Abstract
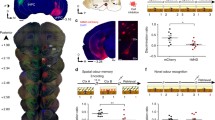
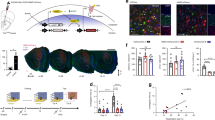
We examined the effects of hippocampal (HPC) damage on odour recognition memory, using a novel odour recognition task that was adapted from the more common novel object recognition task. Three separate experiments were conducted. In Experiment 1, we tested rats in novel odour recognition across different retention intervals (i.e. 15 min, 24 h, 1 week, 5 weeks). Given a single acquisition session, rats’ performance deteriorated after 24 h, but given multiple acquisition sessions (i.e. four sessions over 2 days), rats were able to perform well after retention intervals up to 5 weeks. In Experiment 2, we examined the possible anterograde amnesic effects of HPC damage on novel odour recognition, finding that pre-training damage to the entire HPC failed to cause amnesia for retention delays extending up to 5 weeks. In Experiment 3, we examined whether post-training HPC damage would cause retrograde amnesia, but failed to find any evidence of an impairment. The combined results suggest that the neural network supporting odour recognition is independent of the HPC.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bekinschtein P, Katche C, Slipczuk L et al (2010) Persistence of long-term memory storage: new insights into its molecular signatures in the hippocampus and related structures. Neurotox Res 18:377–385. doi:10.1007/s12640-010-9155-5
Broadbent NJ, Squire LR, Clark RE (2007) Rats depend on habit memory for discrimination learning and retention. Learn Mem 14:145–151. doi:10.1101/lm.455607
Broadbent NJ, Gaskin S, Squire LR, Clark RE (2010) Object recognition memory and the rodent hippocampus. Learn Mem 17:794–800. doi:10.1101/lm.1650110
Clark RE, Squire LR (2010) An animal model of recognition memory and medial temporal lobe amnesia: history and current issues. Neuropsychologia 48:2234–2244. doi:10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2010.02.004
Clark RE, Zola SM, Squire LR (2000) Impaired recognition memory in rats after damage to the hippocampus. J Neurosci 20:8853–8860
Clark RE, West AN, Zola SM, Squire LR (2001) Rats with lesions of the hippocampus are impaired on the delayed nonmatching-to-sample task. Hippocampus 11:176–186
Driscoll I, Howard SR, Prusky GT, Rudy JW, Sutherland RJ (2005) Seahorse wins all races: hippocampus participates in both linear and non-linear visual discrimination learning. Behav Brain Res 164:29–35
Ennaceur A, Delacour J (1988) A new one-trial test for neurobiological studies of memory in rats. 1: behavioral data. Behav Brain Res 31:47–59
Epp J, Keith JR, Spanswick SC, Stone JC, Prusky GT, Sutherland RJ (2008) Retrograde amnesia for visual memories after hippocampal damage in rats. Learn Mem 15:214–221. doi:10.1101/lm.788008
Feinberg LM, Allen TA, Ly D, Fortin NJ (2012) Recognition memory for social and non-social odors: differential effects of neurotoxic lesions to the hippocampus and perirhinal cortex. Neurobiol Learn Mem 97:7–16. doi:10.1016/j.nlm.2011.08.008
Frankland PW, Cestari V, Filipkowski RK, McDonald RJ, Silva AJ (1998) The dorsal hippocampus is essential for context discrimination but not for contextual conditioning. Behav Neurosci 112:863–874
Gaskin S, Tremblay A, Mumby DG (2003) Retrograde and anterograde object recognition in rats with hippocampal lesions. Hippocampus 13:962–969
Glenn MJ, Lehmann H, Mumby DG, Woodside B (2005) Differential fos expression following aspiration, electrolytic, or excitotoxic lesions of the perirhinal cortex in rats. Behav Neurosci 119:806–813
Hunsaker MR, Kesner RP (2008) Dissociations across the dorsal-ventral axis of CA3 and CA1 for encoding and retrieval of contextual and auditory-cued fear. Neurobiol Learn Mem 89:61–69. doi:10.1016/j.nlm.2007.08.016
Hunsaker MR, Fieldsted PM, Rosenberg JS, Kesner RP (2008) Dissociating the roles of dorsal and ventral CA1 for the temporal processing of spatial locations, visual objects, and odors. Behav Neurosci 122:643–650. doi:10.1037/0735-7044.122.3.643
Lehmann H, Carfagnini A, Yamin S, Mumby DG (2005) Context-dependent effects of hippocampal damage on memory in the shock-probe test. Hippocampus 15:18–25
Lehmann H, Lecluse V, Houle A, Mumby DG (2006) Retrograde amnesia following hippocampal lesions in the shock-probe conditioning test. Hippocampus 16:379–387
Lehmann H, Glenn MJ, Mumby DG (2007a) Consolidation of object-discrimination memory is independent of the hippocampus in rats. Exp Brain Res 180:755–764
Lehmann H, Lacanilao S, Sutherland RJ (2007b) Complete or partial hippocampal damage produces equivalent retrograde amnesia for remote contextual fear memories. Eur J Neurosci 25:1278–1286
Lehmann H, Sparks FT, O’Brien J, McDonald RJ, Sutherland RJ (2010) Retrograde amnesia for fear-potentiated startle in rats after complete, but not partial, hippocampal damage. Neuroscience 167:974–984. doi:10.1016/j.neuroscience.2010.03.005
Mahut H, Zola-Morgan S, Moss M (1982) Hippocampal resections impair associative learning and recognition memory in the monkey. J Neurosci 2:1214–1220
