract
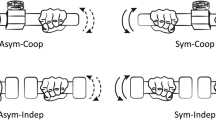
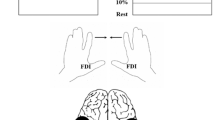
Coordinating bimanual movements is essential for everyday activities. Two common types of bimanual tasks are common goal, where two arms share a united goal, and dual goal, which involves independent goals for each arm. Here, we examine how the neural control mechanisms differ between these two types of bimanual tasks. Ten non-disabled individuals performed isometric force tasks of the elbow at 10% of their maximal voluntary force in both bimanual common and dual goals as well as unimanual conditions. Using transcranial magnetic stimulation, we concurrently examined the intracortical inhibitory modulation (short-interval intracortical inhibition, SICI) as well as the interlimb coordination strategies utilized between common- vs. dual-goal tasks. Results showed a reduction of SICI in both hemispheres during dual-goal compared to common-goal tasks (dominant hemisphere: P = 0.04, non-dominant hemisphere: P = 0.03) and unimanual tasks (dominant hemisphere: P = 0.001, non-dominant hemisphere: P = 0.001). For the common-goal task, a reduction of SICI was only seen in the dominant hemisphere compared to unimanual tasks (P = 0.03). Behaviorally, two interlimb coordination patterns were identified. For the common-goal task, both arms were organized into a cooperative “give and take” movement pattern. Control of the non-dominant arm affected stabilization of bimanual force (R2 = 0.74, P = 0.001). In contrast, for the dual-goal task, both arms were coupled together in a positive fashion and neither arm affected stabilization of bimanual force (R2 = 0.31, P = 0.1). The finding that intracortical inhibition and interlimb coordination patterns were different based on the goal conceptualization of bimanual tasks has implications for future research.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aramaki Y, Honda M, Okada T, Sadato N (2006) Neural correlates of the spontaneous phase transition during bimanual coordination. Cereb Cortex 16:1338–1348. https://doi.org/10.1093/cercor/bhj075
Awiszus F, Feistner H, Urbach D, Bostock H (1999) Characterisation of paired-pulse transcranial magnetic stimulation conditions yielding intracortical inhibition or I-wave facilitation using a threshold-hunting paradigm. Exp Brain Res 129:317–324
Bailey RR, Klaesner JW, Lang CE (2015) Quantifying real-world upper-limb activity in nondisabled adults and adults with chronic stroke. Neurorehabil Neural Repair 29:969–978
Bäumer T, Dammann E, Bock F, Klöppel S, Siebner H, Münchau A (2007) Laterality of interhemispheric inhibition depends on handedness. Exp Brain Res 180:195–203
Cardoso de Oliveira S (2002) The neuronal basis of bimanual coordination: recent neurophysiological evidence and functional models. Acta Psychol (Amst) 110:139–159
Carson RG (2005) Neural pathways mediating bilateral interactions between the upper limbs. Brain Res Rev 49:641–662. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainresrev.2005.03.005
Cattaert D, Semjen A, Summers JJ (1999) Simulating a neural cross-talk model for between-hand interference during bimanual circle drawing. Biol Cybern 81:343–358. https://doi.org/10.1007/s004220050567
Chen JT, Lin YY, Shan DE, Wu ZA, Hallett M, Liao KK (2005) Effect of transcranial magnetic stimulation on bimanual movements. J Neurophysiol 93:53–63. https://doi.org/10.1152/jn.01063.2003
Cohen RG, Sternad D (2009) Variability in motor learning: relocating, channeling and reducing noise. Exp Brain Res 193:69–83. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-008-1596-1
Cunningham DA, Roelle SM, Allexandre D et al (2017) The effect of motor overflow on bimanual asymmetric force coordination. Exp Brain Res 235:1097–1105
Daskalakis ZJ, Christensen BK, Fitzgerald PB, Roshan L, Chen R (2002) The mechanisms of interhemispheric inhibition in the human motor cortex. J Physiol 543:317–326
Davey NJ, Romaiguère P, Maskill DW, Ellaway PH (1994) Suppression of voluntary motor activity revealed using transcranial magnetic stimulation of the motor cortex in man. J Physiol 477:223–235
