Abstract
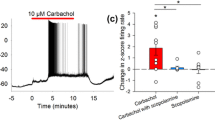
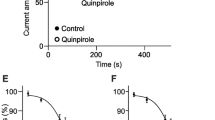
It is widely recognized that neuronal network activity can be modulated via activation of nicotinic and muscarinic acetylcholine receptors located pre- and postsynaptically. It was established in our earlier study that the activation of presynaptic nicotinic receptors greatly facilitates the retinotectal glutamatergic transmission. In the present study, we have determined a transmitter of tectal recurrent excitation and explored the effects of muscarinic acetylcholine receptor activation on the recurrent excitation and the activity of frog tectum column in vivo. Discharge of a single retinal ganglion cell was elicited by a minimal electrical stimulation of the retina. Evoked activity of the tectum column was recorded using the carbon-fiber microelectrode inserted into the tectum layer F. We found the following: 1. The recurrent excitation in the tectum column was not affected by d-tubocurarine (10 μM) and was greatly depressed by the kynurenic acid (500 μM), demonstrating glutamatergic nature of the recurrent excitation. 2. The glutamatergic recurrent excitation was largely reduced by carbamylcholine (100 μM) and oxotremorine-M (10 μM), demonstrating that the activation of muscarinic receptors, located, presumably, on the presynaptic terminals of recurrent pear-shaped neurons, inhibits the recurrent excitation in the tectum column. 3. The muscarinic inhibition of glutamatergic recurrent transmission had critical influence on the activity of the tectum column, preventing the generation of an output signal through suppression of the NMDA receptor activation and establishing necessary conditions for returning of the network to its resting state.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alaburda A, Perrier JF, Hounsgaard J (2002) Mechanisms causing plateau potentials in spinal motoneurones. Adv Exp Med Biol 508:219–226
Baginskas A, Kuras A (2008) Single retina ganglion cell evokes the activation of L-type Ca2+-mediated slow inward current in frog tectal pear-shaped neurons. Neurosci Res 60:412–421
Baginskas A, Kuras A (2009) L-type Ca2+ current in frog tectal recurrent neurons determines the NMDA receptor activation on efferent neuron. Exp Brain Res 193:509–517
Barral J, Galarraga E, Bargas J (1999) Muscarinic presynaptic inhibition of neostriatal glutamatergic afferents is mediated by Q-type Ca2 + channels. Brain Res Bull 49:285–289
Brown DA, Sihra TS (2008) Presynaptic signaling by heterotrimeric G-proteins. Handb Exp Pharmacol 184:207–260
Buno W, Cabezas C, Fernandez de Sevilla D (2006) Presynaptic muscarinic control of glutamatergic synaptic transmission. J Mol Neurosci 30:161–164
Butt CM, Pauly JR, Wilkins LH, Dwoskin LP, Debski EA (2001) Pharmacology, distribution and development of muscarinic acetylcholine receptor subtypes in the optic tectum of Rana pipiens. Neuroscience 104:161–179
Chung SH, Bliss TVP, Keating MJ (1974) The synaptic organization of optic afferents in the amphibian tectum. Proc Roy Soc B (Lond) 187:421–447
Dani JA, Bertrand D (2007) Nicotinic acetylcholine receptors and nicotinic cholinergic mechanisms of the central nervous system. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 47:699–772
Eggermann E, Feldmeyer D (2009) Cholinergic filtering in the recurrent excitatory microcircuit of cortical layer 4. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106:11753–11758
Ewert J-P, Hock FJ, von Wietersheim A (1974) Thalamus, praetectum, tectum: retinale topographie und physiologische interaktionen bei der Krote Bufo bufo (L). J Comp Physiol A 92:343–356
Fernandez de Sevilla D, Buno W (2003) Presynaptic inhibition of Schaffer collateral synapses by stimulation of hippocampal cholinergic afferent fibres. Eur J Neurosci 17:555–558
Forslid A, Ingvar M, Rosen I, Ingvar DH (1986) Carbon dioxide narcosis: influence of short-term high concentration carbon dioxide inhalation on EEG and cortical evoked responses in the rat. Acta Physiol Scand 127:281–287
George SA, Marks WB (1974) Optic nerve terminal arborizations in the frog: shape and orientation inferred from electrophysiological measurements. Exp Neurol 42:467–482
