Abstract
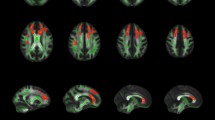
Study of bilingual brain has provided evidence for probable advantageous outcomes of early second language learning and brain structural correlates to these outcomes. DMRI connectometry is a novel approach that tracts fibers based on correlation of the adjacent voxels with a variable of interest or group differences. Using the data deposited by Pliatsikas et al., we investigated through diffusion MRI connectometry and correlation analysis, the structural differences in white matter tracts of 20 healthy sequential bilingual adults who used English as a second language on a daily basis, compared to 25 age matched in fiber differentiation analyses. Connectometry results revealed increased connectivity in corpus callosum (CC), bilateral cingulum, arcuate fasciculus (AF), and left IFOF of sequential bilingual adults. All the above fibers except cingulum had positive association with language immersion period. We introduce cingulum as a tract with increased connectivity in late bilingual adults. We also found an increase in white matter connectivity conventional language-related fibers such as AF, and areas that had been shown in previous studies addressing WM differences between early or late bilinguals and monolinguals, inferior frontooccipital fasciculus, and CC. Pliatsikas reported a confounding effect for the immersion period, as a regressor in TBSS model. Through DMRI connectometry and correlation analysis, we showed that quantitative anisotropy of all of the significant fibers from connectometry analysis, except cingulum, had direct correlation with the duration of immersion period of the bilingual group into the second language.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abutalebi J, Green D (2007) Bilingual language production: the neurocognition of language representation and control. J Neurolinguistics 20(3):242–275
Abutalebi J, Della Rosa PA, Green DW, Hernandez M, Scifo P, Keim R et al (2011) Bilingualism tunes the anterior cingulate cortex for conflict monitoring. Cereb Cortex 22(9):2076–2086
Abutalebi J, Canini M, Della Rosa PA, Sheung LP, Green DW, Weekes BS (2014) Bilingualism protects anterior temporal lobe integrity in aging. Neurobiol Aging 35(9):2126–2133
Abutalebi J, Canini M, Della Rosa PA, Green DW, Weekes BS (2015) The neuroprotective effects of bilingualism upon the inferior parietal lobule: a structural neuroimaging study in aging Chinese bilinguals. J Neurolinguistics 33:3–13
Almairac F, Herbet G, Moritz-Gasser S, de Champfleur NM, Duffau H (2015) The left inferior fronto-occipital fasciculus subserves language semantics: a multilevel lesion study. Brain Struct Funct 220(4):1983–1995
Bach M, Laun FB, Leemans A, Tax CMW, Biessels GJ, Stieltjes B et al (2014) Methodological considerations on tract-based spatial statistics (TBSS). NeuroImage 100:358–369
Benetti S, Pettersson-Yeo W, Allen P, Catani M, Williams S, Barsaglini A et al (2015) Auditory verbal hallucinations and brain dysconnectivity in the perisylvian language network: a multimodal investigation. Schizophr Bull 41(1):192–200
Binder JR, Desai RH, Graves WW, Conant LL (2009) Where is the semantic system? A critical review and meta-analysis of 120 functional neuroimaging studies. Cereb Cortex 19(12):2767–2796
Chang EF, Raygor KP, Berger MS (2015) Contemporary model of language organization: an overview for neurosurgeons. J Neurosurg 122(2):250–261
Cummine J, Boliek CA (2013) Understanding white matter integrity stability for bilinguals on language status and reading performance. Brain Struct Funct 218(2):595–601
Effects of bilingualism on brain structure and function (2015). https://central.xnat.org/app/template/XDATScreen_report_xnat_projectData.vm/search_element/xnat:projectData/search_field/xnat:projectData.ID/search_value/L2struc
García-Pentón L, Fernández García Y, Costello B, Duñabeitia JA, Carreiras M (2016) The neuroanatomy of bilingualism: how to turn a hazy view into the full picture. Lang Cognit Neurosci 31(3):303–327
Gold BT, Johnson NF, Powell DK (2013) Lifelong bilingualism contributes to cognitive reserve against white matter integrity declines in aging. Neuropsychologia 51(13):2841–2846
Hare TA, Camerer CF, Rangel A (2009) Self-control in decision-making involves modulation of the vmPFC valuation system. Science 324(5927):646–648
Hickok G, Poeppel D (2004) Dorsal and ventral streams: a framework for understanding aspects of the functional anatomy of language. Cognition 92(1–2):67–99
Hosoda C, Tanaka K, Nariai T, Honda M, Hanakawa T (2013) Dynamic neural network reorganization associated with second language vocabulary acquisition: a multimodal imaging study. J Neurosci 33(34):13663–13672