Diedrichsen J (2007) Optimal task-dependent changes of bimanual feedback control and adaptation. Current biology: CB 17:1675–1679. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2007.08.051
Diedrichsen J, Dowling N (2009) Bimanual coordination as task-dependent linear control policies. Hum Mov Sci 28:334–347. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.humov.2008.10.003
Diedrichsen J, Hazeltine E, Nurss WK, Ivry RB (2003) The role of the corpus callosum in the coupling of bimanual isometric force pulses. J Neurophysiol 90:2409–2418. https://doi.org/10.1152/jn.00250.2003
Duque J, Davare M, Delaunay L et al (2010) Monitoring coordination during bimanual movements: where is the mastermind? J Cogn Neurosci 22:526–542. https://doi.org/10.1162/jocn.2009.21213
Eliasziw M, Donner A (1991) Application of the McNemar test to non-independent matched pair data. Stat Med 10:1981–1991
Fisher RA (1915) Frequency distribution of the values of the correlation coefficient in samples from an indefinitely large population. Biometrika 10:507–521
Fisher RJ, Nakamura Y, Bestmann S, Rothwell JC, Bostock H (2002) Two phases of intracortical inhibition revealed by transcranial magnetic threshold tracking. Exp Brain Res 143:240–248. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-001-0988-2
Fling BW, Seidler RD (2012) Task-dependent effects of interhemispheric inhibition on motor control. Behav Brain Res 226:211–217. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbr.2011.09.018
Foltys H, Sparing R, Boroojerdi B, Krings T, Meister IG, Mottaghy FM, Topper R (2001) Motor control in simple bimanual movements: a transcranial magnetic stimulation and reaction time study. Clin Neurophysiol 112:265–274
Fox PT, Fox JM, Raichle ME, Burde RM (1985) The role of cerebral cortex in the generation of voluntary saccades: a positron emission tomographic study. J Neurophysiol 54:348–369
Gelfand IM, Latash ML (1998) On the problem of adequate language in motor control. Motor control 2:306–313
Grefkes C, Eickhoff SB, Nowak DA, Dafotakis M, Fink GR (2008) Dynamic intra- and interhemispheric interactions during unilateral and bilateral hand movements assessed with fMRI and DCM. Neuroimage 41:1382–1394. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2008.03.048
Haaland KY, Prestopnik JL, Knight RT, Lee RR (2004) Hemispheric asymmetries for kinematic and positional aspects of reaching. Brain J Neurol 127:1145–1158. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/awh133
Harris CM, Wolpert DM (1998) Signal-dependent noise determines motor planning. Nature 394:780–784. https://doi.org/10.1038/29528
Heuer H, Spijkers W, Steglich C, Kleinsorge T (2002) Parametric coupling and generalized decoupling revealed by concurrent and successive isometric contractions of distal muscles. Acta Psychol (Amst) 111:205–242
Hoffman JI (1976) The incorrect use of Chi-square analysis for paired data. Clin Exp Immunol 24:227–229
Ilic TV, Meintzschel F, Cleff U, Ruge D, Kessler KR, Ziemann U (2002) Short-interval paired-pulse inhibition and facilitation of human motor cortex: the dimension of stimulus intensity. J Physiol 545:153–167
Kagerer FA (2016) Asymmetric interference in left-handers during bimanual movements reflects switch in lateralized control characteristics. Exp Brain Res 234:1545–1553
Kang N, Cauraugh JH (2014) Bimanual force variability and chronic stroke: asymmetrical hand control. PLoS One 9:e101817. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0101817
Kantak S, McGrath R, Zahedi N (2016) Goal conceptualization and symmetry of arm movements affect bimanual coordination in individuals after stroke. Neurosci Lett 626:86–93. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neulet.2016.04.064
Kazennikov O, Perrig S, Wiesendanger M (2002) Kinematics of a coordinated goal-directed bimanual task. Behav Brain Res 134:83–91
Kelso JA (1984) Phase transitions and critical behavior in human bimanual coordination. Am J Physiol 246:R1000-1004