Giocomo LM, Hasselmo ME (2007) Neuromodulation by glutamate and acetylcholine can change circuit dynamics by regulating the relative influence of afferent input and excitatory feedback. Mol Neurobiol 36:184–200
Gutman AM, Kuras AV (1974) Studies on extracellular PSP of single afferent—the quantum of the EEG in tectum opticum of the frog (in Russian). Biofizika 19:894–898
Hamam BN, Sinai M, Poirier G, Chapman CA (2007) Cholinergic suppression of excitatory synaptic responses in layer II of the medial entorhinal cortex. Hippocampus 17:103–113
Hasselmo ME, Bower JM (1992) Cholinergic suppression specific to intrinsic not afferent fiber synapses in rat piriform (olfactory) cortex. J Neurophysiol 67:1222–1229
Hasselmo ME, Schnell E (1994) Laminar selectivity of the cholinergic suppression of synaptic transmission in rat hippocampal region CA1: computational modeling and brain slice physiology. J Neurosci 14:3898–3914
Hasselmo ME, Anderson BR, Bower JM (1992) Cholinergic modulation of cortical associative memory function. J Neurophysiol 67:1230–1246
Heckman CJ, Lee RH, Brownstone RM (2003) Hyperexcitable dendrites in motoneurons and their neuromodulatory control during motor behavior. Trends Neurosci 26:688–695
Hickmott PW, Constantine-Paton M (1993) The contributions of NMDA, non-NMDA, and GABA receptors to postsynaptic responses in neurons of the optic tectum. J Neurosci 13:4339–4353
Hounsgaard J (1978) Presynaptic inhibitory action of acetylcholine in area CA1 of the hippocampus. Exp Neurology 62:787–797
Hounsgaard J, Hultborn H, Jespersen B, Kiehn O (1988) Bistability of alpha-motoneurones in the decerebrate cat and in the acute spinal cat after intravenous 5-hydroxytryptophan. J Physiol 405:345–367
Hultborn H (2002) Plateau potentials and their role in regulating motoneuronal firing. Adv Exp Med Biol 508:213–218
Kimura F (2000) Cholinergic modulation of cortical function: a hypothetical role in shifting the dynamics in cortical network. Neurosci Res 38:19–26
King JG Jr, Lettvin JY, Gruberg ED (1999) Selective, unilateral, reversible loss of behavioral responses to looming stimuli after injection of tetrodotoxin or cadmium chloride into the frog optic nerve. Brain Res 841:20–26
Kremin T, Hasselmo ME (2007) Cholinergic suppression of glutamatergic synaptic transmission in hippocampal region CA3 exhibits laminar selectivity: Implication for hippocampal network dynamics. Neuroscience 149:760–767
Kremin T, Gerber D, Giocomo LM, Huang SY, Tonegawa S, Hasselmo ME (2006) Muscarinic suppression in stratum radiatum of CA1 shows dependence on presynaptic M1 receptors and is not dependent on effects at GABA(B) receptors. Neurobiol Learn Mem 85:153–163
Kuras A, Gutmaniene N (1995) Preparation of carbon-fibre microelectrode for extracellular recording of synaptic potentials. J Neurosci Methods 62:207–212
Kuras A, Gutmaniene N (1997) Multi-channel metallic electrode for threshold stimulation of frog’s retina. J Neurosci Methods 75:99–102
Kuras A, Gutmaniene N (2001) N-cholinergic facilitation of glutamate release from an individual retinotectal fiber in frog. Vis Neurosci 18:549–558
Kuras A, Baginskas A, Batuleviciene V (2004) Suprathreshold excitation of frog tectal neurons by short spike trains of single retinal ganglion cell. Exp Brain Res 159:509–518
Kuras A, Baginskas A, Batulevičiene V (2005) Suprathreshold excitation of network of frog tectal neurons by discharging of single retina moving-edge detector. Medicina 41:949–956
Kuras A, Baginskas A, Batuleviciene V (2006) Non-NMDA and NMDA receptors are involved in suprathreshold excitation of network of frog tectal neurons by a single retinal ganglion cell. Neurosci Res 54:328–337
Kuras A, Baginskas A, Batuleviciene V, Lamanauskas N (2007) Single retinal changing contrast (3rd) detector elicits NMDA receptor response and higher activity level of frog tectum neuron network. Exp Brain Res 179:209–217
Larimer P, Strowbridge BW (2010) Representing information in cell assemblies: persistent activity mediated by semilunar granule cells. Nat Neurosci 13:213–222
