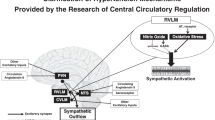
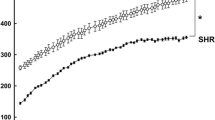
Abstract
To explore the central disturbances resulting from blood pressure changes, spontaneously hypertensive mice (SHM) were compared to normotensive controls for cytochrome oxidase (CO) activity, an index of oxidative capacity in the central nervous system and a marker of long-term regional brain metabolism and neuronal activity. In all brain areas presenting significant enzymatic variations, only increases in CO activity were found in SHM, particularly the central autonomic network. However, only specific regions were affected, namely the insular cortex and the hypothalamic nuclei principally involved in high-order autonomic control. Altered limbic structures included the lateral septum, various hippocampal subregions, as well as prelimbic cortex. CO activity was also elevated in several forebrain regions, including those directly connected to the limbic system, such as the nucleus accumbens, the claustrum, and dorsomedial and reticular thalamic nuclei, as well as subthalamic and ventrolateral thalamic nuclei. In the brainstem, the only regions affected were the locus coeruleus, site of noradrenergic cell bodies, the trigeminal system, and four interconnected regions: the inferior colliculus, the paramedial reticular formation, the medial vestibular, and the cerebellar fastigial nuclei. These data show that specific regions modulating sympathetic nerve discharge are activated in young adult SHM, possibly due to mitochondrial dysfunction and excitotoxicity.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen GV, Cechetto DF (1992) Functional and anatomical organization of cardiovascular pressor and depressor sites in the lateral hypothalamic area. I. Descending projections. J Comp Neurol 15:313–332
Allen GV, Cechetto DF (1993) Functional and anatomical organization of cardiovascular pressor and depressor sites in the lateral hypothalamic area. II. Ascending projections. J Comp Neurol 15:421–438
Aston-Jones G, Shipley M, Grzanna R (1995) The locus coeruleus, A5 and A7 noradrenergic cell groups. In: Paxinos G (ed) The rat nervous system, 2nd edn. Academic Press, New York, pp 183–213
Baumbach GL, Sigmund CD, Faraci FM (2003) Cerebral arteriolar structure in mice overexpressing human renin and angiotensinogen. Hypertension 41:50–55
Bendel P, Eilam R (1992) Quantitation of ventricular size in normal and spontaneously hypertensive rats by magnetic resonance imaging. Brain Res 574:224–228
Brezenoff HE (1972) Cardiovascular responses to intrahypothalamic injections of carbachol and certain cholinesterase inhibitors. Neuropharmacology 11:637–644
Butcher KS, Cechetto DF (1998) Receptors in lateral hypothalamic area involved in insular cortex sympathetic responses. Am J Physiol 275:H689–H696
Choki J, Yamaguchi T, Takeya Y, Morotomi Y, Omae T (1977) Effect of carotid artery ligation on regional cerebral blood flow in normotensive and spontaneously hypertensive rats. Stroke 8:374–379
Delini-Stula A, Hunn C (1985) Neophobia in spontaneous hypertensive (SHR) and normotensive control (WKY) rats. Behav Neur Biol 43:206–211
Fisk GD, Wyss JM (2000) Descending projections of infralimbic cortex that mediate stimulation-evoked changes in arterial pressure. Brain Res 859:83–95
Franklin KBJ, Paxinos G (1997) The mouse brain in stereotaxic coordinates. Academic Press, New York
Fujishima M, Ibayashi S, Fujii K, Mori S (1995) Cerebral blood flow and brain function in hypertension. Hypertens Res 18:111–117
Gentsch C, Lichsteiner M, Feer H (1981) Locomotor activity, defecation score and corticosterone levels during an openfield exposure: a comparison among individually and group-housed rats, and genetically selected rat lines. Physiol Behav 27:183–186
Gentsch C, Lichsteiner M, Feer H (1987) Open field and elevated plus-maze: a behavioural comparison between spontaneously hypertensive (SHR) and Wistar-Kyoto (WKY) rats and the effects of chlordiazepoxide. Behav Brain Res 25:101–107
Geszteli G, Finnegan W, DeMaro JA, Wang J-Y, Chen J-L, Fenstermacher J (1993) Parenchymal microvascular systems and cerebral atrophy in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Brain Res 611:249–257
