Abstract
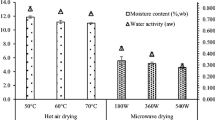
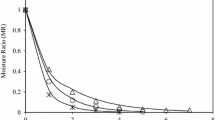
The effects of microwave and infrared drying on the quality of carrot and garlic were studied and compared with the effects of conventional hot air (tray drier for carrot and fluid bed drier for garlic) drying. The quality of carrot and garlic were evaluated by instrumental and sensory analysis. Rehydration, moisture content, water activity, particle density, bulk density, porosity and colour values were obtained for microwave, infrared and hot-air dried vegetables. In addition, total moisture content versus time was represented by drying rate curves of carrot and garlic samples. Finally, free moisture content versus drying rate were compared for the three different drying methods.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mujumdar AS (1995) Handbook of industrial drying 2nd edn,, Vols 1–2. Marcel Dekker, New York
Mazza G (1983)J Food Technol 18:113–123
Namiki H, Nijnuma K, Takemura M, Tou R, Yanagisawa M, Hirabayashi T, Kiyokawa S (1996) J Food Hyg Soc Japan, 37 (6):395–400
Krokida MK, Maroulis ZB (1997) Drying Technol 15 (10):2441–2458
Pan YK, Wu H, Li ZY, Mujumdar AS, Kudra T (1997) Drying Technol 15 (6–8):2037–2043
Domagala A, Witulska M, Janus P (1996) Polish J Food Nutr Sci 5/46 (3):121–130
Choi YH, Youn KS (1995) J Fruits Veg Nuts, IFT Annual Meeting 1995, p.153
Lee HM (1989) Characteristics of freeze-drying of garlic. Annual Report, National Industrial Research Institute, Korea, 39:481–484
Madamba PS, Driscoll RH, Buckle KA (1994) Drying Technol 12(4):937–954
Madamba PS, Driscoll RH, Buckle KA (1994) J Food Eng 23(3):309–319
Mota VM, Alcantar C (1995) ASAE Publication 1–95:31–37
Jebson RS, He Y (1995) A novel technology to produce high quality garlic powder. IFT Annual Meeting 1995, p 72
Madamba P (1996) Thermophysical and colour changes in garlic during dehydration. Dissertation Abstracts International, B., 57 (6):3474–3475
Madamba PS, Driscoll RH, Buckle KA (1996) J Food Eng 29(1):75–97
Madamba PS (1997) Drying Technol 15(1):117–136
Harwitz W, Chichilo P, Clifford PA, Reynolds H (eds) (1965) AOAC official methods of analysis of the Association of Official Agricultural Chemists, 10th edn. AOAC, USA
ATO-DLO Report.AIR-3-CT 94, 2254 (1994) Dehydration of vegetables fruits and herbs, Recent Developments in Drying Techniques and Quality aspects, ATO-DLO Report.AIR-3-CT 94, 2254.
Riva M, Schiraldi A, De Cesare LF (1991)Lebensm WissTechnol 24:479–483
Crewdson BJ, Ormond AL, Nedderman RM (1977) Powder Technol 16:197–207
Sommer K (1988) Size enlargement 7.1–7.36. In: Wolfgang G, Elvers B, Ravenscraft M, Rounsaville JF, Schultz G(eds) Ullmann’s encylopedia of industrial chemistry, 5th edn., Vol. B2, VCH, Germany, pp 284–285
Egan H, Kirk RS, Sawyer R (1981) Pearson’s chemical analysis of foods, 8th edn. Churchill Livingstone, New York, p 591
Pisecky J (1985) Standards, specifications and test methods for dry milk products. In: MacCarthy D (ed) Concentration and drying of foods. Elsevier Applied Science, London, pp 203–209
Hayes GD (1987) Food engineering data handbook. Longman Scientific and Technical, New York, p 172
Kramer A, Twigg BA (1970) Quality control for the food industry, 3rd edn. The AVI Publishing Company, p 560
Geankoplis CJ (1983) Transport processes and unit operations, 2nd edn. Allyn and Bacon Series in Engineering, new York, USA
Gunasekaran S (1999) Drying Technol 17(3):395–412
Tulasidas TN, Raghavan GSV, Mujumdar AS (1995) Drying Technol 13 (8–9):1949–1971
Lu L., Tang J, Ran X (1999) Drying Technol 17(3):413–432
Hashinaga F, Bajgai TR, Isobe S, Barthakur NN (1999) Drying Technol 17(3):479–495
Tulasidas TN, Raghavan GSV, Norris ER (1993) Trans ASAE 3(6):1861–1865
Pezzuti A, Crapiste GH (1997) J Food Eng 31:113–123
Heimdal H, Kühn BF, Poll L, Larsen LM (1995) J Food Sci 60(6):1265–1268, 1276
Sapers DM, Douglas J (1987) In: Harwitz W, Chichilo P, Clifford PA, Reynolds H (eds) AOAC Official Methods of Analysis of the Association of Official Agricultural Chemists, 10th edn. AOAC, USA
Krokida MK, Maroulis ZB (1999) Drying Technol 17(3):446–449
Zogzas MP, Maroulis ZB, Marinos-Kouris D (1994) Drying Technol 12(7):1653–1666
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Baysal, T., Icier, F., Ersus, S. et al. Effects of microwave and infrared drying on the quality of carrot and garlic. Eur Food Res Technol 218, 68–73 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00217-003-0791-3
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00217-003-0791-3