Abstract
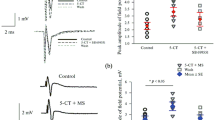
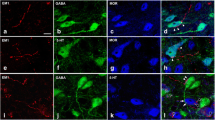
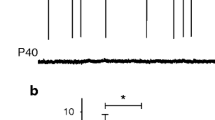
Dorsal horn neurons that express the neurokinin 1 receptor (NK-1R) play an important role in nociceptive processing. The targetting of NK-1R neurons by serotoninergic (5-hydroxytryptamine, 5-HT) axons would provide a straightforward means to exert an inhibitory analgesic effect at spinal level. This study used single cell electrophysiology to analyse and correlate the responses of rat deep DH neurons in vitro to both 5-HT and the NK-1R agonist [Sar9,Met(O2)11]-substance P (SP). Subsequently a combination of immunocytochemistry and confocal imaging was applied to biocytin-filled laminae III–VI neurons to reveal putative 5-HT innervation in this neuronal sample. A population of neurons was identified in which 5-HT (50 µM) significantly attenuated the dorsal root-evoked excitatory postsynaptic potential and [Sar9,Met(O2)11]-SP (2 µM) induced a direct tetrodotoxin-resistant depolarisation. Immunolabelling revealed that all of these neurons were inhibited by 5-HT, including those that were excited by [Sar9,Met(O2)11]-SP, were overlaid by a plexus of 5-HT immunoreactive fibres and in some instances, closely apposed putative contacts with somata and proximal dendrites identified although their incidence was low. Inhibition by 5-HT of deep DH neurons directly responsive to SP may account at least in part for monoamine-induced modulation of nociceptive processing in the spinal cord.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Benoliel R, Tanaka M, Caudle RM, Iadarola MJ (2000) Co-localization of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors and substance P (neurokinin-1) receptors in rat spinal cord. Neurosci Lett 291:61–64
Bleazard L, Hill RG, Morris R (1994) The correlation between the distribution of the NK1 receptor and the actions of tachykinin agonists in the dorsal horn of the rat indicates that substance P does not have a functional role on substantia gelatinosa (lamina II) neurons. J Neurosci 14:7655–7664
Carstens E, Gilly H, Schreiber H, Zimmermann M (1987) Effects of midbrain stimulation and iontophoretic application of serotonin, noradrenaline, morphine and GABA on electrical thresholds of afferent C- and A-fibre terminals in cat spinal cord. Neuroscience 21:395–406
Cuello AC, Ribeiro-da-Silva A, Ma W, De Koninck Y, Henry JL (1993) Organization of substance P primary sensory neurons: ultrastructural and physiological correlates. Regul Peptides 46:155–164
Davies JE, Roberts MH (1981) 5-Hydroxytryptamine reduces substance P responses on dorsal horn interneurones: a possible interaction of neurotransmitters. Brain Res 217:399–404
De Felipe C, Herrero JF, O’Brien JA, Palmer JA, Doyle CA, Smith AJH, Laird JMA, Belmonte C, Cervero F, Hunt SP (1998) Altered nociception, analgesia and aggression in mice lacking the receptor for substance P. Nature 392:394–397
Eide PK, Hole K (1993) The role of 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT) receptor subtypes and plasticity in the 5-HT systems in the regulation of nociceptive sensitivity. Cephalalgia 13:75–85
El Yassir N, Fleetwood-Walker SM, Mitchell R (1988) Heterogeneous effects of serotonin in the dorsal horn of rat: the involvement of 5-HT1 receptor subtypes. Brain Res 456:147–158
Garraway SM, Hochman S (2001) Modulatory actions of serotonin, norepinephrine, dopamine, and acetylcholine in spinal cord deep dorsal horn neurons. J Neurophysiol 86:2183–2194
Headley PM, Duggan AW, Griersmith BT (1978) Selective reduction by noradrenaline and 5-hydroxytryptamine of nociceptive responses of cat dorsal horn neurones. Brain Res 145:185–189
Hill R (2000) NK1 (substance P) receptor antagonists-why are they not analgesic in humans? Trends Pharmacol Sci 21:244–246
Hori Y, Endo K, Takahashi T (1996) Long lasting synaptic facilitation induced by serotonin in superficial dorsal horn neurones of the rat spinal cord. J Physiol (Lond) 492:867–876
King AE, Ackley MA, Slack JR (1997a) Profile of neuronal excitation following selective activation of the neurokinin-1 receptor in rat deep dorsal horn in vitro. Brain Res 767:55–63
King AE, Slack JR, Lopez-Garcia JA, Ackley MA (1997b) Tachykinin actions on deep dorsal horn neurons in vitro: an electrophysiological and morphological study in the immature rat. Eur J Neurosci 9:1037–1046
Li P, Zhuo M (1998) Silent glutamatergic synapses and nociception in mammalian spinal cord. Nature 393:695–698
