Abstract
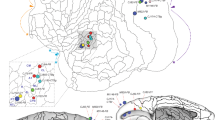
Neurophysiological studies have recently documented multisensory properties in ‘unimodal’ visual neurons of the cat posterolateral lateral suprasylvian (PLLS) cortex, a retinotopically organized area involved in visual motion processing. In this extrastriate visual area, a region has been identified where both visual and auditory stimuli were independently effective in activating neurons (bimodal zone), as well as a second region where visually-evoked activity was significantly facilitated by concurrent auditory stimulation but was unaffected by auditory stimulation alone (subthreshold multisensory region). Given their different distributions, the possible corticocortical connectivity underlying these distinct forms of crossmodal convergence was examined using biotinylated dextran amine (BDA) tracer methods in 21 adult cats. The auditory cortical areas examined included the anterior auditory field (AAF), primary auditory cortex (AI), dorsal zone (DZ), secondary auditory cortex (AII), field of the rostral suprasylvian sulcus (FRS), field anterior ectosylvian sulcus (FAES) and the posterior auditory field (PAF). Of these regions, the DZ, AI, AII, and FAES were found to project to the both the bimodal zone and the subthreshold region of the PLLS. This convergence of crossmodal inputs to the PLLS suggests not only that complex auditory information has access to this region but also that these connections provide the substrate for the different forms (bimodal versus subthreshold) of multisensory processing which may facilitate its functional role in visual motion processing.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allman BL, Meredith MA (2007) Multisensory processing in “unimodal” neurons: cross-modal subthreshold auditory effects in cat extrastriate visual cortex. J Neurophysiol 98:545–549
Allman BL, Keniston LP, Meredith MA (2008a) Sensory requirements for subthreshold multisensory processing: sensitivity to parametric changes in stimulus quality and position. Brain Res. doi:10.1016/brainres.2008.03.086
Allman BL, Bittencourt-Navarrete RE, Keniston LP, Medina A, Wang MY, Meredith MA (2008b) Do cross-modal projections always result in multisensory integration? Cerebral Cortex. doi:10.1093/cercor/bhm230
Clarey JC, Irvine DR (1986) Auditory response properties of neurons in the anterior ectosylvian sulcus of the cat. Brain Res 386:12–19
Clemo HR, Meredith MA (2004) Cortico-cortical relations of cat somatosensory areas SIV and SV. Somatosens Mot Res 21:199–209
Clemo HR, Allman BL, Meredith MA (2006) Multiple sensory representations in the cat rostral suprasylvian sulcal cortex. Soc Neurosci Abstr 36: 639.12
Clemo HR, Allman BL, Donlan MA, Meredith MA (2007a) Sensory and multisensory representations within the cat rostral suprasylvian cortex. J Comp Neurol 503:110–127
Clemo HR, Sharma GK, Allman BL, Meredith MA (2007b) Crossmodal connections underlying subthreshold multisensory processing: auditory cortical projections to extrastriate visual cortex in cat. Soc Neurosci Abstr 37: 614.13
Dehner LR, Keniston LP, Clemo HR, Meredith MA (2004) Cross-modal circuitry between auditory and somatosensory areas of the cat anterior ectosylvian sulcal cortex: a ‘new’ inhibitory form of multisensory convergence. Cereb Cortex 14:387–403
Falchier A, Clavagnier S, Barone P, Kennedy H (2002) Anatomical evidence of multimodal integration in primate striate cortex. J Neurosci 22:5749–5759
Ghazanfar AA, Schroeder CE (2006) Is neocortex essentially multisensory? Trends Cogn Sci 10:278–285
Grant S, Shipp S (1991) Visuotopic organization of the lateral suprasylvian area and of an adjacent area of the ectosylvian gyrus of cat cortex: a physiological and connectional study. Vis Neurosci 6:315–338
Hardy SC, Stein BE (1988) Small lateral suprasylvian cortex lesions produce visual neglect and decreased visual activity in the superior colliculus. J Comp Neurol 273:527–542
He J, Hashikawa T (1998) Connections of the dorsal zone of cat auditory cortex. J Comp Neurol 400:334–348
He J, Hashikawa T, Ojima H, Kinouchi Y (1997) Temporal integration and duration tuning in the dorsal zone of cat auditory cortex. J Neurosci 17:2615–2625
Heath CJ, Jones EG (1971) The anatomical organization of the suprasylvian gyrus of the cat. Ergeb Anat Entwicklungsgesch 45:3–64
Keniston L, Henderson SC, Meredith MA (2006) Confocal identification of multisensory convergence on cortical neurons in cat. Soc Neurosci Abstr 36: 137.18
