Abstract
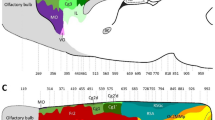
Despite numerous studies stretching over the last 100 years there is still no general agreement on the number of auditory areas in the human cortex or even how to define them by histological methods. Full definition of these areas will require a combination of functional and histological methods but, by using six complementary histological methods, of which most have been used in the monkey, we provide a clearer description of these areas. The primary auditory area was located on the posteromedial two-thirds of the first transverse temporal (Heschl’s) gyrus and was distinguished by a dense band of cytochrome oxidase activity in layer IV and the base of layer III, as well as a relatively thick, pale layer V and VI. Layers V and VI together made up 40% of the cortical thickness. Acetylcholinesterase (AChE)-containing pyramidal cells were sparsely distributed within the primary auditory area. The anterolateral third of Heschl’s gyrus did not have a clear band of high cytochrome oxidase activity but contained a moderately high density of AChE-containing pyramidal cells and thus appeared to be part of the auditory belt. Within Heschl’s sulcus there was a third area, which had a band of high cytochrome oxidase activity and bands of high parvalbumin immunoreactivity and AChE activity in layer IV. This area appeared to be part of the auditory core. Thus the use of staining methods for cytochrome oxidase, AChE and parvalbumin provided additional information which allowed a clearer definition of auditory areas than Nissl or myelin staining alone. Our results suggest that there are two core areas surrounded by at least six belt areas in the human auditory region.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wallace, M.N., Johnston, P.W. & Palmer, A.R. Histochemical identification of cortical areas in the auditory region of the human brain. Exp Brain Res 143, 499–508 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-002-1014-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-002-1014-z