Abstract
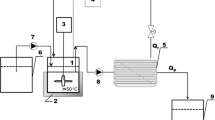
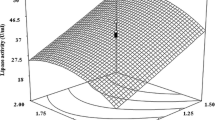
A process for the digestion of residual β-cyclodextrin used for cholesterol reduction in egg using glucoamylase from a mutant strain of Aspergillus niger (CFTRI 1105) was optimized by response surface methodology. The most important parameters influencing β-cyclodextrin digestion were determined to be enzyme activity units per milligram of β-cyclodextrin and digestion temperature. Maximum digestions of 89% for egg yolk and 98% for whole egg were observed, and these values were in good agreement with the values predicted by the models.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 24 March 1999 / Revised version: 9 June 1999
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rao, P., Kumar, S., Rao, D. et al. Optimization of digestion parameters for the elimination of residual β-cyclodextrin used for cholesterol reduction in egg using glucoamylase. Eur Food Res Technol 210, 231–236 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002170050015
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002170050015