Gonzalez-Lima F, Jones D (1994) Quantitative mapping of cytochrome oxidase activity in the central auditory system of the gerbil: a study with calibrated activity standards and metal-intensified histochemistry. Brain Res 660:34–39
Haibara AS, Saad WA, Menani JV, Camargo LA, Renzi A (1994) Role of lateral hypothalamus on fluid, electrolyte, and cardiovascular responses to activation of the MSA. Am J Physiol 266:R496–R502
Haines DE, Dietrichs E, Sowa TE (1984) Hypothalamocerebellar and cerebello-hypothalamic pathways: a review and hypothesis concerning cerebellar circuits which may influence autonomic centers and affective behavior. Brain Behav Evol 24:198–220
Hamet P, Richard L, Dam T-V, Teiger E, Orlov SN, Gaboury F, Tremblay J (1995) Apoptosis in target organs of hypertension. Hypertension 26:642–648
Harper SL, Bohlen HG (1984) Microvascular adaptation in the cerebral cortex of adult spontaneously hypertensive rats. Hypertension 6:408–419
Hayashi T, Nakamura K (1981) Cerebral neuronal activity in spontaneously hypertensive rats as demonstrated by the 14C-deoxyglucose method. Naunyn-Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 316:331–339
Heimer L, Zahm DS, Alheid GF (1995) Basal ganglia. In: Paxinos G (ed) The rat nervous system, 2nd edn. Academic Press, New York, pp 579–628
Hess HH, Pope A (1953) Ultramicrospectrophotometric determination of cytochrome oxidase for quantitative histochemistry. J Biol Chem 204:295–306
Hurley KM, Herbert H, Moga MM, Saper CB (1991) Efferent projections of the infralimbic cortex of the rat. J Comp Neurol 308:249–276
Iadecola C, Springston ME, Reis DJ (1990) Dissociation by chloralose of the cardiovascular and cerebrovascular responses evoked from the cerebellar fastigial nucleus. J Cerebr Blood Flow Metab 10:375–382
Kadekaro M, Savaki HE, Kutyna FA, Davidsen L, Sokoloff L (1983) Metabolic mapping in the sympathetic ganglia and brain of the spontaneously hypertensive rat. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 3:460–467
Katsuta T (1997) Decreased local cerebral blood flow in young and aged spontaneously hypertensive rats. Fukuoka Igaku Zasshi 88:65–74
Kim S-J, Ko KH (1998) Abnormal central serotonergic activities in spontaneously hypertensive rats (SHR). Methods Find Exp Clin Pharmacol 20:473–478
Kimoto-Kinoshita S, Nishida S, Tomura TT (1999) Age-related change of antioxidant capacities in the cerebral cortex and hippocampus of stroke-prone spontaneously hypertensive rats. Neurosci Lett 273:41–44
Krukoff TL (1998) Central regulation of autonomic function: no brakes? Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol 25:474–478
LeDoux JE, Sakaguchi A, Reis DJ (1982) Behaviorally selective cardiovascular hyperactivity in spontaneously hypertensive rats: evidence for hypoemotionality and enhanced appetitive motivation. Hypertension 4:853–863
Malo D, Schlager G, Tremblay J, Hamet P (1989) Thermosensitivity, a possible new locus involved in genetic hypertension. Hypertension 14:121–128
Mori S, Kato M, Fujishima M (1995) Impaired maze learning and cerebral glucose utilization in aged hypertensive rats. Hypertension 25:545–553
Nelson DO, Boulant JA (1981) Altered CNS neuroanatomical organization of spontaneously hypertensive (SHR) rats. Brain Res 226:119–130
Nordborg C, Johansson BB (1980) Morphometric study on cerebral vessels in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Stroke 11:266–270
Nordborg C, Frederiksson K, Johansson BB (1985) The morphometry of consecutive segments in cerebral arteries of normotensive and spontaneously hypertensive rats. Stroke 16:313–320
Oppenheimer S (1993) The anatomy and physiology of cortical mechanisms of cardiac control. Stroke 24:13–15
Oppenheimer SM, Saleh T, Cechetto DF (1992) Lateral hypothalamic area neurotransmission and neuromodulation of the specific cardiac effects of insular cortex stimulation. Brain Res 581:133–142
Reader TA, Strazielle C (1999) Quantitative autoradiography of monoamine uptake sites and receptors in rat and mouse brain. In: Boulton AA, Baker GB, Bateson AN (eds) Neuromethods, vol 33, Cell neurobiology techniques. Humana Press, Totowa, pp 1–51
Risold PY, Swanson LW (1997) Connections of the rat lateral septal complex. Brain Res Rev 24:115–195