Jones DK, Symms MR, Cercignani M, Howard RJ (2005) The effect of filter size on VBM analyses of DT-MRI data. NeuroImage 26(2):546–554
Jones DK, Christiansen KF, Chapman RJ, Aggleton JP (2013) Distinct subdivisions of the cingulum bundle revealed by diffusion MRI fibre tracking: implications for neuropsychological investigations. Neuropsychologia 51(1):67–78
Kondo H, Osaka N, Osaka M (2004) Cooperation of the anterior cingulate cortex and dorsolateral prefrontal cortex for attention shifting. NeuroImage 23(2):670–679
Lebel C, Walker L, Leemans A, Phillips L, Beaulieu C (2008) Microstructural maturation of the human brain from childhood to adulthood. NeuroImage 40(3):1044–1055
Leech R, Sharp DJ (2014) The role of the posterior cingulate cortex in cognition and disease. Brain 137(1):12–32
Leemans A, Jeurissen B, Sijbers J, Jones D (eds) (2009) ExploreDTI: a graphical toolbox for processing, analyzing, and visualizing diffusion MR data. In: 17th annual meeting of intl soc mag reson med
Luk G, Bialystok E, Craik FI, Grady CL (2011) Lifelong bilingualism maintains white matter integrity in older adults. J Neurosci 31(46):16808–16813
Marques P, Soares JM, Alves V, Sousa N (2013) BrainCAT – a tool for automated and combined functional magnetic resonance imaging and diffusion tensor imaging brain connectivity analysis. Front Human Neurosci 7:794. doi:10.3389/fnhum.2013.00794
Mechelli A, Crinion JT, Noppeney U, O’Doherty J, Ashburner J, Frackowiak RS et al (2004) Neurolinguistics: structural plasticity in the bilingual brain. Nature 431(7010):757
Mohades SG, Struys E, Van Schuerbeek P, Mondt K, Van De Craen P, Luypaert R (2012) DTI reveals structural differences in white matter tracts between bilingual and monolingual children. Brain Res 1435:72–80
Mohades SG, Van Schuerbeek P, Rosseel Y, Van De Craen P, Luypaert R, Baeken C (2015) White-matter development is different in bilingual and monolingual children: a longitudinal DTI study. PLoS One 10(2):e0117968
Olulade OA, Jamal NI, Koo DS, Perfetti CA, LaSasso C, Eden GF (2016) Neuroanatomical evidence in support of the bilingual advantage theory. Cereb Cortex 26(7):3196–3204
Pliatsikas C, DeLuca V (2017) Immersive bilingualism reshapes the core of the brain. Brain Struct Funct 222(4):1785–1795
Pliatsikas C, Moschopoulou E, Saddy JD (2015) The effects of bilingualism on the white matter structure of the brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 112(5):1334–1337
Rauschecker JP (2012) Ventral and dorsal streams in the evolution of speech and language. Front Evol Neurosci 4:7
Ressel V, Pallier C, Ventura-Campos N, Diaz B, Roessler A, Avila C et al (2012) An effect of bilingualism on the auditory cortex. J Neurosci 32(47):16597–16601
Schlegel AA, Rudelson JJ, Tse PU (2012) White matter structure changes as adults learn a second language. J Cognit Neurosci 24(8):1664–1670
Tournier J-D, Mori S, Leemans A (2011) Diffusion tensor imaging and beyond. Magn Reson Med 65(6):1532–1556
Valian V (2015) Bilingualism and cognition. Bilingualism Lang Cognit 18(1):3–24
Yeh FC (2017). http://dsi-studio.labsolver.org/course/diffusion-mri-connectomics
Yeh F-C, Verstynen TD, Wang Y, Fernández-Miranda JC, Tseng W-YI (2013) Deterministic diffusion fiber tracking improved by quantitative anisotropy. PLoS One 8(11):e80713
Yeh FC, Badre D, Verstynen T (2016) Connectometry: a statistical approach harnessing the analytical potential of the local connectome. NeuroImage 125:162–171
Zalesky A (2011) Moderating registration misalignment in voxelwise comparisons of DTI data: a performance evaluation of skeleton projection. Magn Reson Imaging 29(1):111–125
Zou L, Ding G, Abutalebi J, Shu H, Peng D (2012) Structural plasticity of the left caudate in bimodal bilinguals. Cortex 48(9):1197–1206
Acknowledgements
This study was performed on diffusion MRI data deposited by Dr. Christos Pliatsikas at https://central.xnat.org/. We also thank Dr. Fang-Chen Yeh for instructions and the question bank provided on DMRI connectometry at http://dsi-studio.labsolver.org.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no potential conflict of interest, nor have received any financial assistance that could potentially confer any conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rahmani, F., Sobhani, S. & Aarabi, M.H. Sequential language learning and language immersion in bilingualism: diffusion MRI connectometry reveals microstructural evidence. Exp Brain Res 235, 2935–2945 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-017-5029-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-017-5029-x