Kelso JA, Southard DL, Goodman D (1979) On the nature of human interlimb coordination. Science 203:1029–1031
Kennedy DM, Boyle JB, Wang C, Shea CH (2016) Bimanual force control: cooperation and interference? Psychol Res 80:34–54. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00426-014-0637-6
Kugler PN, Kelso JS, Turvey MT (1980) On the concept of coordinative structures as dissipative structures: I. Theoretical lines of convergence. Tutor Motor Behav 3:3–47
Kujirai T, Caramia MD, Rothwell JC et al (1993) Corticocortical inhibition in human motor cortex. J Physiol 471:501–519
Latash ML, Scholz JF, Danion F, Schoner G (2001) Structure of motor variability in marginally redundant multifinger force production tasks. Exp Brain Res 141:153–165. https://doi.org/10.1007/s002210100861
Latash ML, Scholz JP, Schoner G (2007) Toward a new theory of motor synergies. Motor control 11:276–308
Maki Y, Wong KF, Sugiura M, Ozaki T, Sadato N (2008) Asymmetric control mechanisms of bimanual coordination: an application of directed connectivity analysis to kinematic and functional MRI data. Neuroimage 42:1295–1304. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2008.06.045
Oldfield RC (1971) The assessment and analysis of handedness: the Edinburgh inventory. Neuropsychologia 9:97–113
Ortu E, Deriu F, Suppa A, Tolu E, Rothwell JC (2008) Effects of volitional contraction on intracortical inhibition and facilitation in the human motor cortex. J Physiol 586:5147–5159
Peper CE, Beek PJ, van Wieringen PC (1995) Frequency-induced phase transitions in bimanual tapping. Biol Cybern 73:301–309
Perez MA, Butler JE, Taylor JL (2014) Modulation of transcallosal inhibition by bilateral activation of agonist and antagonist proximal arm muscles. J Neurophysiol 111:405–414
Rossi S, Hallett M, Rossini PM, Pascual-Leone A (2009) Safety, ethical considerations, and application guidelines for the use of transcranial magnetic stimulation in clinical practice and research. Clin Neurophysiol 120:2008–2039. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clinph.2009.08.016
Rossini PM, Burke D, Chen R et al (2015) Non-invasive electrical and magnetic stimulation of the brain, spinal cord, roots and peripheral nerves: basic principles and procedures for routine clinical and research application. An updated report from an I.F.C.N. Committee. Clin Neurophysiol 126:1071–1107
Rothwell JC, Hallett M, Berardelli A, Eisen A, Rossini P, Paulus W (1999) Magnetic stimulation: motor evoked potentials. The International Federation of Clinical Neurophysiology. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 52:97–103
Sainburg RL (2002) Evidence for a dynamic-dominance hypothesis of handedness. Exp Brain Res 142:241–258. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-001-0913-8
Sainburg RL, Kalakanis D (2000) Differences in control of limb dynamics during dominant and nondominant arm reaching. J Neurophysiol 83:2661–2675
Sainburg R, Good D, Przybyla A (2013) Bilateral synergy: a framework for post-stroke rehabilitation. J Neurol Transl Neurosci 1:1025
Serrien DJ, Spapé MM (2009) The role of hand dominance and sensorimotor congruence in voluntary movement. Exp Brain Res 199:195–200
Serrien DJ, Cassidy MJ, Brown P (2003) The importance of the dominant hemisphere in the organization of bimanual movements. Hum Brain Mapp 18:296–305. https://doi.org/10.1002/hbm.10086
Shabbott BA, Sainburg RL (2008) Differentiating between two models of motor lateralization. J Neurophysiol 100:565–575. https://doi.org/10.1152/jn.90349.2008
Shmuelof L, Krakauer JW, Mazzoni P (2012) How is a motor skill learned? Change and invariance at the levels of task success and trajectory control. J Neurophysiol 108:578–594. https://doi.org/10.1152/jn.00856.2011
Silver NC, Dunlap WP (1987) Averaging correlation coefficients: should Fisher’s z transformation be used? J Appl Psychol 72:146
Stewart KC, Cauraugh JH, Summers JJ (2006) Bilateral movement training and stroke rehabilitation: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Neurol Sci 244:89–95