Las L, Shapira AH, Nelken I (2008) Functional gradients of auditory sensitivity along the anterior ectosylvian sulcus of the cat. J Neurosci 28:3657–3667
Malhotra S, Lomber SG (2007) Sound localization during homotopic and heterotopic bilateral cooling deactivation of primary and nonprimary auditory cortical areas in the cat. J Neurophysiol 97:26–43
Malhotra S, Hall AJ, Lomber SG (2004) Cortical control of sound localization in the cat: unilateral cooling deactivation of 19 cerebral areas. J Neurophysiol 92:1625–1643
Meredith MA, Keniston LR, Dehner LR, Clemo HR (2006) Crossmodal projections from somatosensory area SIV to the auditory field of the anterior ectosylvian sulcus (FAES) in cat: further evidence for subthreshold forms of multisensory processing. Exp Brain Res 172:472–484
Middlebrooks JC, Dykes RW, Merzenich MM (1980) Binaural response-specific bands in primary auditory cortex (AI) of the cat: topographical organization orthogonal to isofrequency contours. Brain Res 181:31–48
Middlebrooks JC, Clock AE, Xu L, Green DM (1994) A panoramic code for sound location by cortical neurons. Science 264:842–844
Norita M, Kase M, Hoshino K, Meguro R, Funaki S, Hirano S, McHaffie JG (1996) Extrinsic and intrinsic connections of the cat’s lateral suprasylvian visual area. Prog Brain Res 112:231–250
Palmer LA, Rosenquist AC, Tusa RJ (1978) Retinotopic organization of lateral suprasylvian visual areas in cat. J Comp Neurol 177:237–256
Raczkowski D, Rosenquist AC (1983) Connections of the multiple visual cortical areas with the lateral posterior-pulvinar complex and adjacent thalamic nuclei in the cat. J Neurosci 10:1912–1942
Rauschecker JP, von Grunau MW, Poulin C (1987) Centrifugal organization of direction preferences in the cat’s lateral suprasylvian visual cortex and its relation to flow field processing. J Neurosci 7:943–958
Reale RA, Imig TJ (1980) Tonotopic organization in auditory cortex of the cat. J Comp Neurol 192:265–291
Robitaille N, Lepore F, Bacon BA, Ellemberg D, Guillemot JP (2008) Receptive field properties and sensitivity to edges defined by motion in the postero-lateral lateral suprasylvian (PLLS) area of the cat. Brain Res 1187:82–94
Rockland KS, Ojima H (2003) Multisensory convergence in calcarine visual areas in macaque monkey. Int J Psychophysiol 50:19–26
Rouiller EM, Simm GM, Villa AE, de Ribaupierre Y, de Ribaupierre F (1991) Auditory corticocortical interconnections in the cat: evidence for parallel and hierarchical arrangement of the auditory cortical areas. Exp Brain Res 86:483–505
Schreiner CE, Cynader MS (1984) Basic functional organization of second auditory cortical field (AII) of the cat. J Neurophysiol 51:1284–1305
Sherk H (1986) Location and connections of visual cortical areas in the cat’s suprasylvian sulcus. J Comp Neurol 247:1–31
Shore SE, Vass Z, Wys NL, Altschuler RA (2000) Trigeminal ganglion innervates the auditory brainstem. J Comp Neurol 419:271–285
Spear PD, Miller S, Ohman L (1983) Effects of lateral suprasylvian visual cortex lesions on visual localization, discrimination, and attention in cats. Behav Brain Res 10:339–359
Stecker GC, Harrington IA, Macpherson EA, Middlebrooks JC (2005) Spatial sensitivity in the dorsal zone (area DZ) of cat auditory cortex. J Neurophysiol 94:1267–1280
Symonds LL, Rosenquist AC (1984) Corticocortical connections among the visual areas in the cat. J Comp Neurol 229:1–38
van der Gucht E, Vandesande F, Arckens L (2001) Neurofilament protein: a selective marker for the architectonic parcellation of the visual cortex in adult cat brain. J Comp Neurol 441:345–368
Veenman CL, Reiner A, Honig MG (1992) Biotinylated dextran amine as an anterograde tracer for single- and double-labeling studies. J Neurosci Methods 41:239–254
Yaka R, Notkin N, Yinon U, Wollberg Z (2002) Visual, auditory and bimodal activity in the banks of the lateral suprasylvian sulcus in the cat. Neurosci Behav Physiol 32:103–108
Acknowledgments
We thank Les Keniston for excellent technical assistance. Supported by NIH Grant NS39460 to MAM and by NIH-NINDS Center Core Grant to VCU Anatomy and Neurobiology Microscopy Facility.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ruth Clemo, H., Sharma, G.K., Allman, B.L. et al. Auditory projections to extrastriate visual cortex: connectional basis for multisensory processing in ‘unimodal’ visual neurons. Exp Brain Res 191, 37–47 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-008-1493-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-008-1493-7