LeBeau FE, El Manira A, Griller S (2005) Tuning the network: modulation of neuronal microcircuits in the spinal cord and hippocampus. Trends Neurosci 28:552–561
Luscher H-R, Ruenzel PW, Henneman E (1983) Effects of impulse frequency, PTP, and temperature on responses elicited in large populations of motoneurons by impulse in single Ia-fibres. J Neurophysiol 50:1045–1058
Martoft L, Stodkilde-Jorgensen H, Forslid A, Pedersen HD, Jorgensen PF (2003) CO2 induced acute respiratory acidosis and brain tissue intracellular pH: a 31P NMR study in swine. Lab Anim 37:241–248
Maturana HR, Lettvin JY, McCulloch WS, Pitts WH (1960) Anatomy and physiology of vision in the frog (Rana pipiens). J Gen Physiol 43:129–175
Mike A, Castro NG, Albuquerque EX (2000) Choline and acetylcholine have similar kinetic properties of activation and desensitization on the alpha7 nicotinic receptors in rat hippocampal neurons. Brain Res 882:155–168
Mitsuda H, Ishida Y, Yoshikawa H, Ueno S (1988) Effects of high concentration of CO2 on electrocardiograms in the carp, Cyprinus carpio. Comp Biochem Physiol A 91:749–757
Nahir B, Bhatia C, Frazier CJ (2007) Presynaptic inhibition of excitatory afferents to hilar mossy cells. J Neurophysiol 97:4036–4047
Pakhotin P, Bracci E (2007) Cholinergic interneurons control the excitatory input to the striatum. J Neurosci 27:391–400
Qian J, Saggau P (1997) Presynaptic inhibition of synaptic transmission in the rat hippocampus by activation of muscarinic receptors: involvement of presynaptic calcium influx. Br J Pharmacol 122:511–519
Raastad M (1995) Extracellular activation of unitary excitatory synapses between hippocampal CA3 and CA1 pyramidal cells. Eur J Neurosci 7:1882–1888
Rogers M, Sargent PB (2003) Rapid activation of presynaptic nicotinic acetylcholine receptors by nerve-released transmitter. Eur J Neurosci 18:2946–2956
Scanziani M, Gahwiler BH, Thompson SM (1995) Presynaptic inhibition of excitatory synaptic transmission by muscarinic and metabotropic glutamate receptor activation in the hippocampus: are Ca2 + channels involved? Neuropharmacology 34:1549–1557
Schwindt P, Crill W (1980) Role of a persistent inward current in motoneuron bursting during spinal seizures. J Neurophysiol 43:1296–1318
Shen WX, Horn JP (1996) Presynaptic muscarinic inhibition in bullfrog sympathetic ganglia. J Physiol 491:413–421
Sim JA, Griffith WH (1996) Muscarinic inhibition of glutamatergic transmissions onto rat magnocellular basal forebrain neurons in a thin-slice preparation. Eur J Neurosci 8:880–891
Stern P, Edwards FA, Sakmann B (1992) Fast and slow components of unitary EPSCs on stellate cells elicited by focal stimulation in slices of rat visual cortex. J Physiol 449:247–278
Svirskis G, Hounsgaard J (1998) Transmitter regulation of plateau properties in Turtle Motoneurons. J Neurophysiol 79:45–50
Szekely G, Lazar G (1976) Cellular and synaptic architecture of the optic tectum. In: Llinas R, Precht W (eds) Frog neurobiology. Springer, Berlin, pp 406–433
Vogt KE, Regehr WG (2001) Cholinergic modulation of excitatory synaptic transmission in the CA3 area of the hippocampus. J Neurosci 21:75–83
Yajeya J, De La Fuente A, Criado JM, Bajo V, Sanchez-Riolobos A, Heredia M (2000) Muscarinic agonist carbachol depresses excitatory synaptic transmission in the rat basolateral amygdala in vitro. Synapse 38:151–160
Yu CJ, Debski EA (2003) The effects of nicotinic and muscarinic receptor activation on patch-clamped cells in the optic tectum of Rana pipiens. Neuroscience 118:135–144
Zhang HM, Chen SR, Pan HL (2007) Regulation of glutamate release from primary afferents and interneurons in the spinal cord by muscarinic receptor subtypes. J Neurophysiol 97:102–109
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Ministry of Education and Science of Lithuania.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Baginskas, A., Kuras, A. Muscarinic inhibition of recurrent glutamatergic excitation in frog tectum column prevents NMDA receptor activation on efferent neuron. Exp Brain Res 208, 323–334 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-010-2484-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-010-2484-z