Abstract
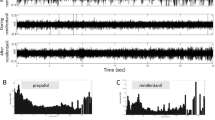
In Parkinson’s disease, the subthalamic nucleus (STN) is a common target for functional neurosurgery. Recent investigations have suggested that physiological non-motor stimuli may dramatically alter STN firing properties. By maintaining long-lasting micro-recordings of STN single units in Parkinson’s disease (PD) patients, here we show that the neurons that are responsive to passive movements are also strongly modulated by altered vigilance state (awake vs. sleep). In addition, sleep was characterized by a distinctive irregular train-like firing pattern. These findings suggest that the reduction of the somato-sensory input modifies rigidity and, hence, STN discharge mode. Further, it is suggested that specific STN electrophysiological features are potential targets for future therapeutic interventions.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baunez C, Dias C, Cador M, Amalric M (2005) The subthalamic nucleus exerts opposite control on cocaine and ‘natural’ rewards. Nat Neurosci 8:484–489
Benedetti F, Colloca L, Torre E, Lanotte M, Melcarne A, Pesare M, Bergamasco B,Lopiano L (2004) Placebo-responsive Parkinson patients show decreased activity in single neurons of subthalamic nucleus. Nat Neurosci 7:587–588
Bergman H, Wichmann T, Karmon B, DeLong MR (1994) The primate subthalamic nucleus. II. Neuronal activity in the MPTP model of parkinsonism. J Neurophysiol 72:507–520
Cicolin A, Lopiano L, Zibett M, Torre E, Tavella A, Guastamacchia G, Terreni A, Makrydakis G, fattori E, Lanotte MM, Bergamasco B, Mutani R (2004) Effects of deep brain stimulation of the subthalamic nucleus on sleep architecture in parkinsonian patients. Sleep Med 5:207–210
Do MT, Bean BP (2003) Subthreshold sodium currents and pacemaking of subthalamic neurons: modulation by slow inactivation. Neuron 39:109–120
Kaneoke Y, Vitek JL (1996) Burst and oscillation as disparate neuronal properties (1996). J Neurosci Methods 68:211–223
Levy R, Dostrovsky JO, Lang AE, Sime E, Hutchison WD, Lozano AM (2001) Effects of apomorphine on subthalamic nucleus and globus pallidus internus neurons in patients with Parkinson’s disease. J Neurophysiol 86:249–260
Magill PJ, Bolam JP, Bevan MD (2000) Relationship of activity in the subthalamic nucleus-globus pallidus network to cortical electroencephalogram. J Neurosci 20:820–833
Monaca C, Ozsancak C, Kacquesson JM, Poirot I, Blond S, Destee A, Guieu JD, Derambure P (2004) Effects of bilateral subthalamic stimulation on sleep in parkinson’s disease. J Neurol 251:214–218
Peppe A, Pierantozzi M, Bassi A, Altibrandi MG, Brusa L, Stefani A, Stanzione P, Mazzone P (2004) Stimulation of the subthalamic nucleus compared with the globus pallidusinternus in patients with Parkinson disease. J Neurosurg 101:195–200
Pierantozzi M, Sabato AF, Leonardis F, Marciani MG, Cicardi C, Giacomini P, Bernardi G, Stanzione P (2000) Curariform peripheral block of muscular tone selectively increases precentral N30 somatosensory evoked potentials component. A pharmacological study carried out on healthy subjects and parkinsonian syndromes. Exp Brain Res 133:368–376
Rossini PM, Babiloni F, Bernardi G, Cecchi L, Johnson PB, Malentacca A, Stanzione P, Urbano A (1989) Abnormalities of short-latency somatosensory evoked potentials in parkinsonian patients. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 74:277–289
Schroeder U, Kuehler A, Haslinger B, Erhard P. Fogel W, Tronnier VM, Lange KW, Boecker H, Ceballos-Baumann (2002) Subthalamic nucleus stimulation affects striato-anterior cingulate cortex circuit in a response conflict task: a PET study. Brain 125:1995–2004
Stefani A, Stanzione P, Bassi A, Mazzone P, Vangelista T, Bernardi G (1997) Effects of increasing doses of apomorphine during stereotaxic neurosurgery in Parkinson’s disease: clinical score and internal globus pallidus activity. J Neural Transm 104:895–904
Stefani A, Bassi A, Mazzone P, Pierantozzi M, Gattoni G, Altibrandi MG, Giacomini P, Peppe A, Bernardi G, Stanzione P (2002) Subdyskinetic apomorphine responses in globus pallidus and subthalamus of parkinsonian patients: lack of clear evidence for the ‘indirect pathway’. Clin Neurophysiol 113:91–100
Stefani A, Fedele E, Galati S, Pepicelli O, Frasca S, Pierantozzi M, Peppe A,Brusa L, Orlacchio A, Hainsworth AH, Gattoni G, Stanzione P, Bernardi G, Raiteri M, Mazzone P (2005) Subthalamic stimulation activates internal pallidus: evidence from cGMP microdialysis in PD patients. Ann Neurol 57:448–452
Traversa R, Pierantozzi M, Semprini R, Loberti M, Peppe A, Cicardi MC, Stanzione A (1996) N30 wave of somatosensory evoked potentials in Parkinson’s disease: a pharmacological approach. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol Suppl 46:193–200
Urbain N, Vautrelle N, Dahan L, Savasta M, Chouvet G (2004) Glutamatergic-receptors blockade does not regularize the slow wave sleep bursty pattern of subthalamic neurons. Eur J Neurosci 20:392–402
Welter ML, Houeto JL, Bonnet AM, Bejjani PB, Mesnage V, Dormont D, Navarro S, Cornu P, Agid Y, Pidoux B (2004) Effects of high-frequency stimulation on subthalamic neuronal activity in parkinsonian patients. Arch Neurol 61:89–96
Wigmore MA, Lacey MG (2000) A Kv3-like persistent, outwardly rectifying, Cs+-permeable, K+ current in rat subthalamic nucleus neurones. J Physiol 527:493–506
Acknowledgement
This manucript was supported by Ministero della Salute Grants to AS and Regione Piemonte Grant to PS
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stefani, A., Galati, S., Peppe, A. et al. Spontaneous sleep modulates the firing pattern of Parkinsonian subthalamic nucleus. Exp Brain Res 168, 277–280 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-005-0175-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-005-0175-y