Abstract
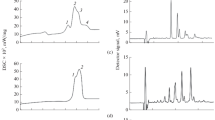
Differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) has been used to determine the oil content in dried olive pulp of Cassanese and Carolea tree cultivars and to follow their inoliation trends from September to January. DSC was performed by cooling samples of olive dried pulp from –10 to –60 °C at 1 °C/min and the amount of oil calculated from the peak area obtained. The enthalpy and temperature range of the crystallization peak for the pure oil were 61 J/g and –34 to –40 °C for the first cultivar and 54 J/g and –35 to –42 °C for the second one. The proposed DSC method is fast, specific, and reliable. It does not use solvents, requires smaller samples (<100 mg) than conventional solvent methods, and can detect real absence of water in the sample.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 13 March 2000
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Iannotta, N., Oliviero, C., Ranieri, G. et al. Determination of the oil content in olives by the DSC technique. Eur Food Res Technol 212, 240–243 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002170000239
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002170000239