Abstract
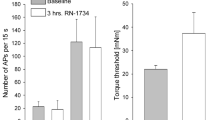
Voltage-gated Ca2+ channels play an important role in the central processing of nociceptive information. Recently, it has been shown that L- and N-type voltage-gated Ca2+ channels are also present on peptidergic, fine afferent nerve fibers in the knee joint capsule. Therefore, the influence of specific blockers for L-type (verapamil) or N-type (ω-conotoxin GVIA) Ca2+ channels on the mechanosensitivity of slowly conducting afferents was tested in the rat knee joint. Topical application of 100 μM verapamil onto the receptive field reduced the mean response to knee joint rotation to 67±8% (SEM, n=12), obtained by outward rotations with a torque of 10 mNm above the mechanical threshold and compared with control movements. In the presence of 50 μM ω-conotoxin GVIA, the mean response decreased to 44±5% (n=12), a reduction that was also observed during rotations of other intensities. Simultaneous application of both substances further reduced the response to 25±11% (n=6). In additional experiments it was shown that L- and N-type voltage-gated Ca2+ channels do not influence activity-dependent changes of the mechanical excitability. In conclusion, the data of the present study indicate that voltage-gated Ca2+ channels may also be involved in the regulation of the mechanosensitivity of nociceptive nerve fiber endings.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdulla F, Smith P (1999) Nerve injury increases an excitatory action of neuropeptide Y and Y2-agonists on dorsal root ganglion neurons. Neuroscience 89:43–60
Akopian A (2000) Neuromodulation of ligand- and voltage-gated channels in the amphibian retina. Microsc Res Tech 50:403–410
Bileviciute I, Lundeberg T, Ekblom A, Theodorsson E (1993) Bilateral changes of substance P-, neurokinin A-, calcitonin gene-related peptide- and neuropeptide Y-like immunoreactivity in rat knee joint synovial fluid during acute monoarthritis. Neurosci Lett 153:37–40
Cordoba-Rodriguez R, Moore KA, Kao JP, Weinreich D (1999) Calcium regulation of a slow post-spike hyperpolarization in vagal afferent neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 14:7650–7657
Ebinger M, Schmidt RF, Heppelmann B (2001) Composition of the medial and posterior articular nerves of the mouse knee joint. Somatosens Mot Res 18:62–65
Evans A, Nicol G, Vasko M (1996) Differential regulation of evoked peptide release by voltage-sensitive calcium channels in rat sensory neurons. Brain Res 712:265–273
Gippetti P, Holzer P (1996) Neurogenic inflammation. CRC Press, Boca Ratan, FL
Harding LM, Beadle DJ, Bermudez I (1999) Voltage-dependent calcium channel subtypes controlling somatic substance P release in the peripheral nervous system, Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 23:1103–1112
Harper AA, Catacuzzeno L, Trequattrini C, Petris A, Franciolini F (2001) Verapamil block of large-conductance Ca-activated K channels in rat aortic myocytes. J Membr Biol 179:103–111
Heppelmann B, Pawlak M (1997a) Inhibitory effect of somatostatin on the mechanosensitivity of articular afferents in normal and inflamed knee joints of the rat. Pain 73:377–382
Heppelmann B, Pawlak M (1997b) Sensitization of articular afferents in normal and inflamed knee joints by substance P in the rat. Neurosci Lett 223:97–100
Heppelmann B, Pfeffer A, Schaible H-G, Schmidt RF (1986) Effects of acetylsalicylic acid and indomethacin on single groups III and IV sensory units from acutely inflamed joints. Pain 26:337–351
Heppelmann B, Heuss C, Schmidt RF (1988) Fibre size distribution of myelinated and unmyelinated axons in the medial and posterior articular nerves of the cat's knee joint. Somatosens Res 5:273–281
Just S, Heppelmann B (2001) Neuropeptide Y changes the excitability of fine afferent units in the rat knee joint. Br J Pharmacol 132:703–708
