Abstract
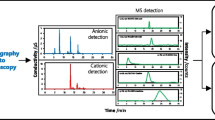
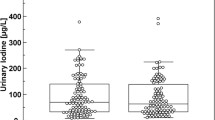
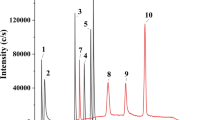
A variety of parameters affecting the determination of iodide in biological materials by ion-pair chromatography and electrochemical detection were examined in detail. It became apparent that the pH value, the ion-pair concentration, the proportion of organic solvent and of organic bases as a component of the buffer solution, as well as the salt concentration in the eluent system could effectively influence the retention characteristics of iodide in the chromatographic system, resulting in the separation of potential interfering substances. The presence of other anions in the sample matrix has to be taken into consideration, particularly thiocyanate because of its long retention time. Investigations of the electrochemical detection mechanism revealed that the reaction hitherto assumed to be responsible for detector signal generation (formation of AgI) is incorrect. In addition, a much more sensitive detection of iodide than that cited in the literature to date is possible if the detector potential is optimally selected and any anticipated interfering substances are removed by chromatography. Use of a gold electrode rather than a silver electrode also considerably enhances the reliability of the procedure.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Below, H., Kahlert, H. Determination of iodide in urine by ion-pair chromatography with electrochemical detection. Fresenius J Anal Chem 371, 431–436 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002160101080
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002160101080