Abstract
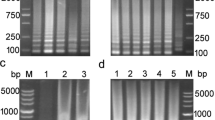
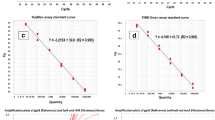
A loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP) assay for the rapid detection of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in bottled water was developed and evaluated. Four primers, including two outer primers and two inner primers, were specially designed by targeting the ecfX gene. The LAMP assay showed high specificity, with no false-positive or false-negative results among the 108 bacterial strains tested, including 81 strains of P. aeruginosa. The detection limit in pure culture was 15.7 CFU/mL, which is approximately 100-fold more sensitive than that of ecfX-PCR. In artificially contaminated water samples spiked with low level (3.1 CFU/250 mL) of P. aeruginosa, the LAMP assay could detect the target organisms accurately after 10 h of enrichment, in contrast to 12 h of enrichment for ecfX-PCR. In the case of bottled water samples, 9.17 % (10/109) of the samples were found to be positive by LAMP, which was in accordance with the results from GB 8538-2008 method. The LAMP assay established in this study is a simple, sensitive, and rapid protocol for the detection of P. aeruginosa. It provides an important diagnostic tool for the drinking water produce industry and regulatory agencies to better control potential risks associated with consumption of bottled water.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Silby MW, Winstanley C, Godfrey SA, Levy SB, Jackson RW (2011) Pseudomonas genomes: diverse and adaptable. FEMS Microbiol Rev 35(4):652–680
Baumgartner A, Grand M (2006) Bacteriological quality of drinking water from dispensers (coolers) and possible control measures. J Food Prot 69(12):3043–3046
Zamberlan da Silva ME, Santana RG, Guilhermetti M, Filho IC, Endo EH, Ueda-Nakamura T, Nakamura CV, Dias Filho BP (2008) Comparison of the bacteriological quality of tap water and bottled mineral water. In J Hyg Environ Health 211(5–6):504–509
László V (2011) Bacteriological quality of bottled natural mineral waters commercialized in Hungar. Food Control 22(3–4):591–595
Venieri D, Vantarakis A, Komninou G, Papapetropoulou M (2006) Microbiological evaluation of bottled non-carbonated (‘‘still’’) water fromdomestic brands in Greece. Int J Food Microbiol 107(1):68–72
Marzano MA, Ripamonti B, Balzarett CM (2011) Monitoring the bacteriological quality of Italian bottled spring water from dispensers. Food Control 22(2):333–336
Spilker T, Coenye T, Vandamme P, LiPuma JJ (2004) PCR-based assay for differentiation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa from other pseudomonas species recovered from cystic fibrosis patients. J Clin Microbiol 42(5):2074–2079
Lee CS, Wetzel K, Buckley T, Wozniak D, Lee J (2011) Rapid and sensitive detection of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in chlorinated water and aerosols targeting gyrB gene using real-time PCR. J Appl Microbi 111(4):893–903
Lavenir R, Jocktane D, Laurent F, Nazaret S, Cournoyer B (2007) Improved reliability of Pseudomonas aeruginosa PCR detection by the use of the species-specific ecfX gene target. J Microbiol Methods 70(1):20–29
Anuj SN, Whiley DM, Kidd TJ, Bell SC, Wainwright CE, Nissen MD, Sloots TP (2009) Identification of Pseudomonas aeruginosa by a duplex real-time polymerase chain reaction assay targeting the ecfX and the gyrB genes. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis 63(2):127–131
Notomi T, Okayama H, Masubuchi H, Yonekawa T, Watanabe K, Amino N, Hase T (2000) Loop mediated isothermal amplification of DNA. Nucleic Acids Res 28(12):E63
Wang F, Jiang L, Yang QR, Prinyawiwatkul W, Ge BL (2012) Rapid and specific detection of Escherichia coli Serogroups O26, O45, O103, O111, O121, O145, and O157 in ground beef, beef trim, and produce by loop-mediated isothermal amplification. Appl Environ Microbiol. doi:10.1128/AEM.07975-11
Wang L, Shi L, Alam MJ, Geng Y, Li L (2008) Specific and rapid detection of food-borne Salmonella by loop-mediated isothermal amplification method. Food Res Int 41(1):69–74
Yamazaki W, Ishibashi M, Kawahara R, Inoue K (2008) Development of a loop-mediated isothermal amplification assay for sensitive and rapid detection of Vibrio parahaemolyticus. BMC Microbiol 8:163–169
Yang H, Ma XY, Zhang XZ, Wang Y, Zhang W (2011) Development and evaluation of a loop-mediated isothermal amplification assay for the rapid detection of Staphylococcus aureus in food. Eur Food Res Technol 232(5):769–776
Goto M, Shimada K, Sato A, Takahashi E, Fukasawa T, Takahashi T, Ohka S, Taniguchi T, Honda E, Nomoto A, Ogura A, Kirikae T, Hanaki K (2010) Rapid detection of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in mouse feces by colorimetric loop-mediated isothermal amplification. J Microbiol Methods 81(3):247–252
Zhao XH, Wang L, Li YM, Xu ZB, Li L, He XW, Liu Y, Wang JH, Yang LS (2011) Development and application of a loop-mediated isothermal amplification method on rapid detection of Pseudomonas aeruginosa strains. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 27(1):181–184
Elomari M, Coroler L, Izard D, Leclerc H (1995) A numerical taxonomic study of fluorescent Pseudomonas strains isolated from natural mineral waters. J Appl Bacteriol 78(1):71–81
Morais PV, Mesquita C, da Andrade JL, Costa MS (1997) Investigation of persistent colonization by Pseudomonas aeruginosa-like strain in a spring water bottling plant. Appl Environ Microbiol 63(3):851–856
Zhao X, Li Y, Wang L, You L, Xu Z, Li L, He X, Liu Y, Wang J, Yang L (2010) Development and application of a loop-mediated isothermal amplification method on rapid detection Escherichia coli O157 strains from food samples. Mol Biol Rep 37(5):2183–2188
Prompamorn P, Sithigorngul P, Rukpratanporn S, Longyant S, Sridulyakul P, Chaivisuthangkura P (2011) The development of loop-mediated isothermal amplification combined with lateral flow dipstick for detection of Vibrio parahaemolyticus. Lett Appl Microbiol 52(4):344–351
Kaneko H, Kawana T, Fukushima E, Suzutani T (2007) Tolerance of loop-mediated isothermal amplification to a culture medium and biological substances. J Bioch Bio 70(3):499–501
De Vos D, Lim JA, Pirnay JP, Struelens M, Vandenvelde C, Duinslaeger L, Vanderkelen A, Cornelis P (1997) Direct detection and identification of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in clinical samples such as skin biopsy specimens and expectorations by multiplex PCR based on two outer membrane lipoprotein genes, oprI and oprL. J Clin Microbiol 35(6):1295–1299
Acknowledgments
Shuhong Zhang and Xiaoke Xu contributed equally to this work. This work was supported by research grants from the Science and Technology Planning Project of Guangdong Province (2010B031000020). We would like to express our gratitude to Dr Treena Burgess (Murdoch University, Australia) for constructive comments. We are also thankful to the reviewers for their valuable suggestions and comments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, S., Xu, X., Wu, Q. et al. Rapid and sensitive detection of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in bottled water by loop-mediated isothermal amplification. Eur Food Res Technol 236, 209–215 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00217-012-1876-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00217-012-1876-7