Manns JR, Hopkins RO, Reed JM, Kitchener EG, Squire LR (2003) Recognition memory and the human hippocampus. Neuron 37:171–180
Maren S (2001) Neurobiology of Pavlovian fear conditioning. Annu Rev Neurosci 24:897–931
Maren S (2008) Pavlovian fear conditioning as a behavioral assay for hippocampus and amygdala function: cautions and caveats. Eur J Neurosci 28:1661–1666. doi:10.1111/j.1460-9568.2008.06485.x
Maren S, Aharonov G, Fanselow MS (1997) Neurotoxic lesions of the dorsal hippocampus and Pavlovian fear conditioning in rats. Behav Brain Res 88:261–274
Martin SJ, de Hoz L, Morris RG (2005) Retrograde amnesia: neither partial nor complete hippocampal lesions in rats result in preferential sparing of remote spatial memory, even after reminding. Neuropsychologia 43:609–624
Mouton PR (2002) Principles and practices of unbiased stereology: an introduction for bioscientists. The Johns Hopkins University Press, Baltimore
Mumby DG, Astur RS, Weisend MP, Sutherland RJ (1999) Retrograde amnesia and selective damage to the hippocampal formation: memory for places and object discriminations. Behav Brain Res 106:97–107
Mumby DG, Gaskin S, Glenn MJ, Schramek TE, Lehmann H (2002) Hippocampal damage and exploratory preferences in rats: memory for objects, places, and contexts. Learn Mem 9:49–57
Mumby DG, Tremblay A, Lecluse V, Lehmann H (2005) Hippocampal damage and anterograde object-recognition in rats after long retention intervals. Hippocampus 15:1050–1056. doi:10.1002/hipo.20122
Mumby DG, Piterkin P, Lecluse V, Lehmann H (2007) Perirhinal cortex damage and anterograde object-recognition in rats after long retention intervals. Behav Brain Res 185:82–87. doi:10.1016/j.bbr.2007.07.026
O’Brien N, Lehmann H, Lecluse V, Mumby DG (2006) Enhanced context-dependency of object recognition in rats with hippocampal lesions. Behav Brain Res 170:156–162. doi:10.1016/j.bbr.2006.02.008
Parsons TC, Otto T (2010) Time-limited involvement of dorsal hippocampus in unimodal discriminative contextual conditioning. Neurobiol Learn Mem 94:481–487. doi:10.1016/j.nlm.2010.08.015
Reed JM, Squire LR (1997) Impaired recognition memory in patients with lesions limited to the hippocampal formation. Behav Neurosci 111:667–675
Rosenbaum RS, Kohler S, Schacter DL et al (2005) The case of K.C.: contributions of a memory-impaired person to memory theory. Neuropsychologia 43:989–1021. doi:10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2004.10.007
Rudy JW, Sutherland RJ (1989) The hippocampal formation is necessary for rats to learn and remember configural discriminations. Behav Brain Res 34:97–109
Rudy JW, Sutherland RJ (2008) Is it systems or cellular consolidation? Time will tell. An alternative interpretation of the Morris group’s recent science paper. Neurobiol Learn Mem 89:366–369. doi:10.1016/j.nlm.2007.07.017
Sparks FT, Lehmann H, Sutherland RJ (2011) Between-systems memory interference during retrieval. Eur J Neurosci 34:780–786. doi:10.1111/j.1460-9568.2011.07796.x
Sutherland RJ, Lehmann H (2011) Alternative conceptions of memory consolidation and the role of the hippocampus at the systems level in rodents. Curr Opin Neurobiol 21:446–451. doi:10.1016/j.conb.2011.04.007
Sutherland RJ, O’Brien J, Lehmann H (2008) Absence of systems consolidation of fear memories after dorsal, ventral, or complete hippocampal damage. Hippocampus
Tse D, Langston RF, Kakeyama M et al (2007) Schemas and memory consolidation. Science 316:76–82
Wible CG, Shiber JR, Olton DS (1992) Hippocampus, fimbria-fornix, amygdala, and memory: object discriminations in rats. Behav Neurosci 106:751–761
Winocur G (1990) Anterograde and retrograde amnesia in rats with dorsal hippocampal or dorsomedial thalamic lesions. Behav Brain Res 38:145–154
Winocur G, McDonald RM, Moscovitch M (2001) Anterograde and retrograde amnesia in rats with large hippocampal lesions. Hippocampus 11:18–26
Winters BD, Reid JM (2010) A distributed cortical representation underlies crossmodal object recognition in rats. J Neurosci: Off J Soc Neurosci 30:6253–6261. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.6073-09.2010
Winters BD, Saksida LM, Bussey TJ (2008) Object recognition memory: neurobiological mechanisms of encoding, consolidation and retrieval. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 32:1055–1070. doi:10.1016/j.neubiorev.2008.04.004
Winters BD, Saksida LM, Bussey TJ (2010) Implications of animal object memory research for human amnesia. Neuropsychologia 48:2251–2261. doi:10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2010.01.023
Acknowledgments
We thank NSERC for funding this research as well as Dr. Deborah Saucier in providing useful comments on an earlier draft of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Scott, G.A., Mtetwa, M. & Lehmann, H. Novel odour recognition memory is independent of the hippocampus in rats. Exp Brain Res 224, 199–209 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-012-3304-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-012-3304-4