Abstract
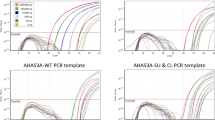
A construct-specific real-time PCR assay was developed for quantitative detection of LibertyLink in rapeseed by using the junction region between the 35S promoter and the pat gene. For validation of precision and accuracy of quantification five external genomic and cloned DNA calibration standards were constructed. Seeds of non-transgenic rapeseed were pooled with appropriate numbers of seeds of transgenic rapeseed. Genomic DNA from transgenic rapeseed was diluted with corresponding volumes of water or genomic DNA from non-transgenic rapeseed. Plasmids containing DNA fragments of the construct-specific and a brassica-specific reference gene were diluted with appropriate volumes of water and last, corresponding amounts of plasmids containing DNA fragments of the construct-specific construct were spiked in genomic DNA from non-transgenic rapeseed. The approximately estimated upper and lower limits of the quantification of calibration standards constructed with mixed seeds, plasmids in genomic background and water-diluted genomic DNA of 206–279 and 21–28 copy numbers were similar, whereas water-diluted plasmid and mixed genomic DNA standards never reached the quantification thresholds of 13 and 26 copy numbers, respectively. The accuracy of quantification for all calibration standards was tested by calculating the recovery of quantification for reference samples. The highest accuracy was obtained by using standards of mixed genomic DNA and plasmids in genomic background. This indicates a significant influence of background DNA on the quantification of genetically modified (GM) contaminations in rapeseed. Since construct-specific plasmids can be produced on a large scale, stored for a long time without loss of quality and spiked in different DNA backgrounds, plasmid standards can be used in GM quantification as 'gold standards'.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
James C (2001) ISAAA Briefs No 24, Ithaca, New York
Hübner P, Waiblinger HU, Pietsch K, Brodmann P (2001) J AOAC Int 84:1855–1864
Vaïtilingom M, Pijnenburg H, Gendre F, Brignon P (1999) J Agric Food Chem 47:5261–5266
Pietsch K, Waiblinger HU (2000) Quantification of genetically modified soybeans in food with the Lightcycler system. In: Meuer S, Wittwer C, Nakagawara K (eds) Rapid cycle real-time PCR. Methods and applications. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York
Taverniers I, Windels P, Van Bockstaele E, De Loose M (2001) Eur Food Res Technol 213:417–424
Sambrock J, Fritsch EF, Maniatis T (1989) Molecular cloning: A laboratory manual. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, New York
Arumuganathan K, Earle ED (1991) Plant Mol Biol Rep 9:208–218
Deutsches Institut für Normierung (2002): DIN 53804–1: Statistische Auswertungen. Berlin: Beuth
Kromidas S (1999) Validierung in der Analytik. Wiley-VCH, Weinheim
Wolf C, Scherzinger M, Wurz A, Pauli U, Hübner P, Lüthy J (2000) Eur Food Res Technol 210:367–372
Holck A, Vaïtilingom M, Didierjean L, Rudi K (2002) Eur Food Res Techol 214:449–453
Terry CF, Harris N (2001) Eur Food Res Technol 213:425–431
Waiblinger HU, Gutmann M, Hädrich J, Pietsch K (2001) Dtsch Lebensm-Rundsch 97:121–125
Zeitler R, Pietsch K, Waiblinger HU (2002) Eur Food Res Technol 214:346–351
Hädrich J, Vogelsang J (1999) Konzept 2000 – Ein statistischer Ansatz für die Praxis, Teil 1: Nachweisgrenze, Erfassungsgrenze und Bestimmungsgrenze. Dtsch Lebensm Rundsch 95:428–436
Acknowledgements
We thank Andrea Müller for her excellent technical assistance. This work was supported by the Bavarian State Ministry for Regional Development and Environmental Affairs.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Block, A., Schwarz, G. Validation of different genomic and cloned DNA calibration standards for construct-specific quantification of LibertyLink in rapeseed by real-time PCR. Eur Food Res Technol 216, 421–427 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00217-003-0665-8
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00217-003-0665-8