Abstract
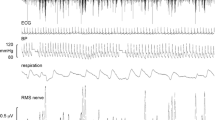
We have previously shown that sinusoidal galvanic vestibular stimulation (sGVS), a means of a selectively modulating vestibular afferent input without affecting other inputs, can cause partial entrainment of muscle sympathetic nerve activity (MSNA). Given that motion sickness causes sweating and pallor, we tested the hypothesis that sGVS also entrains skin sympathetic nerve activity (SSNA), but that the optimal frequencies are closer to those associated with slow postural changes (0.2 Hz). SSNA was recorded via tungsten microelectrodes inserted into the common peroneal nerve in 11 awake-seated subjects. Bipolar binaural sinusoidal GVS (±2 mA, 200 cycles) was applied to the mastoid processes at frequencies of 0.2, 0.5, 0.8, 1.1, 1.4, 1.7 and 2.0 Hz. All subjects reported strong postural illusions of ‘rocking in a boat’ or ‘swaying in a hammock’. Sinusoidal GVS caused a marked entrainment of SSNA at all frequencies. Measured as the modulation index, vestibular modulation ranged from 81.5 ± 4.0% at 0.2 Hz to 76.6 ± 3.6% at 1.7 Hz; it was significantly weaker at 2.0 Hz (63.2 ± 5.4%). Interestingly, pulse-related modulation of SSNA, which is normally weak, increased significantly during sGVS but was stronger at 0.8 Hz (86.2 ± 2.0%) than at 0.2 Hz (69.3 ± 8.3%), the opposite of the pattern seen with vestibular modulation of MSNA. We conclude that vestibular inputs can entrain the firing of cutaneous sympathetic neurones and increase their normally weak pulse-related rhythmicity.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bent LR, Bolton PS, Macefield VG (2006) Modulation of muscle sympathetic bursts by sinusoidal galvanic vestibular stimulation in human subjects. Exp Brain Res 174:701–711
Biaggioni I, Costa F, Kaufmann H (1998) Vestibular influences on autonomic cardiovascular control in humans. J Vest Res 8:35–41
Bini G, Hagbarth K-E, Wallin BG (1981) Cardiac rhythmicity of skin sympathetic activity recorded from peripheral nerves in man. J Auton Nerv System 4:17–24
Blessing WW, Nalivaiko E (2001) Raphe magnus/pallidus neurons regulate tail but not mesenteric arterial blood flow in rats. Neurosci 105:923–929
Bolton PS, Wardman DL, Macefield VG (2004) Absence of short-term vestibular modulation of muscle sympathetic outflow, assessed by brief galvanic vestibular stimulation in human subjects. Exp Brain Res 154:39–43
Carter JR, Ray CA (2008) Sympathetic responses to vestibular activation in humans. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 294:R681–R688
Cathers I, Day BL, Fitzpatrick RC (2005) Otolith and canal reflexes in human standing. J Physiol 563:229–234
Costa F, Lavin P, Robertson D, Biaggioni I (1995) Effect of neurovestibular stimulation on autonomic regulation. Clin Auton Res 5:289–293
Cui J, Mukai C, Iwase S, Sawasaki N, Kitazawa H, Mano T, Sugiyama Y, Wada Y (1997) Response to vestibular stimulation of sympathetic outflow to muscle in humans. Response to vestibular stimulation of sympathetic outflow to muscle in humans. J Auton Nerv Syst 66:154–162
Cui J, Iwase S, Mano T, Katayama N, Mori S (1999) Muscle sympathetic nerve response to vestibular stimulation by sinusoidal linear acceleration in humans. Neurosci Lett 267:181–184
Cui J, Iwase S, Mano T, Katayama N, Mori S (2001) Muscle sympathetic outflow during horizontal linear acceleration in humans. Am J Physiol 281:R625–R634
Dampney RA, Horiuchi J, Tagawa T, Fontes MA, Potts PD, Polson JW (2003a) Medullary and supramedullary mechanisms regulating sympathetic vasomotor tone. Acta Physiol Scand 177:209–218
Dampney RA, Polson JW, Potts PD, Hirooka Y, Horiuchi J (2003b) Functional organization of brain pathways subserving the baroreceptor reflex: studies in conscious animals using immediate early gene expression. Cell Mol Neurobiol 23:597–616
Delius W, Hagbarth K-E, Hongell A, Wallin BG (1972) Manouevres affecting sympathetic outflow in human skin nerves. Acta Physiol Scand 84:177–186
