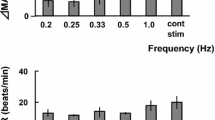
Abstract
The aim of the present study is to investigate the effect of somatostatin (SST). It is well known that SST is a neuromodulator in the central nervous system and is involved in the regulation of metabolic and neuroendocrine functions. Recent experimental and clinical findings indicate a role for SST in the central processing of nociception. Therefore, we tested the hypothesis whether a local release of SST modulates the tooth-pulp (TP)-evoked upper cervical spinal dorsal horn (C1) neuronal activity, using microiontophoretic application and immunohistochemical techniques. Extracelluar single unit recordings were made from 35 C1 neurons responding to TP electrical stimulation (TPS) in pentobarbital anesthetized rats. Microiontophoretic application of SST (30-70 nA) current dependently inhibited TP-evoked C1 neuronal discharges (60%, 21/35). The inhibition of this discharge by 50 nA SST application was abolished by co-application of a SST2 receptor antagonist (Cyanamid-154806, 50 nA). Immunoreactivity for SST2A receptor was found in the superficial layer (Ι–ΙΙΙ) of C1 dorsal horn. These results suggest that a local release of SST modulates the TP-evoked C1 neuronal activity and this may contribute to a useful therapeutic target for the alleviation of tooth pain and trigeminal hyperalgesia.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bartsch T, Levy MJ, Knight YE, Goadsby PJ (2005) Inhibition of nociceptive dural input in the trigeminal nucleus caudalis by somatostatin receptor blockade in the posterior hypothalamus. Pain 117:30–39
Bass RT, Buckwalter BL, Patel BP, Pausch MH, Price LA, Strnad J, Hadcock JR (1996) Identification and characterization of novel somatostatin antagonists. Mol Pharmacol 50(4):709–715
Bassant MH, Simon A, Poindessous-Jazat F, Csaba Z, Epelbaum J, Dournaud P (2005) Medial septal GABAergic neurons express the somatostatin sst2A receptor: functional consequences on unit firing and hippocampal theta. J Neurosci 25:2032–2041
Bereiter DA (1997) Morphine and somatostatin analogue reduce c-Fos expression in trigeminal subnucleus caudalis produced by corneal stimulation in the rat. Neuroscience 77:863–874
Carlton SM, Du J, Davidson E, Zhou S, Coggeshall RE (2001) Somatostatin receptors on the peripheral primary afferent terminals:inhibition of sensitized nociceptors. Pain 90:233–244
Dal Monte M, Petrucci C, Cozzi A, Allen JP, Bagnoli P (2003) Somatostatin inhibits potassium-evoked glutamate release by activation of the sst2 somtatostatin receptor in the mouse retina. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 367:188–192
Epelbaum J, Dournaud P, Fodor M, Viollet C (1994) The neurobiology of somatostatin. Crit Rev Neurobiol 8:25–44
Eschalier A, Aumaitre O, Ardid D, Fialip J, Duchene-Marullaz P (1991) Long-lasting antinociceptive effect of RC-160, a somatostatin analog, in mice and rats. Eur J Pharmacol 199:119–121
Hoyer D, Bell GI, Berelowitz M, Epelbaum J, Feniuk W, Humphrey PP, O’Carroll AM, Patel YC, Schonbrunn A, Taylor JE, Reisine T (1995) Classification and nomenclature of somatostatin receptors. Trends Pharmacol Sci 16:86–88
Ichikawa H, Schulz S, Hollt V, Sugimoto T (2003) The somatostatin sst2A receptor in the rat trigeminal ganglion. Neuroscience 120:807–813
Jiang N, Furue H, Katafuchi T, Yoshimura M (2003) Somatostatin directly inhibits substantia gelatinosa neurons in adult rat spinal dorsal horn in vitro. Neurosci Res 47:97–107
Knight Y, Bartsch T, Kaube H, Goadsby PJ (2002) P/Q-type calcium channel blockade in the periaqueductal gray facilitates trigeminal nociception: a functional genetic link for migraine? J Neurosci 22:RC213
