Abstract
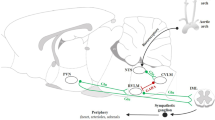
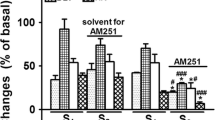
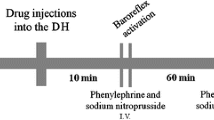
It is known that the caudal ventrolateral medulla (CVLM) plays an important role in controlling blood pressure and mediating the cardiovascular effects of centrally acting antihypertensive drugs such as clonidine. Recently, the effect of clonidine was believed to be related to the functional states of N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptors. The present work was designed to observe the interactions between clonidine and NMDA receptor in the CVLM. Unilaterally injected clonidine (6 nmol) into the CVLM not only produced a pressor action, but also effectively (P<0.01, n=8) antagonized the decreases in both mean arterial pressure (MAP) (−22.3±5.0 to −7.9±2.3 mmHg) and heart rate (HR) (−31.9±5.9 to −10.3±2.7 beats/min) evoked by L-glutamate in the CVLM. Unilaterally injected NMDA receptor antagonist MK801 (200 pmol) into the CVLM significantly increased MAP by 26.5±3.7 mmHg and HR by 37.1±7.6 beats/min, and completely (P<0.01, n=10) abolished the pressor effect (16.1±6.6 to 1.5±2.8 mmHg) of clonidine in the CVLM. In conclusion, these findings show that NMDA receptors within the CVLM contribute to clonidine-induced action, and suggest that the CVLM plays an important role in the interaction between clonidine and NMDA receptors.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aicher SA, Kurucz OS, Reis DJ, Milner TA (1995) Nucleus tractus solitarius efferent terminals synapse on neurons in the caudal ventrolateral medulla that project to the rostral ventrolateral medulla. Brain Res 693:51–63
Allen AM, Guyenet PG (1993) α2-adrenoceptor-mediated inhibition of bulbospinal barosensitive cells of rat rostral ventrolateral medulla. Am J Physiol 265:R1065– R1075
Badoer E, McKinley MJ, Oldfield BJ, McAllen RM (1994) Localization of barosensitive neurons in the caudal ventrolateral medulla which project to the rostral ventrolateral medulla. Brain Res 657:258–268
Chan JY, Yang SM, Chan SH (1998) Mediation by N-methyl-D-aspartate and non-N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors in the expression of Fos protein at the nucleus tractus solitarii in response to baroreceptor activation in the rat. Neuroscience 83:93–105
Dampney RAL (1994) Functional organization of central pathways regulating the cardiovascular system. Physiol Rev 74:323–364
Drolet G, Aslanian V, Minsion J, Morris M, Chalmers J (1990) Differences in the central hypotensive actions of alpha-methyldopa and clonidine in the spontaneously hypertensive rat: contribution of neurons arising from the B3 and the C1 areas of the rostral ventrolateral medulla. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 15:118–123
Ernsberger P, Giuliano R, Willette RN, Reis DJ (1990) Role of imidazoline receptors in the vasodepressor response to clonidine analogs in the rostral ventrolateral medulla. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 253:408–418
Goodchild AK, Dampney RAL, Bandler R (1982) A method for evoking physiological responses by stimulation of cell bodies, but not axons of passage, within localized regions of the central nervous system. J Neurosci Methods 6:351–363
Gordon FJ (1987) Aortic baroreceptor reflexes are mediated by NMDA receptors in caudal ventrolateral medulla. Am J Physiol 252:R628–R633
Guyenet PG (1990) Role of the ventral medulla oblongata in blood pressure regulation. In: Loewy AD, Spyer KM (eds) Central regulation of autonomic functions. Oxford University Press, New York, pp 145–167
Guyenet PG (1997) Is the hypotensive effect of clonidine and related drugs due to imidazoline binding sites? Am J Physiol 273:R1580–R1584
Hayar A, Guyenet PG (1999) α2-adrenoceptor-mediated presynaptic inhibition in bulbospinal neurons of rostral ventrolateral medulla. Am J Physiol 277:H1069–H1080
Jastrzebski Z, Czyzewska-Szafran H, Gozlinska B, Remiszewska M, Mazurek AP (1995) Clonidine hypotension in spontaneously hypertensive rats (SHR) depends on the functional state of GABAergic and glutamatergic systems. Neurosci Lett 184:94–96
Jeske I, Reis DJ, Milner TA (1995) Neurons in the barosensory area of the caudal ventrolateral medulla project monosynaptically on to sympathoexcitatory bulbospinal neurons in the rostral ventrolateral medulla. Neuroscience 65:343–353
Kubo T, Kihara M, Misu Y (1991) Ipsilateral but not contralateral blockade of excitatory amino acid receptors in the caudal ventrolateral medulla inhibits aortic baroreceptor reflex in rats. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 343:46–51
Lin JC, Liu DM, Wang Y (1997) Clonidine antagonizes pressor effect of N-methyl-D-aspartate in the rostral ventrolateral medulla of rats. Clin Exp Hypertens 19:1065–1078