Dodt C, Gunarsson T, Elam M, Karlsson T, Wallin BG (1995) Influence of cardiopulmonary receptors on sympathetic sudomotor nerve traffic in humans. Acta Physiol Scand 155:41–51
Fitzpatrick RC, Day BL (2004) Probing the human vestibular system using galvanic stimulation. J Appl Physiol 96:2301–2316
Grewal T, James C, Macefield VG (2009) Frequency-dependent modulation of muscle sympathetic nerve activity by sinusoidal galvanic vestibular stimulation in human subjects. Exp Brain Res 197:379–386
Hume KM, Ray CA (1999) Sympathetic responses to head-down rotations in humans. J Appl Physiol 86:1971–1976
Jian BJ, Acernese AW, Lorenzo J, Card JP, Yates BJ (2005) Afferent pathways to the region of the vestibular nuclei that participates in cardiovascular and respiratory control. Brain Res 1044:241–250
Kaufmann H, Biaggioni I, Voustianiouk A, Diedrich A, Costa F, Clarke R, Gizzi M, Raphan T, Cohen B (2002) Vestibular control of sympathetic activity. An otolith-sympathetic reflex in humans. Exp Brain Res 143:463–469
Kerman IA, Yates BJ, McAllen RM (2000) Anatomic patterning in the expression of vestibulosympathetic reflexes. Am J Physiol 279:R109–R117
Lobel E, Kleine JF, Bihan DL, Leroy-Willig A, Berthoz A (1998) Functional MRI of galvanic vestibular stimulation. J Neurophysiol 80:2699–2709
Macefield VG, Wallin BG (1996) The discharge behaviour of single sympathetic neurones supplying human sweat glands. J Auton Nerv Syst 61:277–286
Macefield VG, Wallin BG (1999) Respiratory and cardiac modulation of single vasoconstrictor and sudomotor neurones to human skin. J Physiol 516:303–314
McAllen RM, Farrell M, Johnson JM, Trevaks D, Cole L, McKinley MJ, Jackson G, Denton DA, Egan GF (2006) Human medullary responses to cooling and rewarming the skin: a functional MRI study. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103:809–813
Ray CA (2000) Interaction of the vestibular system and baroreflexes on sympathetic nerve activity in humans. Am J Physiol 279:H2399–H2404
Ray CA, Hume KM, Steele SL (1998) Sympathetic nerve activity during natural stimulation of horizontal semicircular canals in humans. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 275:R1274–R1278
Ruggiero DA, Underwood MD, Mann JJ, Anwar M, Arango V (2000) The human nucleus of the solitary tract: visceral pathways revealed with an “in vitro” postmortem tracing method. J Auton Nerv Syst 79:181–190
Shortt TL, Ray CA (1997) Sympathetic and vascular responses to head-down neck flexion in humans. Am J Physiol 272:H1780–H1784
Stephan T, Deutschländer A, Nolte A, Schneider E, Wiesmann M, Brandt T, Dieterich M (2005) Functional MRI of galvanic vestibular stimulation with alternating currents at different frequencies. Neuroimage 26:721–732 (epub 2005 Apr 20)
Voustianiouk A, Kaufmann H, Diedrich A, Raphan T, Biaggioni I, MacDougall H, Ogorodnikov D, Cohen B (2006) Electrical activation of the human vestibulo-sympathetic reflex. Exp Brain Res 171:251–261
Wardman DL, Fitzpatrick RC (2002) What does galvanic vestibular stimulation stimulate? Adv Exp Biol Med 508:119–128
Yates BJ, Miller AD (1994) Properties of sympathetic reflexes elicited by natural vestibular stimulation: implications for cardiovascular control. J Neurophysiol 71:2087–2092
Yates BJ, Yamagata Y, Bolton PS (1991) The ventrolateral medulla of the cat mediates vestibulosympathetic reflexes. Brain Res 552:265–272
Yates BJ, Goto T, Bolton PS (1993) Responses of neurons in the rostral ventrolateral medulla of the cat to natural vestibular stimulation. Brain Res 601:255–264
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
James, C., Stathis, A. & Macefield, V.G. Vestibular and pulse-related modulation of skin sympathetic nerve activity during sinusoidal galvanic vestibular stimulation in human subjects. Exp Brain Res 202, 291–298 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-009-2131-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-009-2131-8