Abstract
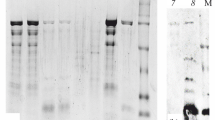
Immunoblotting is a simple method to analyze allergens in biological samples. In previous immunoblotting studies on fish allergens, however, collagen, an important allergen next to parvalbumin (major fish allergen), has not been detected in fish muscle extracts probably due to its unique chemical properties. This study was aimed to develop an extraction method suitable for immunoblotting analysis of fish allergens including collagen as well as parvalbumin. When various extracts from the Japanese eel white muscle were analyzed by SDS–PAGE, heating of the muscle homogenate at 80 °C for 20 min was found to be the most effective method to extract collagen as well as parvalbumin. The same extraction method was also effective for the other five species of fish analyzed (rainbow trout, Japanese horse mackerel, crimson sea bream, Pacific mackerel, and Japanese flounder). Furthermore, parvalbumin and/or collagen were successfully identified as allergens in the six species of fish by immunoblotting using the heated extracts prepared by the method described above. It can be concluded that the extraction method (heating of the muscle homogenate at 80 °C for 20 min) developed in this study is useful not only for analyzing fish allergens by immunoblotting but also for preparing antigens for diagnosis of fish allergy by RAST (radioallergosorbent test).





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Elsayed S, Aas K (1971) Isolation of purified allergens (cod) by isoelectric focusing. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol 40:428–438
Elsayed S, Bennich H (1975) The primary structure of allergen M from cod. Scand J Immunol 4:203–208
Bugajska-Schretter A, Pastore A, Vangelista L, Rumpold H, Valenta R, Spitzauer S (1999) Molecular and immunological characterization of carp parvalbumin, a major fish allergen. Int Arch Allergy Immunol 118:306–308
Swoboda I, Bugajska-Schretter A, Verdino P, Keller W, Sperr WR, Valent P, Valenta R, Spitzauer S (2002) Recombinant carp parvalbumin, the major cross-reactive fish allergen: a tool for diagnosis and therapy of fish allergy. J Immunol 168:4576–4584
Lindstrøm CD-V, van Dô T, Hordvik I, Endresen C, Elsayed S (1996) Cloning of two distinct cDNAs encoding parvalbumin, the major allergen of Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar). Scand J Immunol 44:335–344
Hamada Y, Tanaka H, Ishizaki S, Ishida M, Nagashima Y, Shiomi K (2003) Purification, reactivity with IgE and cDNA cloning of parvalbumin as the major allergen of mackerels. Food Chem Toxicol 41:1149–1156
Shiomi K, Hamada Y, Sekiguchi K, Shimakura K, Nagashima Y (1999) Two classes of allergens, parvalbumins and higher molecular weight substances, in Japanese eel and bigeye tuna. Fish Sci 65:943–948
Sakaguchi M, Toda M, Ebihara T, Irie S, Hori H, Imai A, Yanagida M, Miyazawa H, Ohsuna H, Ikezawa Z, Inouye S (2000) IgE antibody to fish gelatin (type I collagen) in patients with fish allergy. J Allergy Clin Immunol 106:579–584
Hamada Y, Nagashima Y, Shiomi K (2001) Identification of collagen as a new fish allergen. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 65:285–291
Das Dores S, Chopin C, Romano A, Galland-Irmouli AV, Quaratino D, Pascual C, Fleurence J, Guéant JL (2002) IgE-binding and cross-reactivity of a new 41 kDa allergen of codfish. Allergy 57(Suppl. 72):84–87
Kondo Y, Komatsubara R, Nakajima Y, Yasuda T, Kakami M, Tsuge I, Urisu A (2006) Parvalbumin is not responsible for cross-reactivity between tuna and marlin: a case report. J Allergy Clin Immunol 118:1382–1383
Hamada Y, Nagashima Y, Shiomi K, Shimojo N, Kohno Y, Shibata R, Nishima S, Ohsuna H, Ikezawa Z (2003) Reactivity of IgE in fish-allergic patients to fish muscle collagen. Allergol Int 52:139–147
Pascual C, Esteban MM, Crespo JF (1992) Fish allergy: evaluation of the importance of cross-reactivity. J Pediatr 121:S29–S34
Bernhisel-Broadbent J, Scanlon SM, Sampson HA (1992) Fish hypersensitivity. I. In vitro and oral challenge results in fish-allergic patients. J Allergy Clin Immunol 89:730–737
Hansen TK, Bindslev-Jensen C, Skov PS, Poulsen LK (1997) Codfish allergy in adults: IgE cross-reactivity among fish species. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol 78:187–194
James JM, Helm RM, Burks AW, Lehrer SB (1997) Comparison of pediatric and adult IgE antibody binding to fish proteins. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol 79:131–137
Bugajska-Schretter A, Elfman L, Fuchs T, Kapiotis S, Rumpold H, Valenta R, Spitzauer S (1998) Parvalbumin, a cross-reactive fish allergen, contains IgE-binding epitopes sensitive to periodate treatment and Ca2+ depletion. J Allergy Clin Immunol 101:67–74
Yamada S, Nolte H, Zychlinsky E (1999) Identification and characterization of allergens in two species of tuna fish. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol 82:395–400
Van Dô T, Elsayed S, Florvaag E, Hordvik I, Endresen C (2005) Allergy to fish parvalbumins: studies on the cross-reactivity of allergens from 9 commonly consumed fish. J Allergy Clin Immunol 116:1314–1320
Kobayashi A, Tanaka H, Hamada Y, Ishizaki S, Nagashima Y, Shiomi K (2006) Comparison of allergenicity and allergens between fish white and dark muscles. Allergy 61:357–363
Kuehn A, Scheuermann T, Hilger C, Hentges F (2010) Important variations in parvalbumin content in common fish species: a factor possibly contributing to variable allergenicity. Int Arch Allergy Immunol 153:359–366
Vuorio E, de Crombrugghe B (1990) The family of collagen genes. Annu Rev Biochem 59:837–872
Weber P, Steinhart H, Paschke A (2010) Characterization, antigenicity and detection of fish gelatin and isinglass used as processing aids in wines. Food Addit Contam 27:273–282
Miller EJ, Rhodes RK (1982) Preparation and characterization of the different types of collagen. Methods Enzymol 82:33–64
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Drs. N. Shimojo and Y. Kohno, Department of Pediatrics, Chiba University, Dr. A. Urisu, Fujita Health University School of Medicine, and Drs. H. Ohsuna and Z. Ikezawa, Department of Dermatology, Yokohama City University, for providing patient sera. This study was partly supported by a Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research (No. 19380120) from the Ministry of Education, Science, Sports, and Culture of Japan and a grant (H21-Food-General-004) from the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare of Japan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kanamori, M., Tanaka, H., Hamada, Y. et al. New extraction method suitable for immunoblotting analysis of fish allergens. Eur Food Res Technol 233, 991–997 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00217-011-1602-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00217-011-1602-x