Masuda N, Ootsuka Y, Terui N (1992) Neurons in the caudal ventrolateral medulla mediate the somato-sympathetic inhibitory reflex responses via GABA receptors in the rostral ventrolateral medulla. J Auton Nerv Syst 40:91–98
Milhaud D, Fagni L, Bockaert J, Lafon-Cazal M (2000) Imidazoline-induced neuroprotective effects results from blockade of NMDA receptor channels in neuronal cultures. Neuropharmacology 39:2244–2254
Miyawaki T, Suzuki S, Minson J, Arnolda L, Chalmers J, Smith IL, Pilowsky P (1997) Role of AMPA/kainate receptors in transmission of the sympathetic baroreflex in rat CVLM. Am J Physiol 272:R800–R812
Olmos G, Ribera J, Garcia-Sevilla JA (1996) Imidazoli(di)ne compounds interact with the phencyclidine site of NMDA receptors in the rat brain. Eur J Pharmacol 310:273–276
Olmos G, DeGregorio-Rocasolano N, Paz RM, Gasull T, Assumpcio BM, Trullas R, Villarroel A, Lerma J, Garcia-Sevilla JA (1999) Protection by imidazol(ine) drugs and agmatine of glutamate-induced neurotoxicity in cultured cerebellar granule cells through blockade of NMDA receptor. Br J Pharmacol 127:1317–1326
Paxinos G, Watson C (1986) The rat brain in stereotaxic coordinates, 2nd edn. Academic Press, New York
Punnen S, Urbanskis R, Krieger AJ, Sapru HN (1987) Ventrolateral medullary pressor area: site of hypotensive action of clonidine. Brain Res 422:336–346
Reis DJ (1996) Neurons and receptors in the rostraventrolateral medulla mediating the antihypertensive actions of drugs acting at imidazoline receptors. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 27:S11–S18
Schreihofer AM, Guyenet PG (2000) Role of presympathetic C1 neurons in the sympatholytic and hypotensive effects of clonidine in rats. Am J Physiol 279:R1753–R1762
Seller H, Czachurski J, Zanzinger J (1999) Sympathoinhibitory effects of clonidine are transmitted by the caudal ventrolateral medulla in cats. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 33:521–526
Sesoko S, Muratani H, Yamazato M, Teruya H, Takishita S, Fukiyama K (1998) Contribution of α2-adrenoceptors in caudal ventrolateral medulla to cardiovascular regulation in rat. Am J Physiol 274:R1119–1124
Tingley FD 3rd, Arneric SP (1990) Evidence for clonidine presynaptcially modulating amino acid release in the rostral ventrolateral medulla: role in hypertension. Brain Res 537:175–181
Wang WZ, Yuan WJ, Ren AJ, Pan YX, Tang CS, Su DF (2003a) Role of I1-imidazoline receptors within the caudal ventrolateral medulla in cardiovascular responses to clonidine in rats. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 42:1-9
Wang WZ, Yuan WJ, Su DF (2003b) Blockade of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors within the rostral ventrolateral medulla antagonizes clonidine-induced cardiovascular effects. Auton Neurosci 109:21–28
Wang WZ, Yuan WJ, Bai J, Pan YX, Liao MY, Tang CS (2003c) Non-NMDA receptors within the caudal ventrolateral medulla involved in the transmission of baroreflex of rats. Acta Pharmacol Sin 24:783–789
Willette RN, Punnen NS, Krieger AJ, Sapru HN (1984) Interdependence of rostral and caudal ventrolateral medulla areas in the control of blood pressure. Brain Res 321:169–174
Wong EH, Kemp JA, Priestley T, Knight AR, Woodruff GN, Iversen LL (1986) The anticonvulsant MK-801 is a potent N-methyl-D-aspartate antagonist. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 83:7104–7108
Wong EH, Knight AR, Woodruff GN (1988) [3H]MK-801 labels a site on the N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor channel complex in rat brain membranes. J Neurochem 50:274–281
Yang XC, Reis DJ (1999) Agmatine selectively blocks the N-methyl-D-aspartate subclass of glutamate receptor channels in rat hippocampal neurons. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 288:544–549
Zhang J, Abdel-Rahman AA (2002) The hypotensive action of rilmenidine is dependent on functional N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor in the rostral ventrolateral medulla of conscious spontaneously hypertensive rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 303:204–210
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Major State Basic Research Development Program of People’s Republic of China (No. G2000056905) and the Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 30070306). We thank Dr. J. Lu for his expert statistical assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, WZ., Yuan, WJ., Pan, YX. et al. Interaction between clonidine and N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors in the caudal ventrolateral medulla of rats. Exp Brain Res 158, 259–264 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-004-1902-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-004-1902-5