Matharu MS, Levy MJ, Meeran K, Goadsby PJ (2004) Subcutaneous octreotide in cluster headache: randomized placebo-controlled double-blind crossover study. Ann Neurol 56:488–494
Matsumoto S, Takeda M, Tanimoto T (1999) Effects of electrical stimulation of the tooth pulp and phrenic nerve fibers on C1 spinal neurons in the rat. Exp Brain Res 126:351–358
Matucci-Cerinic M, Borrelli F, Generini S, Cantelmo A, Marcucci I, Martelli F, Romagnoli P, Bacci S, Conz A, Marinelli P, Marabini S (1995) Somatostatin-induced modulation of inflammation in experimental arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 38(11):1687–1693
Nishikawa T, Takeda M, Tanimoto T, Matsumoto S (2004) Convergence of nociceptive information from temporomandibular joint and tooth pulp afferents on C1 spinal neurons in the rat. Life Sci 75(12):1465–1478
Oshima K, Takeda M, Tanimoto T, Katsuumi I, Matsumoto S (2005) Tooth-pulp-evoked rostral spinal trigeminal nucleus neuron activity is inhibited by conditioning sciatic nerve stimulation in the rat: possible role of 5-HT3 receptor mediated GABAergic inhibition. Brain Res Bull 65(1):31–40
Oshima K, Takeda M, Tanimoto T, Katsuumi I, Matsumoto S (2006) Tooth-pulp-evoked rostral spinal trigeminal neuronal excitation is attenuated by the activation of 5-HT3 receptors via GABAergic interneurons in the rat. Brain Res 1109(1):70–73
Patel YC (1999) Somatostatin and its receptor family. Front Neuroendocrinol 20:157–198
Pawlak M, Schmidt RF (2004) Octreotide, a somatostatin analogue, attenuates movement evoked discharges of fine afferent units from inflamed knee joints of rats. Neurosci Lett 361(1–3):180–183
Pintér E, Helyes Z, Szolcsányi J (2006) Inhibitory effect of somatostatin on inflammation and nociception. Pharmacol Ther 112:440–456
Randic M, Miletic V (1978) Depressant actions of methionine-enkephalin and somatostatin in cat dorsal horn neurones activated by noxious stimuli. Brain Res 152:196–202
Reubi JC, Waser B, Markusse HM, Krenning EP, VanHagen M, Laissue JA (1994) Vascular somatostatin receptors in synovium from patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Eur J Pharmacol 271(2–3):371–378
Selmer I, Schinder M, Allen JP, Humphrey PP, Emson PC (2000) Advances in understanding neuronal somatostatin receptors. Regul Pept 90:1–18
Takeba Y, Suzuki N, Takeno M, Asai T, Tsuboi S, Hoshino T, Sakane T (1997) Modulation of synovial cell function by somatostatin in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 40(12):2128–2138
Takeda M, Tanimoto T, Ito M, Nasu M, Matsumoto S (2005) Role of capsaicin-sensitive afferent inputs from the masseter muscle in the C1 spinal neurons responding to tooth-pulp stimulation in rats. Exp Brain Res 160:107–117
Takeda M, Kadoi J, Takahashi M, Nasu M, Matsumoto S (2007) Somatostatin inhibit the excitability of rat small-diameter trigeminal ganglion neurons that innervate nasal mucosa and project to the upper cervical dorsal horn via activation of somatostatin 2a receptor. Neuroscience 148(3):744–756
Tanimoto T, Takeda M, Matsumoto S (2002) Suppressive effect of vagal afferents on cervical dorsal horn neurons responding to tooth pulp electrical stimulation in the rat. Exp Brain Res 145(4):468–479
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Takahashi, M., Takeda, M. & Matsumoto, S. Somatostatin inhibits tooth-pulp-evoked rat cervical dorsal horn neuronal activity. Exp Brain Res 184, 617–622 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-007-1261-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-007-1261-0