Light AR, Kavookjian AM, Petrusz P (1983) The ultrastructure and synaptic connections of serotonin-immunoreactive terminals in spinal laminae I and II. Somatosens Res 1:33–50
Littlewood NK, Todd AJ, Spike RC, Watt C, Shehab SAS (1995) The types of neuron in spinal dorsal horn which possess neurokinin-1 receptors. Neuroscience 66:597–608
Liu Z, Zhuang D, Lunderberg T, Yu L (2002) Involvement of 5-hydroxytryptamine (1A) receptors in the descending anti-nociceptive pathway from periaqueductal gray to the spinal dorsal horn in intact rats, rats with nerve injury and rats with inflammation. Neuroscience 112:399–407
Lopez-Garcia JA (1998) Serotonergic modulation of the responses to excitatory amino acids of rat dorsal horn neurons in vitro: implications for somatosensory transmission. Eur J Neurosci 10:1341–1349
Lopez-Garcia JA, King AE (1996) Pre- and post-synaptic actions of 5-hydroxytryptamine in the rat lumbar dorsal horn in vitro: Implications for somatosensory transmission. Eur J Neurosci 8:2188–2197
Marshall GE, Shehab SAS, Spike RC, Todd AJ (1996) Neurokinin-1 receptors on lumbar spinothalamic neurons in the rat. Neuroscience 72:255–263
Maxwell DJ, Leranth C, Verhofstad AA (1983) Fine structure of serotonin-containing axons in the marginal zone of the rat spinal cord. Brain Res 266:253–259
McGonigle DJ, Maxwell DJ, Shehab SAS, Kerr R (1996) Evidence for the presence of neurokinin-1 receptors on dorsal horn spinocerebellar tract cells in the rat. Brain Res 742:1–9
Millan MJ (2002) Descending control of pain. Prog Neurobiol 66:355–474
Naim M, Spike RC, Watt C, Shehab SAS, Todd AJ (1997) Cells in laminae III and IV of the rat spinal cord that possess the neurokinin-1 receptor and have dorsally directed dendrites receive a major synaptic input from tachykinin-containing primary afferents. J Neurosci 17:5536–5548
Naim MM, Shehab SA, Todd AJ (1998) Cells in laminae III and IV of the rat spinal cord which possess the neurokinin-1 receptor receive monosynaptic input from myelinated primary afferents. Eur J Neurosci 10:3012–3019
Polgar E, Puskar Z, Watt C, Matesz C, Todd AJ (2002) Selective innervation of lamina I projection neurones that possess the neurokinin 1 receptor by serotonin-containing axons in the rat spinal cord. Neuroscience 109:799–809
Radhakrishnan V, Henry JL (1991) Novel substance P antagonist, CP-96:345, blocks responses of cat spinal dorsal horn neurons to noxious cutaneous stimulation and to substance P. Neurosci Lett 132:39–43
Ruda MA, Coffield J, Steinbusch HW (1982) Immunocytochemical analysis of serotonergic axons in laminae I and II of the lumbar spinal cord of the cat. J Neurosci 2:1660–1671
Sandkuhler J (1996) The organization and function of endogenous antinociceptive systems. Prog Neurobiol 50:49–81
Stewart W, Maxwell DJ (2000) Morphological evidence for selective modulation by serotonin of a subpopulation of dorsal horn cells which possess the neurokinin-1 receptor. Eur J Neurosci 12:4583–4588
Thompson SWN, King AE, Woolf CJ (1990) Activity-dependent changes in rat ventral horn neurones in vitro; summation of prolonged afferent evoked postsynaptic depolarizations produce a d-APV sensitive windup. Eur J Neurosci 2:638–649
Todd AJ, Millar J (1983) Receptive fields and responses to ionophoretically applied noradrenaline and 5-hydroxytryptamine of units recorded in laminae I–III of cat dorsal horn. Brain Res 288:159–167
Todd AJ, Spike RC, Polgar E (1998) A quantitative study of neurons which express neurokinin-1 or somatostatin sst2a receptor in rat spinal dorsal horn. Neuroscience 85:459–473
Todd AJ, McGill MM, Shehab SAS (2000) Neurokinin 1 receptor expression by neurons in laminae I, III and IV of the rat spinal dorsal horn that project to the brainstem. Eur J Neurosci 12:689–700
Willcockson WS, Chung JM, Hori Y, Lee KH, Willis WD (1984) Effects of iontophoretically released amino acids and amines on primate spinothalamic tract cells. J Neurosci 4:732–740
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to The Wellcome Trust for financial support. M.A. Worsley was in receipt of a University of Leeds Postgraduate Studentship. Technical assistance was provided by Mrs. J. Daniel.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Worsley, M.A., Todd, A.J. & King, A.E. Serotoninergic-mediated inhibition of substance P sensitive deep dorsal horn neurons: a combined electrophysiological and morphological study in vitro. Exp Brain Res 160, 360–367 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-004-2018-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-004-2018-7