Stinear JW, Byblow WD (2004) An interhemispheric asymmetry in motor cortex disinhibition during bimanual movement. Brain Res 1022:81–87. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainres.2004.06.062
Stucchi N, Viviani P (1993) Cerebral dominance and asynchrony between bimanual two-dimensional movements. J Exp Psychol Hum Percept Perform 19:1200–1220
Swinnen SP (2002) Intermanual coordination: from behavioural principles to neural-network interactions. Nat Rev Neurosci 3:348–359. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrn807
Swinnen SP, Jardin K, Meulenbroek R (1996) Between-limb asynchronies during bimanual coordination: effects of manual dominance and attentional cueing. Neuropsychologia 34:1203–1213
Swinnen SP, Dounskaia N, Levin O, Duysens J (2001) Constraints during bimanual coordination: the role of direction in relation to amplitude and force requirements. Behav Brain Res 123:201–218
Tazoe T, Sasada S, Sakamoto M, Komiyama T (2013) Modulation of interhemispheric interactions across symmetric and asymmetric bimanual force regulations. Eur J Neurosci 37:96–104
Toyokura M, Muro I, Komiya T, Obara M (1999) Relation of bimanual coordination to activation in the sensorimotor cortex and supplementary motor area: analysis using functional magnetic resonance imaging. Brain Res Bull 48:211–217
Tseng YW, Scholz JP (2005) Unilateral vs. bilateral coordination of circle-drawing tasks. Acta Psychol (Amst) 120:172–198. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actpsy.2005.04.001
Tseng YW, Scholz JP, Galloway JC (2009) The organization of intralimb and interlimb synergies in response to different joint dynamics. Exp Brain Res 193:239–254. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-008-1616-1
Turvey MT (1990) Coordination. Am Psychol 45:938
Van Delden A, Peper CLE, Kwakkel G, Beek PJ (2012) A systematic review of bilateral upper limb training devices for poststroke rehabilitation. Stroke Res Treat 2012:972069. https://doi.org/10.1155/2012/972069
Vines BW, Nair D, Schlaug G (2008) Modulating activity in the motor cortex affects performance for the two hands differently depending upon which hemisphere is stimulated. Eur J Neurosci 28:1667–1673. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1460-9568.2008.06459.x
Viviani P, Perani D, Grassi F, Bettinardi V, Fazio F (1998) Hemispheric asymmetries and bimanual asynchrony in left- and right-handers. Exp Brain Res 120:531–536
Walsh RR, Small SL, Chen EE, Solodkin A (2008) Network activation during bimanual movements in humans. Neuroimage 43:540–553. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage
Wassermann EM (1998) Risk and safety of repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation: report and suggested guidelines from the International Workshop on the Safety of Repetitive Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation, June 5–7, 1996. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 108:1–16
Whitall J, Waller SM, Silver KH, Macko RF (2000) Repetitive bilateral arm training with rhythmic auditory cueing improves motor function in chronic hemiparetic stroke. Stroke 31:2390–2395
Yahagi S, Kasai T (1999) Motor evoked potentials induced by motor imagery reveal a functional asymmetry of cortical motor control in left-and right-handed human subjects. Neurosci Lett 276:185–188
Ziemann U, Hallett M (2001) Hemispheric asymmetry of ipsilateral motor cortex activation during unimanual motor tasks: further evidence for motor dominance. Clin Neurophysiol 112:107–113
Acknowledgements
We thank study participants who devoted their time and efforts in this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liao, Ww., Whitall, J., Barton, J.E. et al. Neural motor control differs between bimanual common-goal vs. bimanual dual-goal tasks. Exp Brain Res 236, 1789–1800 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-018-5261-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-018-5261-z