Abstract.
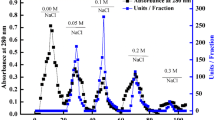
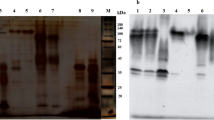
Soluble peroxidase was extracted from oranges (Citrus sinenses (L.) Osbeck). Small amounts of purified anionic and cationic isoperoxidases have been obtained by gel filtration and ion-exchange chromatography. It has been shown that peroxidase activity present in crude extracts of oranges (juice, albedo, and peel) is less stable to heat than the enzymes activity of highly purified individual orange isoperoxidases. For the purified isoperoxidases heat-inactivation is still non-linear. It is suggested that this may be due to micro heterogeneity in covalently bound oligosaccharide residues at the molecular level. The higher activity was detected in the crude extract from the peel, around 3.2 and 7.8 times more than the fractions from the albedo and juice respectively. The crude soluble peroxidase fractions were particularly heat stable. The pI (4.5, 5.2, and 9.0) of the purified isoperoxidase (A1, A3, and C1) from the peel soluble fraction was measured using a surface electrode and the molecular weight (42 kDa, 30 kDa, and 26 kDa) was estimated by gel-filtration.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Clemente, E. Peroxidase from oranges (Citrus sinenses (L.) Osbeck. Eur Food Res Technol 215, 164–168 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00217-002-0516-z
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00217-002-0516-z