Just S, Heppelmann B (2002) Frequency dependent reduction of mechanosensitivity of rat knee joint afferents after antidromic saphenous nerve stimulation. Neuroscience 112:783–789
Just S, Pawlak M, Heppelmann B (2000) Responses of primary afferent nerve fibres innervating the rat knee joint to defined torque. J Neurosci Meth 103:157–162
Just S, Leipold-Büttner C, Heppelmann B (2001) Histological demonstration of voltage dependent calcium channels on calcitonin gene-related peptide-immunoreactive nerve fibres in the mouse knee joint. Neurosci Lett 312:133–136
Kress M, Izydorczyk I, Kuhn A (2001) N- and L- but not P/Q-type calcium channels contribute to neuropeptide release from rat skin in vitro. Neuroreport 12:867–870
Larsson J, Ekblom A, Henriksson K, Lundeberg T, Theodorsson E (1991) Concentration of substance P, neurokinin A, calcitonin gene-related peptide, neuropeptide Y and vasoactive intestinal polypeptide in synovial fluid from knee joints in patients suffering from rheumatoid arthritis. Scand J Rheumatol 20:326–335
Loescher AR, Boissonade FM, Robinson PP (2001) Calcitonin gene-related peptide modifies the ectopic discharge from damaged nerve fibres in the ferret. Neurosci Lett 300:71–74
Mansvelder H, Kits K (2000) Calcium channels and the release of large dense core vesicles from neuroendocrine cells: spatial organization and functional coupling. Prog Neurobiol 62:427–441
Mayer C, Quasthoff S, Grafe P (1999) Confocal imaging reveals activity-dependent intracellular Ca2+ transients in nociceptive human C fibre. Pain 81:317–322
Meyer A, Campbell J, Raja N (1988) Antidromic stimulation in monkey does not sensitize unmyelinated nociceptors to heat. Brain Res 441:168–172
Millan M (1999) The induction of pain: an integrative review. Prog Neurobiol 57:1–164
Nasu F (1999) Analysis of calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP)-containing nerve fibres in the rat spinal cord using light and electron microscopy. J Electron Microsc (Tokyo) 48:267–275
Neugebauer V, Schaible H-G, Schmidt RF (1989) Sensitization of articular afferents to mechanical stimuli by bradykinin. Pflugers Arch 415:330–335
Pozo MA, Gallego R, Gallar J, Belmonte C (1992) Blockade by calcium antagonists of chemical excitation and sensitisation of polymodal nociceptors in the cat's cornea. J Physiol (Lond) 450:179–189
Schaible H-G, Grubb B (1993) Afferent and spinal mechanisms of joint pain. Pain 55:5–54
Su X, Wachtel R, Gebhart G (1998) Inhibition of calcium currents in rat colon sensory neurons by κ- but not μ- or δ-opioids. J Neurophysiol 80:3112–3119
Vanegas H, Schaible H-G (2000) Effects of antagonists to high-threshold calcium channels upon spinal mechanisms of pain, hyperalgesia and allodynia. Pain 85:9–18
Vergara C, Latorre R, Marrion NV, Adelman JP (1998) Calcium-activated potassium channels. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 3:321–329
Wegner H, Reeh P, Brehm S, Kreysel H, Steen K (1996) Diltiazem blocks the pH-induced excitation of rat nociceptors together with their mechanical and electrical excitability in vitro. J Neurophysiol 75:1–10
Yusaf SP, Goodman J, Pinnock RD, Dixon AK, Lee K (2001) Expression of voltage-gated calcium channel subunits in rat dorsal root ganglion neurons. Neurosci Lett 311:137–141
Xia XM, Zeng X, Lingle CJ (2002) Multiple regulatory sites in large-conductance calcium-activated potassium channels. Nature 418:880–884
Acknowledgements
We thank Mrs. Barbara Beckmann for skilful technical assistance. This work was supported by the Wilhelm Sander-Stiftung (98.057.1).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Just, S., Heppelmann, B. Voltage-gated calcium channels may be involved in the regulation of the mechanosensitivity of slowly conducting knee joint afferents in rat. Exp Brain Res 150, 379–384 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-003-1465-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-003-1465-x