Abstract.
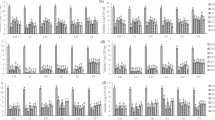
The antimicrobial activity of the essential oils of nine plant spices (savory, laurel, oregano, basil, cumin, seafennel, myrtle, pickling herb, and mint) were tested at three concentrations (1, 10, and 15%) and tested on various microorganisms (Salmonella typhimurium, Bacillus cereus, Staphylococcus aureus, Enterococcus faecalis, Escherichia coli, Yersinia enterocolitica, Saccharomyces cerevisiae, Candida rugosa, Rhizopus oryzae and Aspergillus niger). The results showed that the essential oils tested varied in their antimicrobial activity. Individual or combinations of plant essential oils may provide an efficacious mixture for the inactivation of pathogenic and spoilage microorganisms, and to achieve adequate shelf-life of foods.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Revised version: 21 December 2000
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Özcan, .M., Erkmen, O. Antimicrobial activity of the essential oils of Turkish plant spices. Eur Food Res Technol 212, 658–660 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002170100310
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002170100310