Abstract
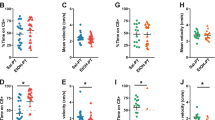
Brailowsky and Garcia (1999) proposed the existence of a relationship between epilepsy and addiction. To prove this hypothesis, pentylenetetrazol kindled rats were tested in the conditioned place preference (CPP) paradigm for their reaction to various addictive drugs with different modes of action (morphine, cocaine and ethanol). In separate experiments, locomotor activity and body temperature after application of the same drugs were tested in kindled and non-kindled rats. In the CPP experiment there were significant differences between both groups of rats. Non-kindled animals showed place preference to morphine (5.0 mg/kg) or cocaine (20.0 mg/kg). This reaction was abolished in the kindled rats. Moreover, control rats demonstrated aversion to 2.0 g/kg ethanol. However, ethanol aversion was not detectable in kindled rats. Moreover, there was no difference between non-kindled and kindled rats in locomotor activity and body temperature after morphine (1.0 and 5.0 mg/kg), cocaine (10.0 and 20.0 mg/kg), or ethanol (0.5 and 2.0 g/kg) application. This suggests alterations in reward systems as a consequence of kindling. It is hypothesised that GABAergic neurones in the ventral tegmental area might play a major role in the alterations found.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alderson HL, Jenkins TA, Kozak R, Latimer MP, Winn P (2001) The effects of excitotoxic lesions of the pedunculopontine tegmental nucleus on conditioned place preference to 4%, 12% and 20% sucrose solutions. Brain Res Bull 56:599–605
Bardo MT (1998) Neuropharmacological mechanisms of drug reward: beyond dopamine in the nucleus accumbens. Crit Rev Neurobiol 12:37–67
Bartoletti M, Gaiardi M, Gubellini C, Bacchi A, Babbini M (1990) Morphine attenuation of a conditioned emotional response in post-dependent rats. Eur J Pharmacol 185:163–167
Becker A, Grecksch G, Rüthrich H-L, Pohle W, Marx B, Matthies H (1992) Kindling and its consequences on learning in rats. Behav Neural Biol 57:37–43
Becker A, Grecksch G, Matthies H (1994) The influence of diazepam on learning processes impaired by pentylenetetrazol. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Arch Pharmacol 349:492–496
Becker A, Grecksch G, Brosz M (1995) Antiepileptic drugs–their effects on kindled seizures and kindling-induced learning impairments. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 52:453–459
Becker A, Grecksch G, Thiemann W, Höllt V (2000) Pentylenetetrazol-kindling modulates stimulated dopamine release in the nucleus accumbens of rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 66:425–428
Blanchard DC, Weatherspoon A, Shepherd J, Rodgers RJ, Weiss SM, Blanchard RJ (1991) “Paradoxical" effects of morphine on antipredator defense reactions in wild and laboratory rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 40:819–828
Brailowsky S, Garcia O (1999) Ethanol, GABA and epilepsy. Arch Med Res 30:3–9
Carr GD, Fibiger HC, Phillips AG (1989) Conditioned place preference as a measure of drug reward. In: Liebmann JM, Cooper S (eds) The neuropharmacological basis of reward. Clarendon, Oxford, pp 264–319
Chang L, Cloak CC, Ernst T (2003) Magnetic resonance spectroscopy studies of GABA in neuropsychiatric disorders. J Clin Psychiatry 64(Suppl 3):7–14
Corda MG, Giorgi O, Longoni B, Orlandi M, Biggio G (1990) Decrease in the function of the gamma-aminobutyric acid-coupled chloride channel produced by the repeated administration of pentylenetetrazol to rats. J Neurochem 55:1216–1221
Corda MG, Orlandi M, Lecca D, Carboni G, Frau V, Giorgi O (1991) Pentylenetetrazol-induced kindling in rats: effect of GABA function inhibitors. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 40:329–333
Craft RM, Howard JL, Pollard GT (1988) Conditioned defensive burying as a model for identifying anxiolytics. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 30:775–780
Cunningham CL, Henderson CM (2000) Ethanol-induced conditioned place aversion in mice. Behav Pharmacol 11:591–602
Di Chiara G (2002) Nucleus accumbens shell and core dopamine: differential role in behavior and addiction. Behav Brain Res 137:75–114
File SE, Mabbutt PS, Becker A, Gonzalez LE, Fluck E (1996) Short-term rebound anxiolytic effects and long-term changes in platelet benzodiazepine binding after pentylenetetrazole-kindling in two strains of rat. Anxiety 2:109–116
Fritschy JM, Kiener T, Bouilleret V, Loup F (1999) GABAergic neurons and GABA(A)-receptors in temporal lobe epilepsy. Neurochem Int 34:435–445
Fujimori S, Yoneda Y (2004) Neuropsychiatric disorders and GABA. Nihon Shinkei Seishin Yakurigaku Zasshi 24:265–271
