Abstract
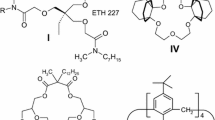
Arylboronic acids are used as novel carriers for membrane electrodes suitable for direct potentiometric determination of the catecholamine drug dobutamine. The carriers are capable of binding diol groups of catecholamines; solvent extraction data confirm the formation of an 1 : 1 complex. For the electrode based on octyloxyphenylboronic acid, the slope of electrode function is S = 58 mV decade–1; the detection limit is 1.7 · 10–5 mol/L, the linear range 5 · 10–4– 1 · 10–2 mol/L, the response time 10–20 s. The results suggest the potential use of boronic carriers for the detection of biogenic catecholamines.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 25 November 1998 / Revised: 2 March 1999 / Accepted: 11 March 1999
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pletnev, I., Shvedene, N., Lyutikova, I. et al. Arylboronic compounds – novel carriers for catecholamine selective membrane electrodes. Fresenius J Anal Chem 364, 682–685 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002160051413
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002160051413