Abstract
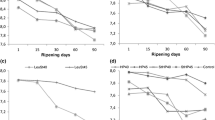
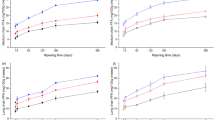
Three batches of Manchego cheese were manufactured using one of the following starter culture systems: (1) a defined strain starter culture comprising Lactococcus lactis subsp. lactis and Leuconostoc mesenteroides subsp. dextranicum; (2) the above-defined strain starter culture and an adjunct culture (Lactobacillus plantarum), all these strains being isolated from high-quality Manchego cheeses and (3) a commercial starter consisting of two strains of Lactococcus lactis. Differences in volatile profile and the sensory characteristics of these cheeses were studied. After 4 months of ripening, the two batches of cheese made with the defined strain starter cultures obtained the highest scores for sensory attributes and for the overall impression. Additionally, Purge & Trap and SDE analysis showed a more complex volatile profile in these cheeses than in those made with the commercial starter. Extending the maturation time to 8 months for cheeses made with the defined starter cultures led to significant higher levels of free fatty acids and ethyl esters in those cheeses made without adjunct culture. However, panelists did not find significant differences among the sensory characteristics of the two cheeses.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ayad EHE, Verheul A, De Jong C, Wouters JTM, Smit G (1999) Int Dairy J 9:725–735
McSweeney PLH, Sousa MJ (2000) Lait 80:293–324
Núñez M, Medina M, Gaya P (1989) J Dairy Res 56:303–321
Grappin R, Beuvier E (1997) Int Dairy J 7:751–761
Peterson SD, Marshall RT (1990) J Dairy Sci 73:1395–1410
Lynch CM, McSweeney PLH, Fox PF, Cogan TM, Drinan FD (1996) Int Dairy J 6:851–867
Irigoyen A, Ortigosa M, Juansaras M, Oneca M, Torre P (2007) Food Chem 100:71–80
Kleter G (1977) Neth Milk Dairy J 31:177–187
Urbach G (1993) Int Dairy J 3:389–422
Ramos M, Barneto R, Ordóñez JA (1981) Milchwissenschaft 36:528–531
Poveda JM, Sousa MJ, Cabezas L, McSweeney PLH (2003) Int Dairy J 13:169–178
Poveda JM, Cabezas L, McSweeney PLH (2004) Food Chem 84:213–218
García A, Palop L, Cabezas L (1997) Microbiol Aliments Nutr 15:237–240
Gómez-Ruiz JA, Ballesteros C, González-Viñas MA, Cabezas L, Martínez-Castro I (2002) Lait 82:613–628
Godefroot M, Sandra P, Verzele M (1981) J Chromatogr 203:325–335
ISO 6564 (1985) Sensory Analysis-Methodology-Flavour Profile Methods. Geneva, Switzerland, p 6
ISO 11036 (1994) Sensory Analysis-Methodology-Texture Profile. Geneva, Switzerland, p 14
González-Viñas MA, Poveda JM, Cabezas L (2001) J Food Qual 24:157–165
González-Viñas MA, Poveda JM, García-Ruiz A, Cabezas L (2001) J Sens Stud 16:61–371
ISO 8589 (1988) Sensory Analysis. Guide for the Installation of a Chamber for Sensory Analysis. Geneva, Switzerland, p 9
Román Piñana M (1975) Lait 547:401–413
Núñez M (1976) Ann INIA Ser Gen 4:57–65
Cogan TM, Barbosa M, Beuvier E, Bianchi-Salvadori B, Cocconcelli P, Fernández I, Gómez J, Kalantzopoulos G, Ledda A, Medina M, Rea M, Rodríguez E (1997) J Dairy Res 64:409–421
Sablé S, Cottenceau G (1999) J Agr Food Chem 47:4825–4836
Moio L, Addeo F (1998) J Dairy Res 65:317–333
Careri M, Manini P, Spagnoli S, Barbieri G, Bolzoni L (1994) Chromatographia 38:386–394
Bosset JO, Gubler M, Bütikofer U, Gauch R (2000) Trav Chem Aliment Hyg 91:287–299
Johnson AE, Nursten HE, Self R (1969) Chem Ind 4:10–14
Cogan TM, Kieran NJ (1994) J Dairy Sci 77:2704–2717
González J, Mas M, Tabla R, Moriche J, Rao I, Rebollo JE, Cáceres P (2003) Lait 83:193–202
Martínez-Castro I, Sanz J, Amigo L, Ramos M, Martín-Álvarez P (1991) J Dairy Res 58:239–246
Barbieri G, Bolzoni L, Careri M, Manglia A, Parolari G, Spagnoli S, Virgili R (1994) J Agr Food Chem 42:1170–1176
Jordan KN, O’Donoghue M, Condon S, Cogan TM (1996) FEMS Microbiol Lett 143:291–297
Urbach G (1997) Int J Dairy Technol 50:79–89
Behnke U (1980) Nahrung 24:71–83
Tungjaroenchai W, Drake MA, White CH (2001) J Dairy Sci 84:2117–2124
Hynes E, Bach C, Lamberet G, Ogier JC, Son O, Delacroix-Buchet A (2003) Lait 83:31–43
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Spanish Ministry of Education and Culture and EU (FEDER Program 1FD97-0166). J.A. Gómez-Ruiz acknowledges Comunidad de Madrid for a scholarship.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gómez-Ruiz, J.Á., Cabezas, L., Martínez-Castro, I. et al. Influence of a defined-strain starter and Lactobacillus plantarum as adjunct culture on volatile compounds and sensory characteristics of Manchego cheese. Eur Food Res Technol 227, 181–190 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00217-007-0708-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00217-007-0708-7