Ritter S, Dinh TT (1986) Progressive postnatal dilation of brain ventricles in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Brain Res 370:327–332
Ritter S, Dinh TT, Stone S, Ross N (1988) Cerebroventricular dilation in spontaneously hypertensive rats (SHRs) is not attenuated by reduction of blood pressure. Brain Res 450:354–359
Saper CB (1995) Central autonomic system. In: Paxinos G (ed) The rat nervous system, 2nd edn. Academic Press, New York, pp 107–115
Schlager G (1966) Systolic blood pressure in 8 inbred strains of mice. Nature 212:519–520
Schlager G (1981) The genetically hypertensive mouse. Trends Arter Hypertens 17:321–331
Schlager G, Freeman R, Sustarsic SS (1979) Brain catecholamines and organ weight of mice genetically selected for high and low blood pressure. Experientia 35:67–69
Sladek CD, Blair ML (1984) Cholinergic stimulation of vasopressin release in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Hypertension 6:855–860
Strazielle C, Krémarik P, Ghersi-Egea J-F, Lalonde R (1998) Regional brain variations of cytochrome oxidase activity and motor coordination in Lurcher mutant mice. Exp Brain Res 121:35–45
Strazielle C, Sturchler-Pierrat C, Staufenbiel M, Lalonde R (2003) Regional brain cytochrome oxidase activity in β-amyloid precursor protein transgenic mice with the Swedish mutation. Neuroscience 118:1151–1163
Takenaka K, Sasaki S, Uchida A, Fujita H, Nakamura K, Ichida T, Itoh H, Nakata T, Takeda K, Nakagawa M (1996) GABAB-ergic stimulation in hypothalamic pressor area induces larger sympathetic and cardiovascular depression in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Am J Hypertens 9:964–972
Thifault S, Lalonde R, Hamet P (1999) Neurobehavioral evaluation of high blood pressure and low blood pressure mice. Psychobiology 27:415–425
Thifault S, Lalonde R, Sanon N, Hamet P (2001) Longitudinal analysis of motor activity and coordination, anxiety, and spatial learning in mice with altered blood pressure. Brain Res 910:99–105
Toyoda K, Fujii K, Ibayashi S, Kitazono T, Nagao T, Takaba H, Fujishima M (1998) Attenuation and recovery of brain stem autoregulation in spontaneously hypertensive rats. J Cerebr Blood Flow Metab 18:305–310
Tsukamoto K, Sved AF, Ito S, Komatsu K, Kanmatsuse K (2000) Enhanced serotonin-mediated responses in the nucleus tractus solitarius of spontaneously hypertensive rats. Brain Res 863:1–8
Watanabe H, Kumon Y, Ohta S, Sakaki S, Matsuda S, Sakanaka M (1998) Changes in protein synthesis and calcium homeostasis in the thalamus of spontaneously hypertensive rats with focal cerebral ischemia. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 18:686–696
Wei L, Lin S-Z, Tajima A, Nakata H, Acuff V, Patlak C, Pettigrew K, Fenstermacher J (1992) Cerebral glucose utilization and blood flow in adult spontaneously hypertensive rats. Hypertension 20:501–510
Wible JH, Luft FC, DiMicco JA (1988) Hypothalamic GABA suppresses sympathetic outflow to the cardiovascular system. Am J Physiol 254:R680–R687
Wong-Riley MTT (1979) Changes in the visual system of monocularly sutured or enucleated cats demonstrable with cytochrome oxidase histochemistry. Brain Res 171:11–28
Wong-Riley MTT (1989) Cytochrome oxidase: an endogenous metabolic marker for neuronal activity. Trends Neurosci 12:94–101
Yasui Y, Breder CD, Saper CB, Cechetto DF (1991) Autonomic responses and efferent pathways from the insular cortex in the rat. J Comp Neurol 303:355–374
Zilles K, Wree A (1995) Cortex: areal and laminar structure. In: Paxinos G (ed) The rat nervous system, 2nd edn. Academic Press, New York, pp 649–685
Zou C-J, Gu Y-H (1992) Functional connections between the pressor responses induced by glutamate injection into habenula and lateral septum. Chin J Physiol Sci 8:300–308
Acknowledgements.
This study was supported by a Canadian Institute of Health Research grant to P.H. S.T. received a doctoral scholarship during the course of this study from the Canadian Heart and Stroke Foundation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Strazielle, C., Lalonde, R., Thifault, S. et al. Regional brain variations of cytochrome oxidase activity in spontaneously hypertensive mice. Exp Brain Res 157, 255–264 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-004-1841-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-004-1841-1