Genkova-Papazova MG, Petkova B, Shishkova N, Lazarova-Bakarova M (2001) Effect of the calcium channel blockers nifedipine and diltiazem on pentylenetetrazole kindling-provoked amnesia in rats. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol 11:91–96
Gordon E, Devinsky O (2001) Alcohol and marijuana: effects on epilepsy and use by patients with epilepsy. Epilepsia 42:1266–1272
Kokkinidis L, Borowski TB (1991) Sensitization of mesolimbic brain stimulation reward after electrical kindling of the amygdala. Brain Res Bull 27:791–796
Koob GF (1992) Drugs of abuse: anatomy, pharmacology and function of reward pathways. Trends Pharmacol Sci 13:177–184
Koob GF (2000) Neurobiology of addiction. Toward the development of new therapies. Ann N Y Acad Sci 909:170–185
Lamberty Y, Klitgaard H (2000) Consequences of pentylenetetrazole kindling on spatial memory and emotional responding in the rat. Epilepsy Behav 1:256–261
Linseman MA, Cottrell G, Burnham WM (1994) Decreased voluntary ethanol selection in amygdala-kindled rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 48:31–36
Luthman J, Humpel C (1997) Pentylenetetrazol kindling decreases N-methyl-D-aspartate and kainate but increases gamma-aminobutyric acid-A receptor binding in discrete rat brain areas. Neurosci Lett 239:9–12
Maldonado C, Rodri, guez-Arias M, Aguilar MA, Minarro J (2003) GHB differentially affects morphine actions on motor activity and social behaviours in male mice. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 76:259–265
McBride WJ, Murphy JM, Ikemoto S (1999) Localization of brain reinforcement mechanisms: intracranial self-administration and intracranial place-conditioning studies. Behav Brain Res 101:129–152
McNamara JO, Bonhaus DW, Shin DW, Crain BJ, Gellman RL, Giacchino JL (1986) The kindling model of epilepsy: a critical review. Crit Rev Neurobiol 1:341–391
Meldrum BS (1989) GABAergic mechanisms in the pathogenesis and treatment of epilepsy. Br J Clin Pharmacol 27(Suppl 1):S3–S11
Meldrum BS (1995) Neurotransmission in epilepsy. Epilepsia 36(Suppl 1):S30–S35
Metz GA, Gonzalez CL, Piecharka DM, Whishaw IQ (2003) Acute alcohol administration improves skilled reaching success in intact but not 6-OHDA dopamine depleted rats: a subsystems analysis of the motoric and anxiolytic effects of alcohol. Behav Brain Res 142:167–174
Paine TA, Jackman SL, Olmstead MC (2002) Cocaine-induced anxiety: alleviation by diazepam, but not buspirone, dimenhydrinate or diphenhydramine. Behav Pharmacol 13:511–523
Paredes RG, Muzzi G, Aguirre E, Romero V (2000) Can a generalized kindling seizure induce a reward state? Epilepsy Res 38:249–257
Rauca C, Pohle W, Grunenberg K, Franze S (2000) Hypothermia inhibits pentylenetetrazol kindling and prevents kindling-induced deficit in shuttle-box avoidance. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 65:23–30
Raven MA, Necessary BD, Danluck DA, Ettenberg A (2000) Comparison of the reinforcing and anxiogenic effects of intravenous cocaine and cocaethylene. Exp Clin Psychopharmacol 8:117–124
Schmutz M (1987) Relevance of kindling and related processes to human epileptogenesis. Prog Neuro-Psychopharmacol 11:505–525
Sejima H, Ito M, Kishi K, Tsuda H, Shiraishi H (1997) Regional excitatory and inhibitory amino acid concentrations in pentylenetetrazol kindling and kindled rat brain. Brain Dev 19:171–175
Shippenberg TS, Koob GF (2002) Recent advances in animal models of drug addiction. Lippincott, Williams & Witkins, Washington, Philadelphia, pp 1381–1398
Spanagel R, Weiss F (1999) The dopamine hypothesis of reward: past and current status. Trends Neurosci 22:521–527
Vayer P, Mandel P, Maitre M (1987) Gamma-hydroxybutyrate, a possible neurotransmitter. Life Sci 41:1547–1557
Voigt JP, Morgenstern E (1990) Pentylenetetrazole kindling impairs learning in mice. Biomed Biochim Acta 49:143–145
Wilson MA, Burghardt PR, Ford KA, Wilkinson MB, Primeaux SD (2004) Anxiolytic effects of diazepam and ethanol in two behavioral models: comparison of males and females. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 78:445–458
Xi ZX, Stein EA (2002) GABAergic mechanisms of opiate reinforcement. Alcohol Alcohol 37:485–494
Acknowledgements
We gratefully acknowledge the expert assistance of Ms. P. Dehmel, Ms. R. Domm, Ms. C. Knape and Ms. G. Schulze. We thank Mr. A. K. Toms (UK) for help in improving the English.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Becker, A., Schmitz, M. & Grecksch, G. Kindling modifies morphine, cocaine and ethanol place preference. Exp Brain Res 168, 33–40 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-005-0081-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-005-0081-3